Designing algorithm to solve Ball Sort Puzzle
Last Updated :
20 Mar, 2024
In Ball Sort Puzzle game, we have p balls of each colour and n different colours, for a total of p×n balls, arranged in n stacks. In addition, we have 2 empty stacks. A maximum of p balls can be in any stack at a given time. The goal of the game is to sort the balls by colour in each of the n stacks.
Rules:
- Only the top ball of each stack can be moved.
- A ball can be moved on top of another ball of the same colour
- A ball can be moved in an empty stack.
Refer to the following GIF for an example game play (Level-7):
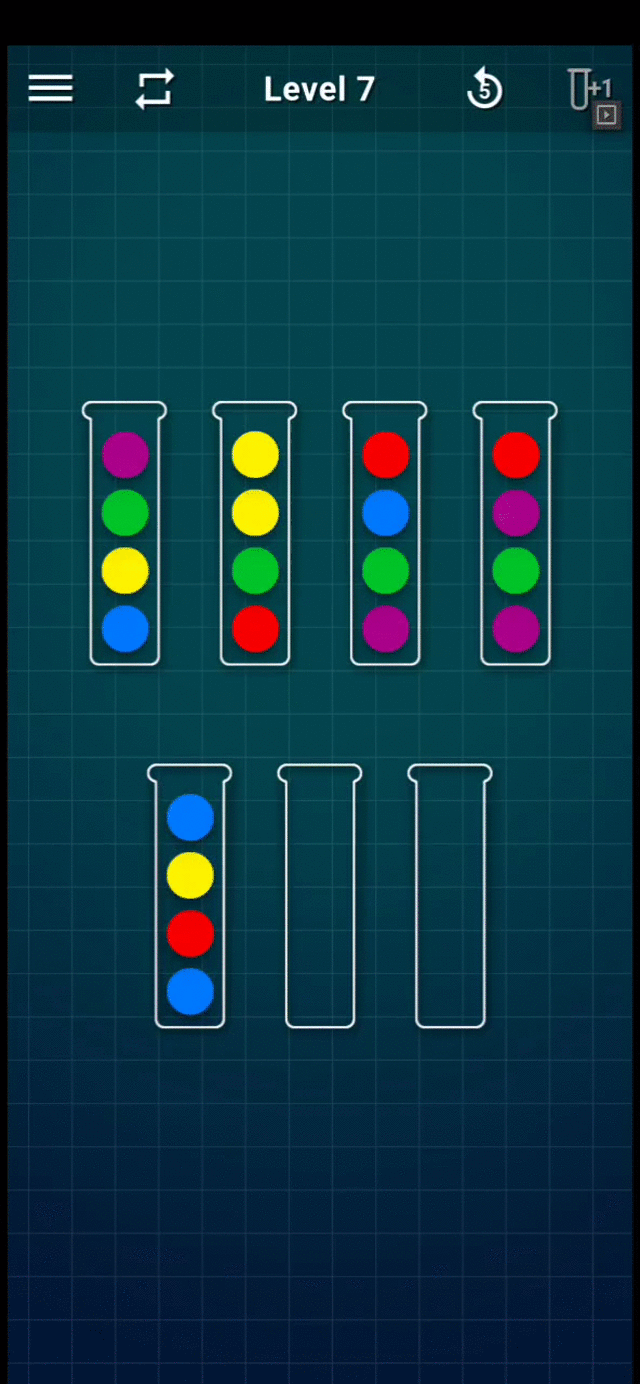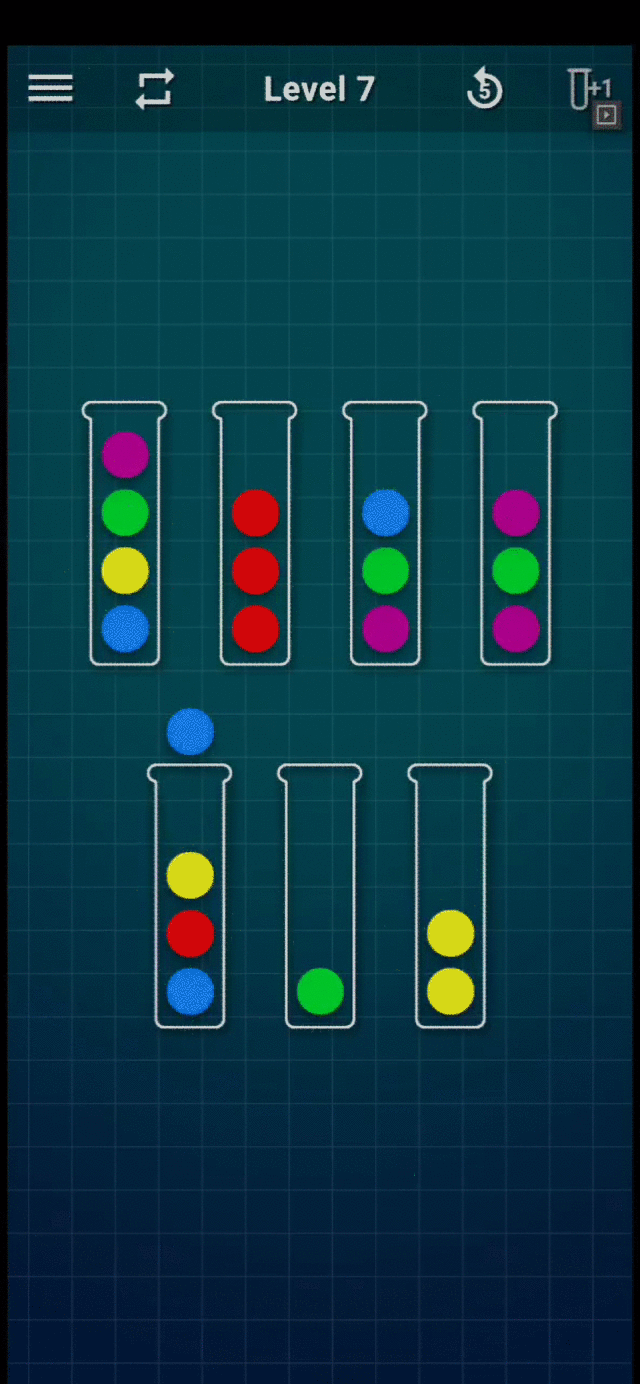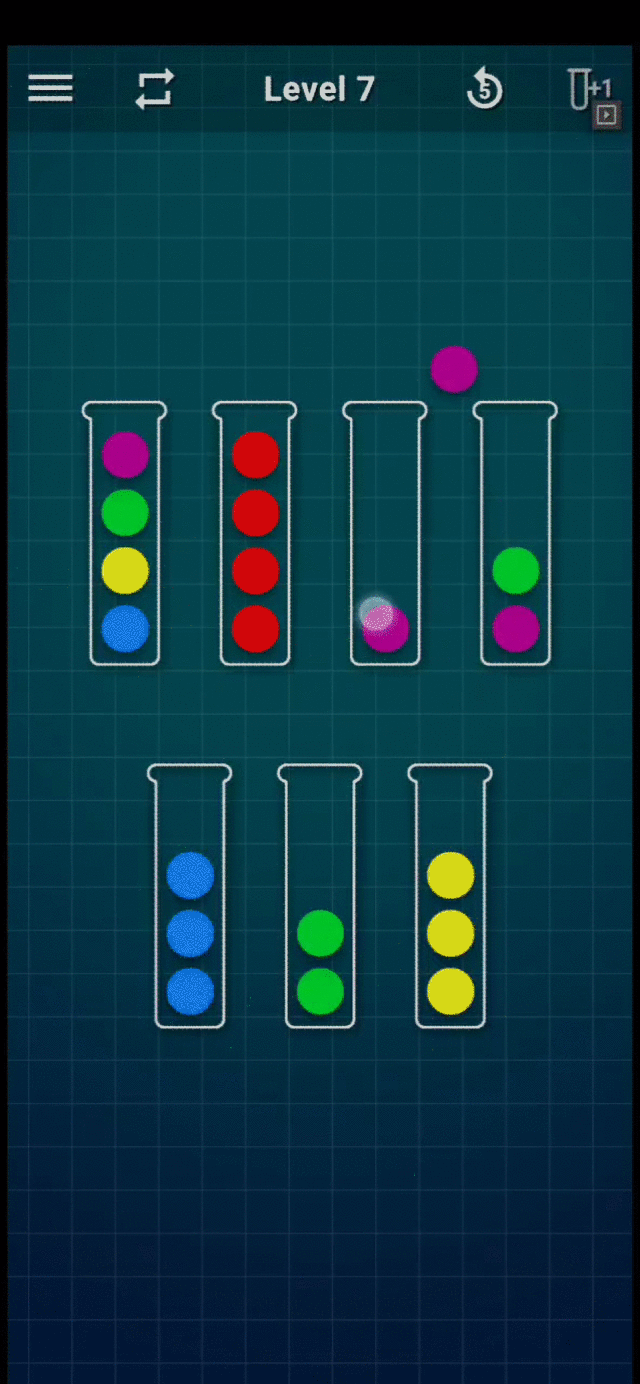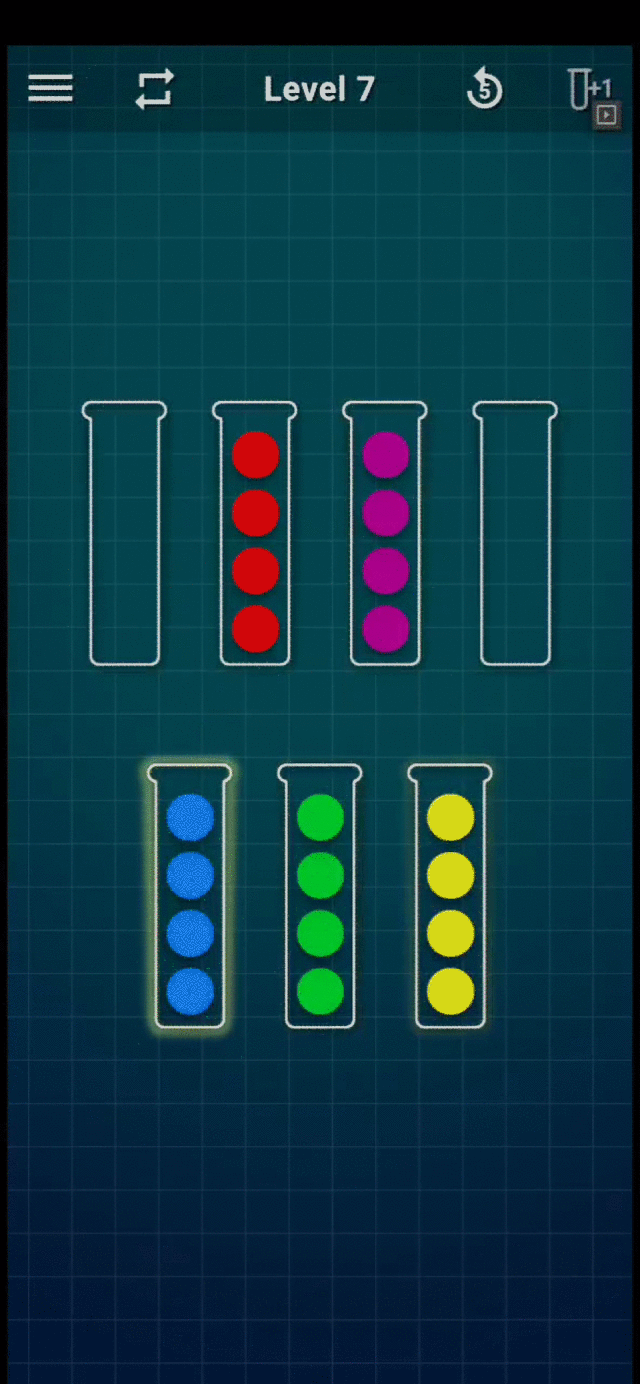
Level 7 Gameplay
Approach I [Recursion and BackTrack]:
- From the given rules, a simple recursive algorithm could be generated as below:
- Start with the given initial position of all the balls
- Create an initial empty Queue.
- loop:
- If the current position is sorted:
- else
- Enqueue all possible moves in a Queue.
- Dequeue the next move from the Queue.
- Go to loop.
However, the approach looks simple and correct, it has few caveats:
- Incorrect:
- We might end up in an infinite loop if there are >1 moves in the Queue which lead to the same position of balls.
- Inefficient:
- We might end up visiting the same position multiple times.
Thus, eliminating the above-mentioned bottlenecks would solve the issue.
Approach II [Memoization using HashMap]:
- Assumptions:
- We’ll represent ball positions as a vector of strings: {“gbbb”, “ybry”, “yggy”, “rrrg”}
- Create a set called Visited of <String> which will contain the visited positions as one long string.
- Create an empty vector for Answer which will store positions<a, b> of the tubes to move the top ball from tube a to and put it in tube b.
- Initialise grid with the initial settings of the balls.
- func solver(grid):
- add grid to Visited
- loop over all the stacks (i):
- loop over all the stacks (j):
- If move i->j is valid, create newGrid with that move.
- if the balls are sorted in newGrid,
- if newGrid is NOT in Visited
- solver(newGrid)
- if solved:
Sample Game Input I:
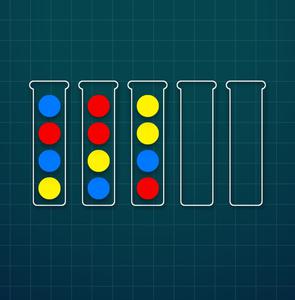
Level 3
Sample Input I:
5
ybrb
byrr
rbyy
Sample Output I:
Move 1 to 4 1 times
Move 1 to 5 1 times
Move 1 to 4 1 times
Move 2 to 5 2 times
Move 1 to 2 1 times
Move 3 to 1 1 times
Move 1 to 2 1 times
Move 3 to 1 1 times
Move 2 to 1 3 times
Move 2 to 3 1 times
Move 3 to 4 1 times
Move 3 to 2 1 times
Move 2 to 4 1 times
Move 3 to 5 1 times
Sample Game Input II:
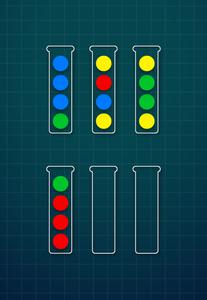
Level 5
Sample Input II:
6
gbbb
ybry
yggy
rrrg
Sample Output II:
Move 1 to 5 3 times
Move 2 to 6 1 times
Move 3 to 6 1 times
Move 1 to 3 1 times
Move 2 to 1 1 times
Move 2 to 5 1 times
Move 2 to 6 1 times
Move 3 to 2 3 times
Move 3 to 6 1 times
Move 4 to 2 1 times
Move 1 to 4 1 times
Refer to the below C++ implementation with the comments for the reference:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using Grid = vector<string>;
Grid configureGrid(string stacks[], int numberOfStacks)
{
Grid grid;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfStacks; i++)
grid.push_back(stacks[i]);
return grid;
}
// Function to find the max
int getStackHeight(Grid grid)
{
int max = 0;
for (auto stack : grid)
if (max < stack.size())
max = stack.size();
return max;
}
// Convert vector of strings to
// canonicalRepresentation of strings
string canonicalStringConversion(Grid grid)
{
string finalString;
sort(grid.begin(), grid.end());
for (auto stack : grid) {
finalString += (stack + ";");
}
return finalString;
}
// Function to check if it is solved
// or not
bool isSolved(Grid grid, int stackHeight)
{
for (auto stack : grid) {
if (!stack.size())
continue;
else if (stack.size() < stackHeight)
return false;
else if (std::count(stack.begin(),
stack.end(),
stack[0])
!= stackHeight)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Check if the move is valid
bool isValidMove(string sourceStack,
string destinationStack,
int height)
{
// Can't move from an empty stack
// or to a FULL STACK
if (sourceStack.size() == 0
|| destinationStack.size() == height)
return false;
int colorFreqs
= std::count(sourceStack.begin(),
sourceStack.end(),
sourceStack[0]);
// If the source stack is same colored,
// don't touch it
if (colorFreqs == height)
return false;
if (destinationStack.size() == 0) {
// If source stack has only
// same colored balls,
// don't touch it
if (colorFreqs == sourceStack.size())
return false;
return true;
}
return (
sourceStack[sourceStack.size() - 1]
== destinationStack[destinationStack.size() - 1]);
}
// Function to solve the puzzle
bool solvePuzzle(Grid grid, int stackHeight,
unordered_set<string>& visited,
vector<vector<int> >& answerMod)
{
if (stackHeight == -1) {
stackHeight = getStackHeight(grid);
}
visited.insert(
canonicalStringConversion(grid));
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) {
// Iterate over all the stacks
string sourceStack = grid[i];
for (int j = 0; j < grid.size(); j++) {
if (i == j)
continue;
string destinationStack = grid[j];
if (isValidMove(sourceStack,
destinationStack,
stackHeight)) {
// Creating a new Grid
// with the valid move
Grid newGrid(grid);
// Adding the ball
newGrid[j].push_back(newGrid[i].back());
// Adding the ball
newGrid[i].pop_back();
if (isSolved(newGrid, stackHeight)) {
answerMod.push_back(
vector<int>{ i, j, 1 });
return true;
}
if (visited.find(
canonicalStringConversion(newGrid))
== visited.end()) {
bool solveForTheRest
= solvePuzzle(newGrid, stackHeight,
visited, answerMod);
if (solveForTheRest) {
vector<int> lastMove
= answerMod[answerMod.size()
- 1];
// Optimisation - Concatenating
// consecutive moves of the same
// ball
if (lastMove[0] == i
&& lastMove[1] == j)
answerMod[answerMod.size() - 1]
[2]++;
else
answerMod.push_back(
vector<int>{ i, j, 1 });
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
// Checks whether the grid is valid or not
bool checkGrid(Grid grid)
{
int numberOfStacks = grid.size();
int stackHeight = getStackHeight(grid);
int numBallsExpected
= ((numberOfStacks - 2) * stackHeight);
// Cause 2 empty stacks
int numBalls = 0;
for (auto i : grid)
numBalls += i.size();
if (numBalls != numBallsExpected) {
cout << "Grid has incorrect # of balls"
<< endl;
return false;
}
map<char, int> ballColorFrequency;
for (auto stack : grid)
for (auto ball : stack)
if (ballColorFrequency.find(ball)
!= ballColorFrequency.end())
ballColorFrequency[ball] += 1;
else
ballColorFrequency[ball] = 1;
for (auto ballColor : ballColorFrequency) {
if (ballColor.second != getStackHeight(grid)) {
cout << "Color " << ballColor.first
<< " is not " << getStackHeight(grid)
<< endl;
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
int main(void)
{
// Including 2 empty stacks
int numberOfStacks = 6;
std::string stacks[]
= { "gbbb", "ybry", "yggy", "rrrg", "", "" };
Grid grid = configureGrid(
stacks, numberOfStacks);
if (!checkGrid(grid)) {
cout << "Invalid Grid" << endl;
return 1;
}
if (isSolved(grid, getStackHeight(grid))) {
cout << "Problem is already solved"
<< endl;
return 0;
}
unordered_set<string> visited;
vector<vector<int> > answerMod;
// Solve the puzzle instance
solvePuzzle(grid, getStackHeight(grid),
visited,
answerMod);
// Since the values of Answers are appended
// When the problem was completely
// solved and backwards from there
reverse(answerMod.begin(), answerMod.end());
for (auto v : answerMod) {
cout << "Move " << v[0] + 1
<< " to " << v[1] + 1
<< " " << v[2] << " times"
<< endl;
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// Function to configure the grid
static ArrayList<String> configureGrid(String[] stacks, int numberOfStacks) {
ArrayList<String> grid = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfStacks; i++)
grid.add(stacks[i]);
return grid;
}
// Function to find the max
static int getStackHeight(ArrayList<String> grid) {
int max = 0;
for (String stack : grid)
if (max < stack.length())
max = stack.length();
return max;
}
// Convert ArrayList of strings to canonicalRepresentation of strings
static String canonicalStringConversion(ArrayList<String> grid) {
Collections.sort(grid);
StringBuilder finalString = new StringBuilder();
for (String stack : grid) {
finalString.append(stack).append(";");
}
return finalString.toString();
}
// Function to check if it is solved or not
static boolean isSolved(ArrayList<String> grid, int stackHeight) {
for (String stack : grid) {
if (stack.length() == 0)
continue;
else if (stack.length() < stackHeight)
return false;
else if (Collections.frequency(Arrays.asList(stack.split("")), String.valueOf(stack.charAt(0))) != stackHeight)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Check if the move is valid
static boolean isValidMove(String sourceStack, String destinationStack, int height) {
// Can't move from an empty stack or to a FULL STACK
if (sourceStack.length() == 0 || destinationStack.length() == height)
return false;
int colorFreqs = Collections.frequency(Arrays.asList(sourceStack.split("")), String.valueOf(sourceStack.charAt(0)));
// If the source stack is same colored, don't touch it
if (colorFreqs == height)
return false;
if (destinationStack.length() == 0) {
// If source stack has only same colored balls, don't touch it
if (colorFreqs == sourceStack.length())
return false;
return true;
}
return (sourceStack.charAt(sourceStack.length() - 1) == destinationStack.charAt(destinationStack.length() - 1));
}
// Function to solve the puzzle
static boolean solvePuzzle(ArrayList<String> grid, int stackHeight, HashSet<String> visited, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> answerMod) {
if (stackHeight == -1) {
stackHeight = getStackHeight(grid);
}
visited.add(canonicalStringConversion(grid));
for (int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) {
// Iterate over all the stacks
String sourceStack = grid.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < grid.size(); j++) {
if (i == j)
continue;
String destinationStack = grid.get(j);
if (isValidMove(sourceStack, destinationStack, stackHeight)) {
// Creating a new Grid with the valid move
ArrayList<String> newGrid = new ArrayList<>(grid);
// Adding the ball
newGrid.set(j, newGrid.get(j) + newGrid.get(i).charAt(newGrid.get(i).length() - 1));
// Removing the ball
newGrid.set(i, newGrid.get(i).substring(0, newGrid.get(i).length() - 1));
if (isSolved(newGrid, stackHeight)) {
answerMod.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(i, j, 1)));
return true;
}
if (!visited.contains(canonicalStringConversion(newGrid))) {
boolean solveForTheRest = solvePuzzle(newGrid, stackHeight, visited, answerMod);
if (solveForTheRest) {
ArrayList<Integer> lastMove = answerMod.get(answerMod.size() - 1);
// Optimisation - Concatenating consecutive moves of the same ball
if (lastMove.get(0) == i && lastMove.get(1) == j)
answerMod.get(answerMod.size() - 1).set(2, answerMod.get(answerMod.size() - 1).get(2) + 1);
else
answerMod.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(i, j, 1)));
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
// Checks whether the grid is valid or not
static boolean checkGrid(ArrayList<String> grid) {
int numberOfStacks = grid.size();
int stackHeight = getStackHeight(grid);
int numBallsExpected = ((numberOfStacks - 2) * stackHeight); // Cause 2 empty stacks
int numBalls = 0;
for (String i : grid)
numBalls += i.length();
if (numBalls != numBallsExpected) {
System.out.println("Grid has incorrect # of balls");
return false;
}
HashMap<Character, Integer> ballColorFrequency = new HashMap<>();
for (String stack : grid)
for (char ball : stack.toCharArray())
ballColorFrequency.put(ball, ballColorFrequency.getOrDefault(ball, 0) + 1);
for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> ballColor : ballColorFrequency.entrySet()) {
if (ballColor.getValue() != getStackHeight(grid)) {
System.out.println("Color " + ballColor.getKey() + " is not " + getStackHeight(grid));
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Including 2 empty stacks
int numberOfStacks = 6;
String[] stacks = { "gbbb", "ybry", "yggy", "rrrg", "", "" };
ArrayList<String> grid = configureGrid(stacks, numberOfStacks);
if (!checkGrid(grid)) {
System.out.println("Invalid Grid");
return;
}
if (isSolved(grid, getStackHeight(grid))) {
System.out.println("Problem is already solved");
return;
}
HashSet<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> answerMod = new ArrayList<>();
// Solve the puzzle instance
solvePuzzle(grid, getStackHeight(grid), visited, answerMod);
// Since the values of Answers are appended when the problem was completely solved and backwards from there
Collections.reverse(answerMod);
for (ArrayList<Integer> v : answerMod) {
System.out.println("Move " + (v.get(0) + 1) + " to " + (v.get(1) + 1) + " " + v.get(2) + " times");
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
class Program
{
// Function to configure the grid from an array of stacks
static List<string> ConfigureGrid(string[] stacks, int numberOfStacks)
{
List<string> grid = new List<string>();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfStacks; i++)
{
grid.Add(stacks[i]);
}
return grid;
}
// Function to find the maximum height of any stack in the grid
static int GetStackHeight(List<string> grid)
{
int max = 0;
foreach (var stack in grid)
{
if (max < stack.Length)
{
max = stack.Length;
}
}
return max;
}
// Function to convert a list of strings to a canonical representation string
static string CanonicalStringConversion(List<string> grid)
{
string finalString = "";
grid.Sort();
foreach (var stack in grid)
{
finalString += (stack + ";");
}
return finalString;
}
// Function to check if the grid is solved or not
static bool IsSolved(List<string> grid, int stackHeight)
{
foreach (var stack in grid)
{
if (stack.Length == 0)
{
continue;
}
else if (stack.Length < stackHeight)
{
return false;
}
else if (stack.Count(c => c == stack[0]) != stackHeight)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Function to check if a move from source to destination is valid
static bool IsValidMove(string sourceStack, string destinationStack, int height)
{
if (sourceStack.Length == 0 || destinationStack.Length == height)
{
return false;
}
int colorFreqs = sourceStack.Count(c => c == sourceStack[0]);
if (colorFreqs == height)
{
return false;
}
if (destinationStack.Length == 0)
{
if (colorFreqs == sourceStack.Length)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
return (sourceStack[sourceStack.Length - 1] == destinationStack[destinationStack.Length - 1]);
}
// Function to solve the Tower of Hanoi puzzle
static bool SolvePuzzle(List<string> grid, int stackHeight, HashSet<string> visited, List<int[]> answerMod)
{
if (stackHeight == -1)
{
stackHeight = GetStackHeight(grid);
}
visited.Add(CanonicalStringConversion(grid));
for (int i = 0; i < grid.Count; i++)
{
string sourceStack = grid[i];
for (int j = 0; j < grid.Count; j++)
{
if (i == j)
{
continue;
}
string destinationStack = grid[j];
if (IsValidMove(sourceStack, destinationStack, stackHeight))
{
List<string> newGrid = new List<string>(grid);
newGrid[j] += newGrid[i][newGrid[i].Length - 1];
newGrid[i] = newGrid[i].Substring(0, newGrid[i].Length - 1);
if (IsSolved(newGrid, stackHeight))
{
answerMod.Add(new int[] { i, j, 1 });
return true;
}
if (!visited.Contains(CanonicalStringConversion(newGrid)))
{
if (SolvePuzzle(newGrid, stackHeight, visited, answerMod))
{
int[] lastMove = answerMod[answerMod.Count - 1];
if (lastMove[0] == i && lastMove[1] == j)
{
answerMod[answerMod.Count - 1][2]++;
}
else
{
answerMod.Add(new int[] { i, j, 1 });
}
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
// Function to check whether the grid is valid or not
static bool CheckGrid(List<string> grid)
{
int numberOfStacks = grid.Count;
int stackHeight = GetStackHeight(grid);
int numBallsExpected = ((numberOfStacks - 2) * stackHeight);
int numBalls = grid.Sum(stack => stack.Length);
if (numBalls != numBallsExpected)
{
Console.WriteLine("Grid has incorrect # of balls");
return false;
}
Dictionary<char, int> ballColorFrequency = new Dictionary<char, int>();
foreach (var stack in grid)
{
foreach (var ball in stack)
{
if (ballColorFrequency.ContainsKey(ball))
{
ballColorFrequency[ball]++;
}
else
{
ballColorFrequency[ball] = 1;
}
}
}
foreach (var ballColor in ballColorFrequency)
{
if (ballColor.Value != stackHeight)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Color {ballColor.Key} is not {stackHeight}");
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Main function
static void Main()
{
// Including 2 empty stacks
int numberOfStacks = 6;
string[] stacks = { "gbbb", "ybry", "yggy", "rrrg", "", "" };
List<string> grid = ConfigureGrid(stacks, numberOfStacks);
// Check if the initial grid is valid
if (!CheckGrid(grid))
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid Grid");
return;
}
// Check if the grid is already solved
if (IsSolved(grid, GetStackHeight(grid)))
{
Console.WriteLine("Problem is already solved");
return;
}
// Set to keep track of visited states
HashSet<string> visited = new HashSet<string>();
// List to store the solution steps
List<int[]> answerMod = new List<int[]>();
// Solve the Tower of Hanoi puzzle
SolvePuzzle(grid, GetStackHeight(grid), visited, answerMod);
// Reverse the solution steps to print them in the correct order
answerMod.Reverse();
// Print the solution steps
foreach (var v in answerMod)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Move {v[0] + 1} to {v[1] + 1} {v[2]} times");
}
}
}
// Function to configure the grid
function configureGrid(stacks, numberOfStacks) {
let grid = [];
for (let i = 0; i < numberOfStacks; i++)
grid.push(stacks[i]);
return grid;
}
// Function to find the max
function getStackHeight(grid) {
let max = 0;
for (let stack of grid)
if (max < stack.length)
max = stack.length;
return max;
}
// Convert ArrayList of strings to canonicalRepresentation of strings
function canonicalStringConversion(grid) {
grid.sort();
let finalString = '';
for (let stack of grid) {
finalString += stack + ";";
}
return finalString;
}
// Function to check if it is solved or not
function isSolved(grid, stackHeight) {
for (let stack of grid) {
if (stack.length == 0)
continue;
else if (stack.length < stackHeight)
return false;
else if (stack.split('').filter(c => c === stack.charAt(0)).length != stackHeight)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Check if the move is valid
function isValidMove(sourceStack, destinationStack, height) {
// Can't move from an empty stack or to a FULL STACK
if (sourceStack.length == 0 || destinationStack.length == height)
return false;
let colorFreqs = sourceStack.split('').filter(c => c === sourceStack.charAt(0)).length;
// If the source stack is same colored, don't touch it
if (colorFreqs == height)
return false;
if (destinationStack.length == 0) {
// If source stack has only same colored balls, don't touch it
if (colorFreqs == sourceStack.length)
return false;
return true;
}
return (sourceStack.charAt(sourceStack.length - 1) == destinationStack.charAt(destinationStack.length - 1));
}
// Function to solve the puzzle
function solvePuzzle(grid, stackHeight, visited, answerMod) {
if (stackHeight == -1) {
stackHeight = getStackHeight(grid);
}
visited.add(canonicalStringConversion(grid));
for (let i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
// Iterate over all the stacks
let sourceStack = grid[i];
for (let j = 0; j < grid.length; j++) {
if (i == j)
continue;
let destinationStack = grid[j];
if (isValidMove(sourceStack, destinationStack, stackHeight)) {
// Creating a new Grid with the valid move
let newGrid = [...grid];
// Adding the ball
newGrid[j] += sourceStack.charAt(sourceStack.length - 1);
// Removing the ball
newGrid[i] = sourceStack.substring(0, sourceStack.length - 1);
if (isSolved(newGrid, stackHeight)) {
answerMod.push([i, j, 1]);
return true;
}
if (!visited.has(canonicalStringConversion(newGrid))) {
let solveForTheRest = solvePuzzle(newGrid, stackHeight, visited, answerMod);
if (solveForTheRest) {
let lastMove = answerMod[answerMod.length - 1];
// Optimisation - Concatenating consecutive moves of the same ball
if (lastMove[0] == i && lastMove[1] == j)
answerMod[answerMod.length - 1][2] += 1;
else
answerMod.push([i, j, 1]);
return true;
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
// Checks whether the grid is valid or not
function checkGrid(grid) {
let numberOfStacks = grid.length;
let stackHeight = getStackHeight(grid);
let numBallsExpected = ((numberOfStacks - 2) * stackHeight); // Cause 2 empty stacks
let numBalls = 0;
for (let stack of grid)
numBalls += stack.length;
if (numBalls != numBallsExpected) {
console.log("Grid has incorrect # of balls");
return false;
}
let ballColorFrequency = new Map();
for (let stack of grid) {
for (let ball of stack.split('')) {
ballColorFrequency.set(ball, (ballColorFrequency.get(ball) || 0) + 1);
}
}
for (let [ball, freq] of ballColorFrequency) {
if (freq != getStackHeight(grid)) {
console.log(`Color ${ball} is not ${getStackHeight(grid)}`);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Driver Code
(function main() {
// Including 2 empty stacks
let numberOfStacks = 6;
let stacks = ["gbbb", "ybry", "yggy", "rrrg", "", ""];
let grid = configureGrid(stacks, numberOfStacks);
if (!checkGrid(grid)) {
console.log("Invalid Grid");
return;
}
if (isSolved(grid, getStackHeight(grid))) {
console.log("Problem is already solved");
return;
}
let visited = new Set();
let answerMod = [];
// Solve the puzzle instance
solvePuzzle(grid, getStackHeight(grid), visited, answerMod);
// Since the values of Answers are appended when the problem was completely solved and backwards from there
answerMod.reverse();
for (let v of answerMod) {
console.log(`Move ${v[0] + 1} to ${v[1] + 1} ${v[2]} times`);
}
})();
def configureGrid(stacks, numberOfStacks):
grid = []
for i in range(numberOfStacks):
grid.append(stacks[i])
return grid
# Function to find the max
def getStackHeight(grid):
max = 0
for stack in grid:
if max < len(stack):
max = len(stack)
return max
# Convert vector of strings to
# canonicalRepresentation of strings
def canonicalStringConversion(grid):
finalString = ""
grid.sort()
for stack in grid:
finalString += (stack + ";")
return finalString
# Function to check if it is solved
# or not
def isSolved(grid, stackHeight):
for stack in grid:
if len(stack) == 0:
continue
elif len(stack) < stackHeight:
return False
elif stack.count(stack[0]) != stackHeight:
return False
return True
# Check if the move is valid
def isValidMove(sourceStack, destinationStack, height):
# Can't move from an empty stack
# or to a FULL STACK
if len(sourceStack) == 0 or len(destinationStack) == height:
return False
colorFreqs = sourceStack.count(sourceStack[0])
# If the source stack is same colored,
# don't touch it
if colorFreqs == height:
return False
if len(destinationStack) == 0:
# If source stack has only
# same colored balls,
# don't touch it
if colorFreqs == len(sourceStack):
return False
return True
return sourceStack[len(sourceStack) - 1] == destinationStack[len(destinationStack) - 1]
# Function to solve the puzzle
def solvePuzzle(grid, stackHeight, visited, answerMod):
if stackHeight == -1:
stackHeight = getStackHeight(grid)
visited.add(canonicalStringConversion(grid))
for i in range(len(grid)):
# Iterate over all the stacks
sourceStack = grid[i]
for j in range(len(grid)):
if i == j:
continue
destinationStack = grid[j]
if isValidMove(sourceStack, destinationStack, stackHeight):
# Creating a new Grid
# with the valid move
newGrid = list(grid)
# Adding the ball
newGrid[j] += newGrid[i][len(newGrid[i]) - 1]
# Removing the ball
newGrid[i] = newGrid[i][:-1]
if isSolved(newGrid, stackHeight):
answerMod.append([i, j, 1])
return True
if canonicalStringConversion(newGrid) not in visited:
if solvePuzzle(newGrid, stackHeight, visited, answerMod):
lastMove = answerMod[len(answerMod) - 1]
# Optimisation - Concatenating
# consecutive moves of the same
# ball
if lastMove[0] == i and lastMove[1] == j:
answerMod[len(answerMod) - 1][2] += 1
else:
answerMod.append([i, j, 1])
return True
return False
# Checks whether the grid is valid or not
def checkGrid(grid):
numberOfStacks = len(grid)
stackHeight = getStackHeight(grid)
numBallsExpected = ((numberOfStacks - 2) * stackHeight)
# Cause 2 empty stacks
numBalls = 0
for i in grid:
numBalls += len(i)
if numBalls != numBallsExpected:
print("Grid has incorrect # of balls")
return False
ballColorFrequency = {}
for stack in grid:
for ball in stack:
if ball in ballColorFrequency:
ballColorFrequency[ball] += 1
else:
ballColorFrequency[ball] = 1
for ballColor in ballColorFrequency:
if ballColorFrequency[ballColor] != getStackHeight(grid):
print("Color", ballColor, "is not", getStackHeight(grid))
return False
return True
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Including 2 empty stacks
numberOfStacks = 6
stacks = ["gbbb", "ybry", "yggy", "rrrg", "", ""]
grid = configureGrid(stacks, numberOfStacks)
if not checkGrid(grid):
print("Invalid Grid")
exit()
if isSolved(grid, getStackHeight(grid)):
print("Problem is already solved")
exit()
visited = set()
answerMod = []
# Solve the puzzle instance
solvePuzzle(grid, getStackHeight(grid), visited, answerMod)
# Since the values of Answers are appended
# When the problem was completely
# solved and backwards from there
answerMod.reverse()
for v in answerMod:
print("Move", v[0] + 1, "to", v[1] + 1, v[2], "times")
OutputMove 1 to 5 3 times
Move 2 to 6 1 times
Move 3 to 6 1 times
Move 1 to 3 1 times
Move 2 to 1 1 times
Move 2 to 5 1 times
Move 2 to 6 1 times
Move 3 to 2 3 times
Move 3 to 6 1 times
Move 4 to 2 1 times
...
Time Complexity: O(n!) where n is the number of stacks.
Auxiliary Space: O(n^2)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...