DataInputStream readUnsignedShort() method in Java with Examples
Last Updated :
05 Jun, 2020
The readUnsignedShort() method of DataInputStream class in Java is used to read two input bytes and returns an integer value. This method reads the next two bytes from the input stream and interprets it into integer type and returns.
Syntax:
public final int readUnsignedShort()
throws IOException
Specified By: This method is specified by the readUnsignedShort() method of DataInput interface.
Parameters: This method does not accept any parameter.
Return value: This method returns the integer value interpreted by the next two bytes of the input stream.
Exceptions:
- EOFException – It throws EOFException if the input stream is ended before two bytes can be read.
- IOException – This method throws IOException if the stream is closed or some other I/O error occurs.
Below programs illustrate readUnsignedShort() method in DataInputStream class in IO package:
Program 1: Assume the existence of file “demo.txt”.
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
short[] buf = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
FileOutputStream outputStream
= new FileOutputStream("c:\\demo.txt");
DataOutputStream dataOutputStr
= new DataOutputStream(outputStream);
for (short b : buf) {
dataOutputStr.writeShort(b);
}
dataOutputStr.flush();
FileInputStream inputStream
= new FileInputStream("c:\\demo.txt");
DataInputStream dataInputStr
= new DataInputStream(inputStream);
while (dataInputStr.available() > 0) {
System.out.println(
dataInputStr.readSignedShort());
}
}
}
|
Output:

Program 2: Assume the existence of file “demo.txt”.
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
short[] buf = { 191, 225, 480, 763, 500 };
FileOutputStream outputStream
= new FileOutputStream("c:\\demo.txt");
DataOutputStream dataOutputStr
= new DataOutputStream(outputStream);
for (short b : buf) {
dataOutputStr.writeShort(b);
}
dataOutputStr.flush();
FileInputStream inputStream
= new FileInputStream("c:\\demo.txt");
DataInputStream dataInputStr
= new DataInputStream(inputStream);
while (dataInputStr.available() > 0) {
System.out.println(
dataInputStr.readUnsignedShort());
}
}
}
|
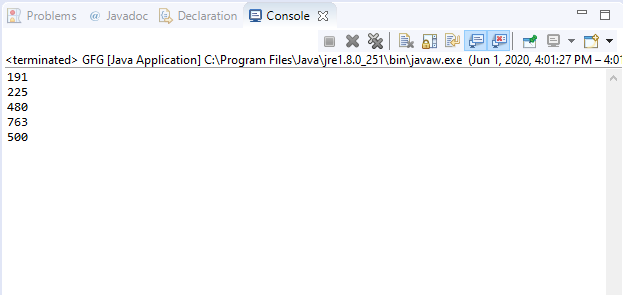
Output:
References:
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/10/docs/api/java/io/DataInputStream.html#readUnsignedShort()
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...