Difference between an array and a tree
Last Updated :
02 Nov, 2023
An array is a collection of homogeneous(same type) data items stored in contiguous memory locations. For example, if an array is of type “int”, it can only store integer elements and cannot allow the elements of other types such as double, float, char, etc.
- The array is a linear data structure in which elements are stored at contiguous memory locations.
- In array, we store elements of the same datatype together.
- It has index-based addressing as elements are stored at contiguous memory locations.
- Index starts from 0 and goes up to (N – 1) where N is the number of elements in the array.
- As the arrays allow random access of elements in O(1). It makes accessing elements by position faster.
- The biggest disadvantage of an array is that its size cannot be increased.
Below is the general representation of the array:
Tree:
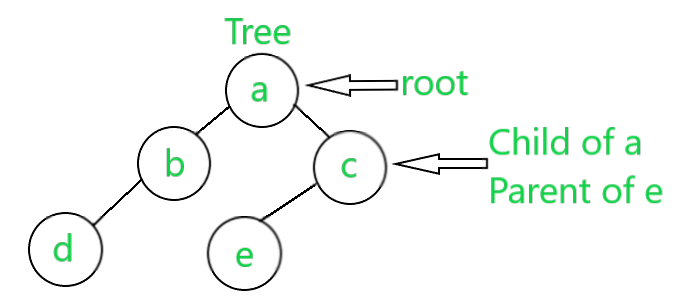
The tree represents the nodes connected by edges. The binary tree or binary search tree specifically. A binary tree is a special data structure used for data storage purposes. A binary tree has a special condition that each node can have a maximum of two children. A binary tree has the benefits of both an ordered array and a linked list as search is as quick as in a sorted array and insertion or deletion operations are as fast as in a linked list.
- A tree is a group of nodes starting from the root node.
- Every node has a specific parent and may or may not have multiple child nodes.
- Each node contains a value and references to the children.
- It’s a kind of graph data structure but does not have cycles and is fully connected.
- The best example to visualize the tree data structure is to visualize a natural rooted tree.
Tabular difference between array and tree:
| Parameter |
Array |
Tree |
| Nature |
It is a linear data structure |
It is a linear non-linear data structure |
| Base Notion |
0th Index of the array |
The root of the Tree |
| Successor |
Element at reference_index + 1 |
Child nodes of the current node. |
| Predecessor |
Element at reference_index – 1 |
Parent of the current node. |
| Natural Intuition |
Staircase model with the base staircase as the ith index |
The best example to visualize the tree data structure is to visualize a natural rooted tree. |
| Order of Insertion |
Usually an element inserted at current_index + 1 |
Depends on the type of tree. |
| Order of Deletion |
At any index but after deletion elements are rearranged |
Depends on the type of tree. |
| Insertion Complexity |
O(1)->Insertion at end.
O(N)->Insertion at random index.
|
Depends on the type for example AVL- O(log2N). |
| Deletion Complexity |
O(1)->Deletion from end.
O(N)->Deletion from a random index.
|
Depends on the type for example AVL- O(log2N). |
| Searching |
O(N) |
Depends on the type for example AVL- O(log2N). |
| Finding Min |
O(N) |
Depends on the type for example Min Heap- O(log2N). |
| Finding Max |
O(N) |
Depends on the type for example Max Heap- O(log2N). |
| IsEmpty |
O(1) |
Mostly O(1) |
| Random Access |
O(1) |
Mostly O(N) |
| Application |
Arrays are used to implement other data structures, such as lists, heaps, hash tables, deques, queues and stacks., |
Fast search, insert, delete, etc. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...