Difference between Data and Metadata
Last Updated :
02 May, 2023
1. DATA : The term data is derived from Latin word ‘Datum’ which refers to ‘something given’. Data is raw and unorganized facts that are useless without proper processing and organising them to retrieve some information for future use . Data is a set of facts and statistics that can be operated, referred or analyzed. It can simply be a piece of information, a list of grocery items, or observations, a story or a description of a certain scenario. 2. METADATA : Metadata is a data about data. Metadata shows basic information about data, which can make finding and working with specific instances of data easier. Metadata increases the accuracy of searching and operating of data from large amount of data. It helps in fetching piece of some data that is required from the bundle of data vastly, Metadata provides the information regarding organization of raw data. It may be created manually or by automatic information processing. Manual processed metadata is more accurate than automatic information processed one because automatic information processed metadata only contains file name, size, extension, time of creation and information about who created the file. 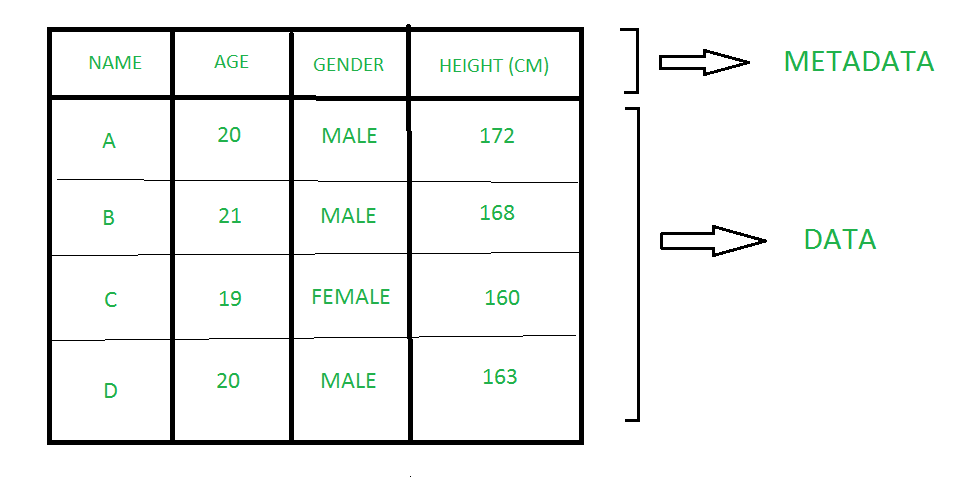
Difference between Data and Metadata :
| S.NO. |
Factors |
Data |
Metadata |
| 1. |
Concept |
Data is any sort of information which is stored in computer memory. This information can later be used for a website, an application or can be used in future. |
Metadata describes relevant information about the data. |
| 2. |
Information |
Data may or may not be informative. |
Metadata is always informative. |
| 3. |
Processing |
Data may or may not have been processed. |
It is always a processed data. |
| 4. |
Storage |
In DBMS data is stored as a file either navigational or hierarchical form. |
It is stored in data dictionary. |
| 5. |
Description |
In DBMS data refers to all the single items that are stored in a database either individually or as a set. |
Metadata refers to name of attributes, their types, user constraints, integrity information and storage information. |
| 6. |
Utilization |
Many different uses can be made of it in the future. |
In a document, it is the supporting data. |
| 7. |
Management |
Depending on the nature and use case, data must be stored and managed differently. |
No matter the data type or the intended use case, data administrators may make metadata management general throughout an organization. |
| 8. |
Example |
If you create a notepad file, then the content of that document is data. |
if you create a notepad file the name of the file, storage description, type of file, size of file all becomes metadata of your file. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...