Destination IP Addresses
Last Updated :
25 Feb, 2021
Each IP datagram contains a Source Address and a Destination Address. Based on the IP addresses in the packet header there is a task of delivering packets in IP from the source host to the destination host. Whatever is the encapsulated data that has to be delivered is defined by the IP packet structure. With source and destination information it defines addressing methods that are used to label the datagram.
Type of use:
TCP / IP: –
- Between computers, there is a protocol communication, used as a standard transmitting data over networks, and form the basis of standard internet protocols. This is known as transmission control protocol or internet protocols.
- It is a combined set of protocols that performs the transfer of data between two computers and a set of rules that establish this method with which data is transmitted over the internets between two computers is the topology of the possible internet.
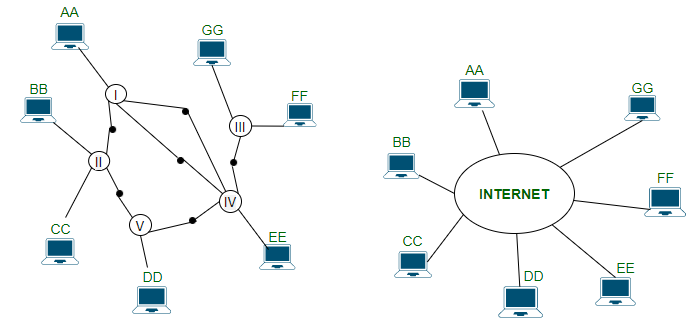
- The host computers are started with the letters AA, BB, CC, etc, solid circle numbers are 1,2,3 these are routers or gateways, the larger ovals containing Roman numbers are separate physical networks.
UDP: –
- With the help of the individual message called a datagram, the user datagram protocol that is a transmission protocol, transfers the data.
- It does not provide reliable and sequential data delivery nor does it establish a new connection, neither it enables error connection for data stream control and is also used for the transfer of small size data or for transmitting their speed that is referred from reliability.
- Example:- DNS, REALTIME AUDIO & VIDEO.
FTP:
- The method to transfer files from one location to another either on a local disk or via the internet is known as File Transfer Protocol.
- It is a common method of moving files between internet sites.
- FTP is a special way to login to another internet site for the purpose of retrieving and sending files.
- This method by which files are transferred is a protocol used to transmit files between the computer on the internet.
TFTP:
- Trivial File Transfer Protocols do not provide password protection for user directory capabilities after transferring the file, as it is a simplified version of FTP which is associated with the TCP for IP family or protocols which depend on the connectionless datagram delivery service UDP.
- Through this a network of servers linked together by a common protocol allowing access to millions of hypertext resources called www (World Wide Web).
- Throughout the world, a collection of documents on computers are connected to each other by clickable hyperlink which needs to run to browser program to access the web.
- HTTP’s servers allow text graphics, sound, and video files to be displayed in computer networks consisting of a collection of internet sites that offer text graphics sound animation resources through the hypertext transfer protocol.
URL:
- Through this, the location of the webpage is identified, as it accesses a web page that requires an address.
- The documents distributed all over this world are easy to access.
- www uses the concept of location identifier and the uniform resource locator.
- URL is a standard for defining any kind of information on the Internet not only things the method host computer and pathname are also defined.
- E.g. URL:http://www.yahoo.com.

- Method –
This is a protocol that is used to retrieve the documents with several protocols like Gopher, FTP, HTTP, news, and Telnet.
- Host –
The hostname identifies the host where the resource is located. For example www.abcd.com, here www is hostname and abcd.com is a domain name.
- Path –
In this information is located which contains slashes that separate directory from subdirectories and files in UNIX operating system.
- HTTP –
Hypertext Transfer Protocol transfer the HTML document of the World Wide Web and is a primary protocol on which this www operates.
DNS:
- This is a domain name system or service in which internet service translates the domain name into IP addresses because these are alphabetic and easy to remember.
- Every time when we use a domain name, a DNS service must translate the name into the corresponding IP addresses.
- However, IP address is really based on the internet, or we can say the internet is really based on IP addresses.
Generic Domain:
This is also known as the organization domain which divides registered hosts as per the generic behavior. Red, left to right, start with the most particular information about the host and become more and more general with each label until they reach the right-most label and describes the larger group affiliation of the named host:
- .com : Commercial organization,
- .edu: Educational institution,
- .gov: Government Institutions,
- .In : International Organization
- .mil : Military group
- .net: Network Provider
- .org: Organization other than those listed above.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...