Difference between Deterministic and Non-deterministic Algorithms
Last Updated :
23 Apr, 2024
In a deterministic algorithm, for a given particular input, the computer will always produce the same output going through the same states but in the case of the non-deterministic algorithm, for the same input, the compiler may produce different output in different runs. In fact, non-deterministic algorithms can’t solve the problem in polynomial time and can’t determine what is the next step. The non-deterministic algorithms can show different behaviors for the same input on different execution and there is a degree of randomness to it. 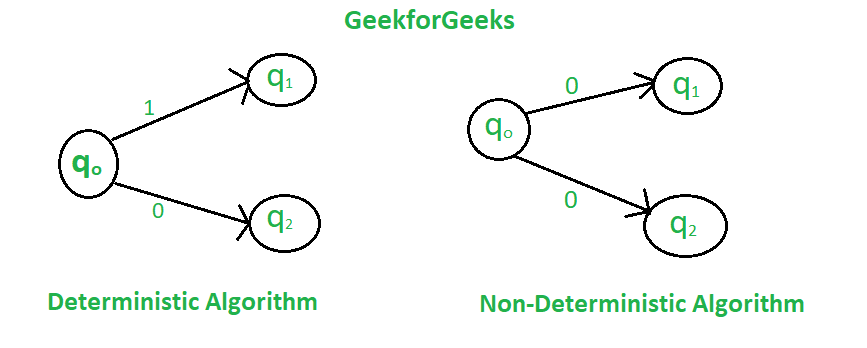
To implement a non-deterministic algorithm, we have a couple of languages like Prolog but these don’t have standard programming language operators and these operators are not a part of any standard programming languages. Some of the terms related to the non-deterministic algorithm are defined below:
- choice(X): chooses any value randomly from the set X.
- failure(): denotes the unsuccessful solution.
- success(): The solution is successful and the current thread terminates.
Example :
Problem Statement : Search an element x on A[1:n] where n>=1, on successful search return j if a[j] is equals to x otherwise return 0.
Non-deterministic Algorithm for this problem :
1.j= choice(a, n)
2.if(A[j]==x) then
{
write(j);
success();
}
3.write(0); failure();
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
// Deterministic search
int deterministic_search(std::vector<int> A, int x) {
for (int j = 0; j < A.size(); j++) {
if (A[j] == x) {
std::cout << "Deterministic Search: Found at index " << j << std::endl;
return j; // success
}
}
std::cout << "Deterministic Search: Not found" << std::endl;
return 0; // failure
}
// Non-deterministic search
int nondeterministic_search(std::vector<int> A, int x) {
// Simulate the non-deterministic choice by iterating over all elements
for (int j = 0; j < A.size(); j++) {
if (A[j] == x) {
std::cout << "Non-deterministic Search: Found at index " << j << std::endl;
return j; // success
}
}
std::cout << "Non-deterministic Search: Not found" << std::endl;
return 0; // failure
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int x = 3;
deterministic_search(A, x);
nondeterministic_search(A, x);
return 0;
}
OutputDeterministic Search: Found at index 2
Non-deterministic Search: Found at index 2
We can classify the problem in one of the following categories:
1. The problem which cannot be even defined in a proper way.
2. The problem which can be defined but cannot be solved.
3.The problem which can be solved theoretically, but computationally they are not feasible. The algorithm takes very long time to solve such problems, and the time is practically not acceptable. For example, cracking the password of 256 characters by brute force method may take years.
Definition
Problem is called intractable or infeasible if it takes too long time to be solved. A solution of such problems has no practical application.
4.Problems which can be solved theoretically and practically in a reasonable amount of time. For such problems, there exists a deterministic Turing machine that can solve the problem in O (p(n)) time, where p(n) is polynomial in n, and n is a problem size.
Definition
If the problem is solvable in polynomial time, it is called tractable. Such problems are denoted by P problems.
5. The problem which is not known whether it is in P or not in P. Such problems falls somewhere in between class 3 and 4.
Definition
- The problem is said to be decision problem if they produce output “Yes” or “No” for given input. An algorithm which solves the decision problem is called decision algorithm.
- An optimization problem aims for the best solution from the set of all feasible solutions. An algorithm which solves optimization problem is called optimization algorithms.
- Optimization algorithm seeks to find best profit or least cost solution. Decision problems are simpler than optimization problem.
Computational complexity: Computational problems have infinite instances. Each instance in the set contains the solution. Typically, the solution to the problem in computational complexity is Boolean ie. ‘Yes’ or ‘No’.
The computational problem can be function problem too. Solution to such problem differs on each execution even for the same input. So such problems are more complex than decision problems.
Definitions
Complexity classes are set of problems of related complexity, like P problems, NP problems, Decision problems, Optimization problems etc. The complexity of any problem in given class falls within certain range. Problems which takes practically unacceptable time i.e. very long time to be solved are called intractable problems.
If the running time of the algorithm is bounded to O(p(n)), where p(n) is some polynomial in n, where n represents the size of the problem, we say that the problem has polynomial time complexity. Satisfiability Problem is to check the correctness of assignment. Satisfiability problem finds out whether for given input an expression is true for that assignment.
Reducibility: Let P1 and P₂ are two problems and there exists some deterministic algorithm A for P1 such that P1 can be solved in polynomial time using A. If the same algorithm can solve the problem P₂ then we can say that P2 is reducible to P1
| Deterministic Algorithm | Non-deterministic Algorithm |
|---|
| A deterministic algorithm is one whose behavior is completely determined by its inputs and the sequence of its instructions. | A non-deterministic algorithm is one in which the outcome cannot be predicted with certainty, even if the inputs are known. |
| For a particular input, the computer will give always the same output. | For a particular input the computer will give different outputs on different execution. |
| Can solve the problem in polynomial time. | Can’t solve the problem in polynomial time. |
| Can determine the next step of execution. | Cannot determine the next step of execution due to more than one path the algorithm can take. |
| Operation are uniquely defined. | Operation are not uniquely defined. |
| Like linear search and binary search | like 0/1 knapsack problem. |
| Deterministic algorithms usually have a well-defined worst-case time complexity. | Time complexity of non-deterministic algorithms is often described in terms of expected running time. |
| Deterministic algorithms are entirely predictable and always produce the same output for the same input. | Non-deterministic algorithms may produce different outputs for the same input due to random events or other factors. |
| Deterministic algorithms usually provide precise solutions to problems. | non-deterministic algorithms often provide approximate solutions to the problems. |
| Deterministic algorithms are commonly used in applications where precision is critical, such as in cryptography, numerical analysis, and computer graphics. | Non-deterministic algorithms are often used in applications where finding an exact solution is difficult or impractical, such as in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and optimization problems. |
| Examples of deterministic algorithms include sorting algorithms like bubble sort, insertion sort, and selection sort, as well as many numerical algorithms. | Examples of non-deterministic algorithms include probabilistic algorithms like Monte Carlo methods, genetic algorithms, and simulated annealing. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...