DDR Full Form
Last Updated :
20 Jun, 2022
DDR stands for Double Data Rate. It is a technique in computing with which a computer bus transfers data at double the rate sending data at rising and falling edges of a clock cycle. This method allows for sending 2 signals per clock cycle.

The simplest way to design an electronic circuit is to make it perform one transfer per clock cycle (SDR technique uses this). This requires the clock signal to change twice per cycle. When operating at high bandwidth, signal integrity limitations constrain the clock frequency. By using both edges of the clock, the data signals operate with the same limiting frequency but doubling the total transmitted data. It was an improved version of SDRAM which uses an SDR technique for data transmission.
This technique was an improvement over its predecessor SDR (single data rate) and has been succeeded by an improved version named QDR (quad data rate). A double data rate clock cycle looks as follows:-
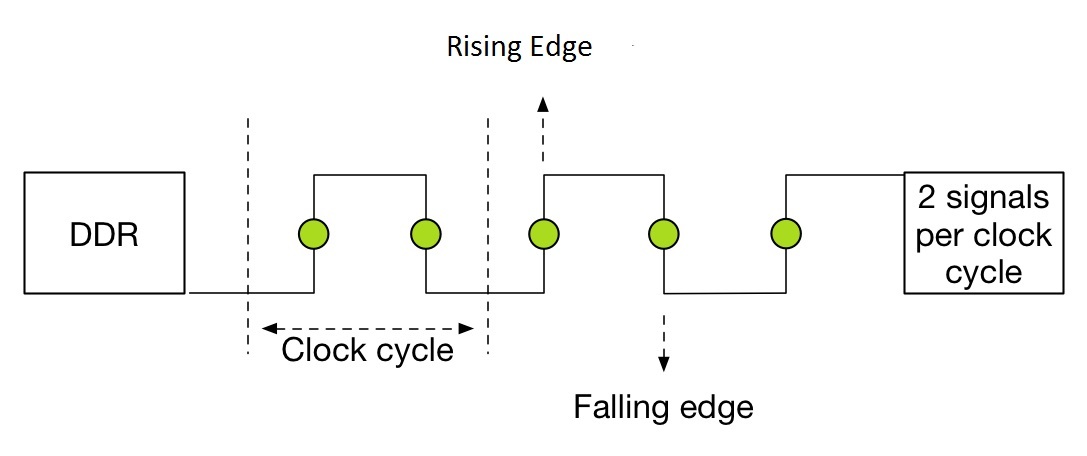
Characteristics of DDR:
- Transmits data twice per cycle (wave/clock), firstly at the rising edge and then at falling edges of a clock cycle
- Each clock cycle has a unidirectional flow of data
- DDR SDRAM technology consumes less power than older SDRAM modules, which expanded 3.3 volts compared to DDR SDRAM’s 2.6 volts.
- DDR operates at same frequency as the clock cycle.
Advantages of DDR:
- Higher levels of transmission speeds are obtained
- Reduces the number of cycles required to perform a task
- Reduces the component cost required
- Allows for smaller form factor computing devices
Disadvantages of DDR:
- Slower compared to QDR (quad data rate) technique
- Devices accommodating DDR technique produces more heat
Applications of DDR:
This technique has widespread acceptance in applications requiring high data transfer speeds such as:
- The technique is used extensively in building Volatile components for a computer (RAM) and is commonly referred to as DDR SDRAM (double data rate synchronized dynamic random access memory). The technique found a lot of success in the field, due to which the same technique has been implemented in later iterations of the technology under the name DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM, DDR4 SDRAM.
- The technique is used to incorporate volatile storage capabilities in Graphics Processors (graphic cards) and is known as GDDR (graphics double data rate). Which is a technology tailored to work with video cards
- Used in analog-to-digital converters
- Used in the bus of certain microprocessors (AMD’s Athlon64 series), allowing transmission of data at faster rate to-from the CPU.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...