Difference Between Application Software and Operating System
Last Updated :
21 Dec, 2023
A computer can only carry out certain tasks with the help of software, which is a set of guidelines or instructions. Software can be broadly divided into two categories: system software and application software. The primary program on a computer that has direct access to the hardware of the system is called system software. It looks after and keeps an eye on all the other computer processes.
What is an Operating System?
An operating system is a computer program, works as interface between user and hardware and provides common services for computer programs. The entire process or functionality of computer system depends on the operating system. It is developed by using c++, c, and assembly languages.
An operating system performs a variety of tasks like, It manages files and directory creation and deletion, process creation, deletion, synchronization, memory allocation, and deallocation. An operating system also prevents the computer system from unauthorized access and secures the resources, information and data. It’s examples are Microsoft Windows, Linux, Unix, DOS. Overall, we can say that without an operating system a computer system is nothing. 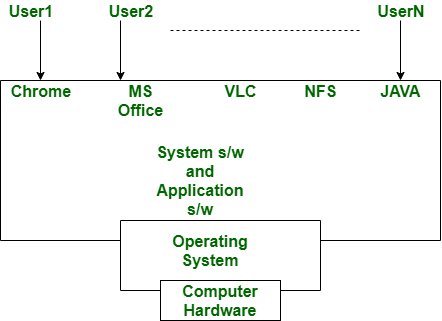
In above diagram, we can clearly see that the system and application program or software depend upon the operating system which is act as the interface between user and computer hardware.
Types of Operating System
Below are some types of Operating System.
- Batch operating system: Enables simultaneous use by numerous users. However, the users are not connected to one another. The OS and hardware don’t communicate directly. Between the OS and the hardware, there are specific operators.
- Time-sharing operating system: Every task has a set amount of time to complete it. The following duty takes over control once the allotted time has elapsed.
- Distributed operating system: In this scenario, an OS is connected to every computer system. Every computer is connected to a single operating system and has its own memory and CPU. Computers that are connected to the network can access a variety of files that are not physically on them.
- Network Operating system: In this case, each computer is linked to a shared server and runs its own operating system.
- Real-time operating systems: These systems are made to finish certain tasks within a given amount of time. They’re utilized in airbags, missiles, etc.
What is Application Software?
Application Software is one of the type of software which runs or executes as per user request. High level languages such as java, c, c++ etc are used to develop the application software. Application software is a specific purpose software which is intended to perform some task grouped together. Without an operating system application software can not be installed. It’s examples are Photoshop, VLC media player, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Google chrome etc.
Types of Application Software
Below are some types of Application Software.
- Freeware: This application software is offered for free, as the name implies. Among the freeware programs are Adobe Reader, Yahoo Messenger, LibreOffice, and others.
- Open source: These programs’ source code is accessible to everyone, allowing for modifications and the addition of new features. Examples of open source software include the GIMP and the Apache web server.
- Shareware: This software has a trial period during which it is free to download; after that, a fee is required to continue using it. Among the shareware applications are Winzip, Adobe Acrobat, Skype, and others.
- Custom software: Software specifically created for a person or organization is known as custom software. Among the custom software solutions are e-commerce and fintech solutions.
- Packaged software: Software that is packaged is software that consists of several related apps. The best illustration for this is Microsoft Office. Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, and other programs are included.
Difference Between Application Software and Operating System
| A computer program which is intended to perform some task classified along. |
A system computer program that manages hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. |
| Application software is downloaded from internet. |
Operating system comes installed on the device purchased. |
| It is developed by using virtual basic, C++, C, and Java. |
It is developed by using C++, C, and assembly languages. |
| The application software’s primary goal is to accomplish a specific task. |
To manage hardware resources efficiently. |
| It is usually in Megabytes(MB). |
It is usually in Gigabytes(GB). |
| The application is only launched when the user wants it. |
When the user turns on the computer, it begins to boot up and continues to run until the user turns it off. |
| It is built to perform some specific tasks. |
It works as an interface between user and hardware and performs a variety of tasks like memory management, scheduling, process management, etc. |
| It always depends upon the operating system. |
But it does not depend upon application software. It provides the path to execute or run the application software. |
| It runs when the user desires to run the application. |
It boots up when the user wants and runs until the user switches off the machine. |
| Its examples are Photoshop, VLC player, etc. |
Its examples are Microsoft Windows, Linux, Unix, and DOS. |
FAQs on Application Software and Operating System
Q.1: What is the full form of the software?
Answer:
The full form of software is System Software And Application for Real-Time Interactive Entertainment.
Q.2: What is PCB in OS?
Answer:
To manage information about a process, Process Control Block (PCB) is a data structure used by the operating system.
Q.3: What is a digital software?
Answer:
A digital software is application software which can be used by a computer, mobile device, or tablet to perform multiple tasks.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...