Coal is considered to be one of the most important and also abundantly available fossil fuel present in India. Coal accounts for over 55% of India’s energy requirements. Coal is a foundational resource for building the industrial sector of India.
With consideration of rapid population growth over the years, eco-conservation restrictions on hydro-power projects, and the geopolitical perception of the nuclear power system in India, coal is supposedly going to continue as an important source of energy in the context of India.
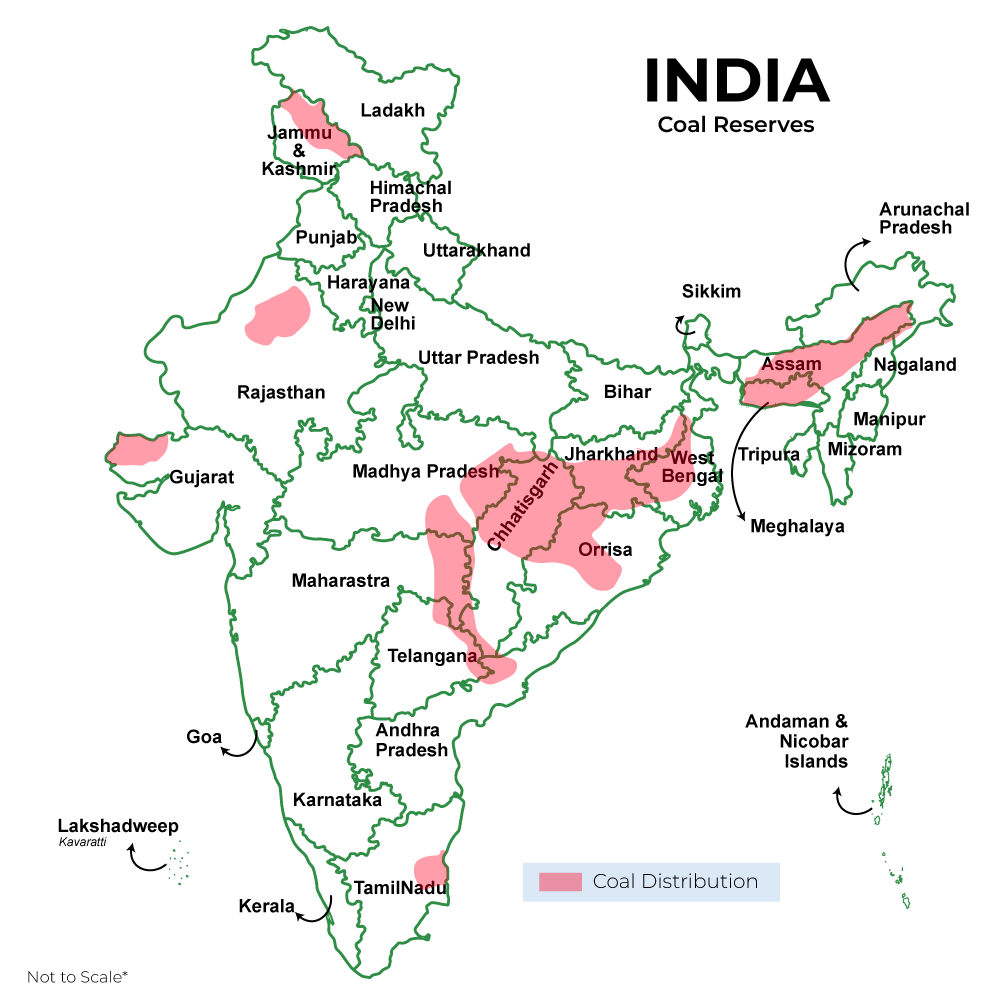
Coal Reserves of India
Characteristics of Coal
Coal is a black-brownish sedimentary rock that is highly combustible. The primary composition of coal is carbon, hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when organic matter is decomposed and buried for millions of years and is acted upon by bacteria and high temperature and pressure. Coal is mostly used for fuel. The usage of coal has highly increased since the onset of the Industrial revolution. It is one of the most important resources in today’s world. It is one of the most important sources to produce electricity. Coal is used highly to produce electricity. Over one-third of the electricity in the world is produced through coal.
Coal is classified into various types based on the amount of carbon present in the coal sample. Peat is the lowest quality coal. Lignite or brown coal is the most harmful to the health of people. It is used only for the production of Electricity. Sub Bituminous coal has more carbon content than lignite and has a wide range of applications. It is mostly used as fuel. Bituminous coal is a dense black in nature and is a sedimentary rock. It has high-quality coal. It is used as a fuel in steam electric power generation and for the manufacturing of coke. Anthracite coal is the highest grade of coal and has the highest quantity of carbon. It is harder glossy, and black in nature.
Classification of Coal
Coal can be classified on the basis of carbon content and also the time period into consideration. The following are some types:
Anthracite
It is one of the best quality coal with a high level of calorific value and the carbon content of it is 80 to 95%. It is found in small quality in Jammu and Kashmir.
Bituminous
A low level of moisture content is present in Bituminous coal, with around 60 to 80% of carbon content, and has a high value of calorific. Some important states with its reserves are Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and Madhya Pradesh.
Lignite
It carries over 40 to 55% carbon content and is mostly brown in color, with a high level of moisture. Important states where they are available are Rajasthan, Lakhimpur (Assam), and Tamil Nadu.
Peat
It refers to the first stage of transformation from wood to that coal, with a low calorific value and carbon content is less than 40%.
Distribution of Coal in India
The coal in India is mostly divided into two categories of distribution:
- Gondwana Coal
- Tertiary Coal
Gondwana Coal
Gondwana coal makes up about 98 percent of the total reserves and 99 percent of the production of coal in India. It forms the metallurgical grade of India and superior quality coal. The Bermuda series is one of the most important coal fields in India and accounts for around 80 percent of the total coal production in India. Coking and also non-coking as well as bituminous coal obtained in the coalfields of Gondwana. They occur in important rivers like Damodar, Mahanadi, Son, Godavari, and Wardha.
Tertiary Coal
Tertiary coal is about 15 to 60 million years old and the content of carbon is very low. It is mainly confined to the extra-Peninsula like Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Assam, and so forth. It has a high percentage of moisture and sulphur. Some important areas include Assam, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Himalayan foothills, and also areas of Tamil Nadu and the Union territory of Pondicherry.
History of Coal Mining in India
The start of coal mining in India can be traced back to 1774, however, the growth remained sluggish. The introduction of the steam locomotives in 1853 helped to hype it up. The production got a boost during the First World War but again became sluggish till the early 30s. The National Coal Development Corporation was set up by the Government of India Undertaking in around 1956.

Coal Mining
Nationalisation of Coal Mines
The nationalization of the coal mines was done in two phases, first in coking coal mines in 1971-72 and the second for the non-coking coal mines in 1973. The Coking Coal Mines (Emergency Provisions) Act, of 1971 was for the public interest of management of coking coal mines and coke plants. This was next followed by the Coking Coal Mines Act of 1972, brought under the Bharat Coking Coal Limited (BCCL). The Coal Mines Act, of 1973 extended the rights of the Government of India.
Coal Reserves in India Statewise
Coal reserves distribution in India, in the context of states, from the highest are as follows:
States
|
Total
|
| Jharkhand |
83152 |
| Odisha |
79295 |
| Chhattisgarh |
57206 |
| West Bengal |
31667 |
| Madhya Pradesh |
27987 |
| Telangana |
21702 |
| Maharashtra |
12299 |
| Andhra Pradesh |
1581 |
| Bihar |
1367 |
| Uttar Pradesh |
1062 |
| Meghalaya |
576 |
| Assam |
525 |
| Nagaland |
410 |
| Sikkim |
101 |
| Arunachal Pradesh |
90 |
Coal Reserves in The world
The United States has over 249 billion tons of coal reserves as of 2020. The coal reserves in the USA are around 23 percent of the total world reserves. Most of the coal in the USA is produced by the states of Wyoming and the Appalachian region. Russia has over 162 billion tons of coal reserves as of 2020. It accounts for 15 percent of the world’s reserves. Central Siberia has the largest coal reserves in Russia. Australia has the third largest coal reserves in the world followed by China and India. The largest coal-producing countries in the world are China, India, the United States, and Indonesia.
Coal Reserves in India
India is the second largest producer and consumer of coal in the world second to only China. Coal has been mined in India since 1774. India has mined coal for more than 777.31 million tomes in the year 2021. To supply the coal for its steel plant India imports 30 percent of the coal required. India Dhanbad is the largest coal-producing city in India. Dhanbad has often been termed the coal capital of India.
Currently, India has the fourth largest coal reserves in the world. According to a survey conducted in the year 2021, there are around 352.13 billion metric tons of coal reserves. Most of the coal is found in the northeastern and south-central regions of India. Three states Jharkhand, Odisha, and Chhattisgarh contribute to almost 70 percent of the total coal reserves present in India. The total lignite coal present in India is 46.02 billion metric tons. Among all the places in India Tamil Nadu has the largest lignite reserves in India. The energy produced by the use of coal is twice when compared to that of oil.
Jharkhand has the largest coal reserves in India. It is located in northeast India. The production of coal from this state accounts for 26 percent of the total production in India. The main coal mining centers in Jharkhand are Dhanbad, Ramgarh, Karanpur, Jharia, Bokaro, Auranga, Giridih, and Hutar. The total coal reserves in Jharkhand are 83.15 billion tons. The mines in Jharkhand are known to produce high-quality bituminous coal.
After Jharkhand Odisha has the highest coal reserves in India. The coal reserves in India are 79.30 billion tonnes. It is located in the east of India. The coal reserves in this area account for 24 percent of India. This state produces 15 percent of the total coal produced in India.
Chhattisgarh has around 17 percent of the total coal reserves of the country. It comes next to Odisha. It is located in central India. Most of the coal reserves in Chhattisgarh are located in Chirimiri, Johilla, and Jhilimili. The largest coalfield in Chhattisgarh is the Hasdeo-Arand coalfield, second is the Korba coalfield. The total coal reserves in India are around 57 billion tons.
West Bengal accounts for 11 percent of the coal reserves in India. The most coal-producing and important mine in West Bengal is the Raniganj coalfield. The coal from this field has around 50 to 65 percent carbon content. The coal reserves in west Bengal are 31.67 billion tons.
The 5 largest coal reserves in India are present in Madhya Pradesh. The total coal reserves in India are 28 billion tons. It accounts for 8 percent of the coal deposits in India. The main coal reserves of this area are Muhpani, Sohagpur, Singrauli, and Satpura. The coal produced in this region is mainly used in the thermal power plants present in Singrauli and Obra.
Threats to Coal Sector in India
Some of the main threats, which is felt in the coal sector in India are as follows:
- Problems for land acquisition in the context of the coal mining area.
- The problems related to delayed environment and also delayed forest clearances have led to the reduction of mining areas.
- The available technology needs to be improved.
- Higher operation as well as maintenance costs for the coal plants.
- Control Boards for pollution are ineffective at the state level.
- Debt financing through which the coal plants are founded leads to pressure on states.
Government Initiative
- In the year 2018, The Ministry of Coal launched UTTAM ( Unlocking Transparency by Third Party Assessment of Mined Coal. The main objective of it was the ensure transparency and efficiency in coal quality.
- Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved the new coal linkage policy, for adequate supplies to the power plants in a more organized manner.
- A system of Coal Allocation Monitoring system was developed for monitoring the allocation of coal.
FAQs on Coal in India
Question 1: What troubles the coal sector in India?
Answer:
Some aspects which troubles the coal sector in India includes the coal dust in mines and near pits, which creates environmental pollution.
Question 2: List some efforts to reduce the pollution due to coal mining.
Answer:
Some efforts to reduce the pollution due to coal mining are as follows:
- Proper waste disposal
- Improving manufacturing process
- Reduce outputs
Question 3: What are the types of coal in India?
Answer:
Four types of coal in India are as follows:
- Anthracite
- Bituminous
- Sub-bituminous
- Lignite
Question 4: What is coal mostly composed of?
Answer:
Carbons and hydrocarbons.
Question 5: Which type of coal has the most energy?
Answer:
Anthracite has the most energy in terms of coal.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...