Difference between Direct and Immediate Addressing Modes
Last Updated :
29 Jun, 2022
Prerequisite – Addressing Modes
1. Direct Addressing Mode: In direct addressing mode, the address field contains the address of the operand.
Effective Address (EA) = address field of operand
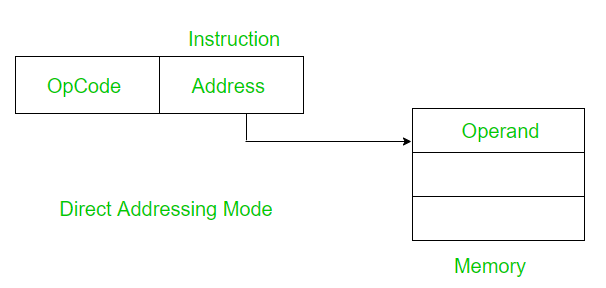
Example: Add the contents of register 1303 to the accumulator.
Add (1303)
Only a single memory reference is required to access data. So no additional calculations are required to work out the effective address.
2. Immediate Addressing Mode: In immediate addressing mode, the operand is a part of the instruction.
Here the Operand = Address Field
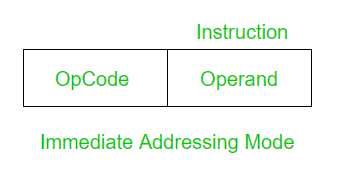
Example: Add 3 to the accumulator.
ADD 3
No memory reference is required to fetch data. So no additional calculations are required to work out the effective address. It is a fast method. But the downside is that it has a limited range. Now let’s compare Direct and Immediate addressing modes.
| S. No. |
Parameters |
Direct Addressing Mode |
Immediate Addressing Mode |
| 1. |
Address Field |
Address fields contain the effective address of the operand. |
There is no address field as an operand is a part of the instruction. In place of address field, immediate addressing mode has operand field. |
| 2. |
Memory Referencing |
It requires one reference to memory. |
It does not require any reference to memory. |
| 3. |
Process Speed |
It is slower compared to the immediate mode. |
It is faster compared to the direct addressing mode. |
| 4. |
Range |
It has more range than in immediate mode. |
It has a limited range. |
| 5. |
Example |
Add (1303) |
ADD 3 |
| 6. |
Advantage |
Easy as direct reference to memory |
There is no memory reference for fetching data. |
| 7. |
Disadvantage |
Restricted address space |
Constrained operand magnitude |
| 8. |
Application |
It assists in accessing static data and implementing variables. |
Set the register to a constant value. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...