Difference between CAN and MAN
Last Updated :
18 Mar, 2023
Campus Area Network (CAN) is a group of interconnected Local Area Networks (LAN) within a limited geographical area like school campus, university campus, military bases, or organizational campuses and corporate buildings etc. A Campus Area Network is larger than Local Area Network but smaller than Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN). 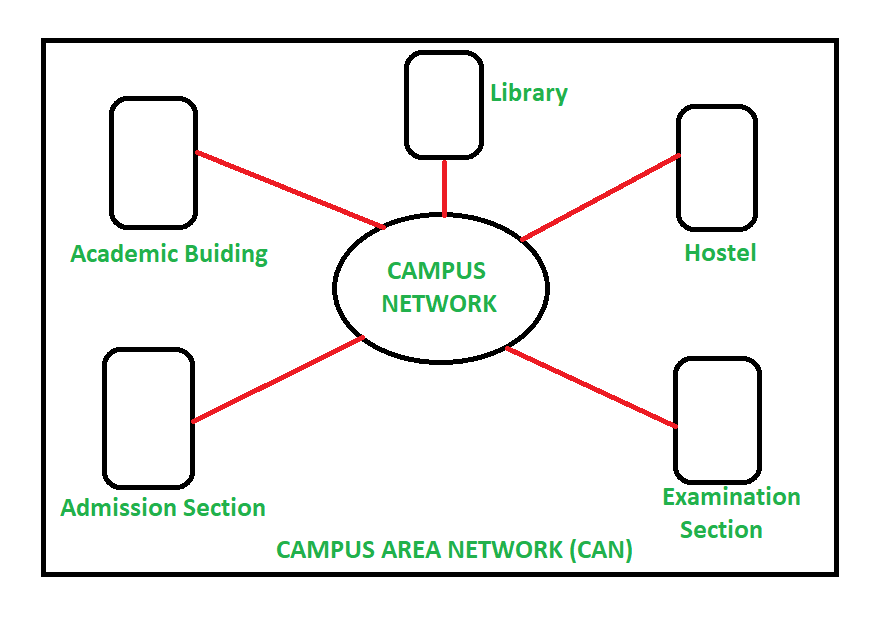
Advantages of CAN:
- High-speed connectivity: CANs provide high-speed connectivity within a campus or a local area, making it possible for businesses, organizations, and educational institutions to communicate and share resources quickly and efficiently.
- Cost-effective: CANs are typically less expensive than MANs, as they cover a smaller area and require less specialized infrastructure and equipment.
- Centralized Management: CANs can be centrally managed, allowing IT administrators to monitor and manage the network from a central location.
- Scalability: CANs are scalable and can be expanded to accommodate more users or additional locations as a business grows.
- Low Latency: CANs offer low latency, which means that data can be transmitted quickly and efficiently between devices within the network.
Disadvantages of CAN:
- Limited coverage: CANs are limited to a specific geographic area, making it difficult to connect geographically dispersed locations.
- Limited bandwidth: CANs can be subject to bandwidth limitations, particularly during periods of high usage, which can impact performance and user experience.
- Vulnerable to security risks: CANs can be vulnerable to security breaches, particularly if proper security measures are not implemented and maintained.
- Dependent on infrastructure: CANs rely on existing physical infrastructure, such as copper wires or fiber-optic cables, which can limit flexibility and scalability.
- Cost of maintenance: CANs require regular maintenance to ensure proper functionality and to address any issues that arise, which can be costly.
MAN covers the largest area than LAN such as: Small towns, City etc. MAN connects 2 or a lot of computers that area unit apart however resides within the same or completely different cities. MAN is expensive and should or might not be owned by one organization. 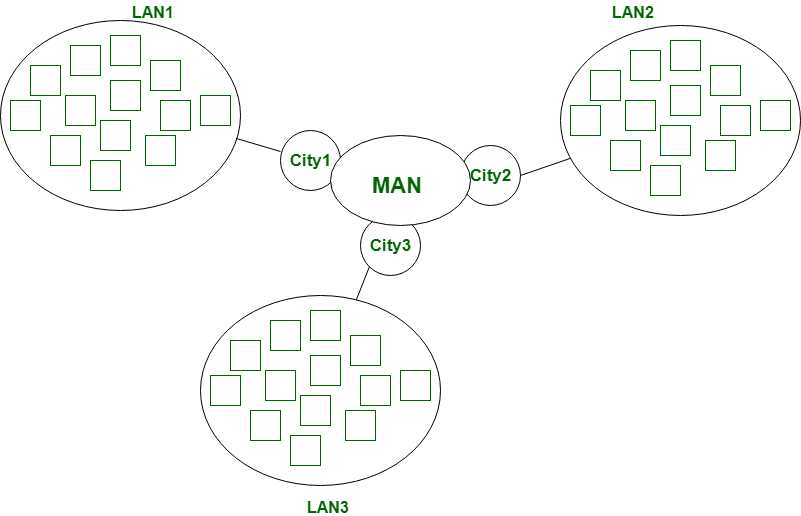
Advantages of MAN:
- High-speed connectivity: MANs provide high-speed connectivity within a metropolitan area, making it possible for businesses and organizations to communicate and share resources quickly and efficiently.
- Cost-effective: MANs are typically less expensive than WANs, as they cover a smaller area and require less specialized infrastructure and equipment.
- Scalability: MANs are scalable and can be expanded to accommodate more users or additional locations as a business grows.
- Centralized Management: MANs can be centrally managed, allowing IT administrators to monitor and manage the network from a central location.
- Low Latency: MANs offer low latency, which means that data can be transmitted quickly and efficiently between devices within the network.
Disadvantages of MAN:
- Limited coverage: MANs are limited to a specific geographic area, making it difficult to connect geographically dispersed locations.
- Limited bandwidth: MANs can be subject to bandwidth limitations, particularly during periods of high usage, which can impact performance and user experience.
- Vulnerable to security risks: MANs can be vulnerable to security breaches, particularly if proper security measures are not implemented and maintained.
- Dependent on infrastructure: MANs rely on existing physical infrastructure, such as copper wires or fiber-optic cables, which can limit flexibility and scalability.
- Cost of maintenance: MANs require regular maintenance to ensure proper functionality and to address any issues that arise, which can be costly.
Similarities between them:
- Connectivity: Both CAN and MAN provide high-speed connectivity to devices over a geographic area, although the scale differs. CANs are typically used to connect devices within a campus or local area, while MANs are used to connect devices within a city or metropolitan area.
- Cost-effective: Both CAN and MAN are typically less expensive than larger networks, such as WANs (Wide Area Networks), as they cover a smaller area and require less specialized infrastructure and equipment.
- Scalability: Both CAN and MAN are scalable and can be expanded to accommodate more users or additional locations as a business grows.
- Centralized Management: Both CAN and MAN can be centrally managed, allowing IT administrators to monitor and manage the network from a central location.
- Low Latency: Both CAN and MAN offer low latency, which means that data can be transmitted quickly and efficiently between devices within the network.
- Vulnerable to security risks: Both CAN and MAN can be vulnerable to security breaches, particularly if proper security measures are not implemented and maintained.
- Dependence on infrastructure: Both CAN and MAN rely on existing physical infrastructure, such as copper wires or fiber-optic cables, to function.
Difference between CAN and MAN :
| S.No. |
CAN |
MAN |
| 1. |
CAN stands for Campus Area Network. |
MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network. |
| 2. |
Connects two or more LANs within a campus. |
Interconnects network in a town or a city. |
| 3. |
It covers a privately-owned campus with an area of 5 to 10 KM. |
It covers larger areas than LAN but a small area than WAN with an area or 2 to 100 KM. |
| 4. |
Expensive then LAN. |
Expensive than LAN and CAN. |
| 5. |
The data transmission rate is variable. |
The data transmission rate is variable. |
| 6. |
It doesn’t Uses the IEEE 802 standard. |
Uses the IEEE 802 standard. |
| 7. |
The networking devices such as a hub, switch, Bridge, and gateway are used. |
Networking devices such as a hub, switch, gateway, router, and router are used. |
| 8. |
More congestion compare LAN. |
More congestion compare LAN and MAN. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, CAN and MAN are two types of networks used to connect devices over different geographic areas. CAN covers a smaller area than MAN, typically a single campus or building, while MAN covers a larger area, spanning a city or a large campus. Understanding the differences between CAN and MAN can help you choose the right network for your specific needs, whether you are connecting devices within a single building or interconnecting different locations within a metropolitan area.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...