DataInputStream readChar() method in Java with Examples
Last Updated :
05 Jun, 2020
The readChar() method of DataInputStream class in Java is used to read two input bytes and returns a char value. This method basically reads the bytes as character that are written by writechar() method of DataOutputStream class.
Syntax:
public final char readChar()
throws IOException
Specified By: This method is specified by readChar() method of DataInput interface.
Parameters: This method does not accept any parameter.
Return value: This method returns the char value interpreted by the two bytes of input stream.
Exceptions:
- EOFException – It throws EOFException if the input stream is ended before two bytes can be read.
- IOException – This method throws IOException if the stream is closed or some other I/O error occurs.
Below programs illustrate readChar() method in DataInputStream class in IO package:
Program 1: Assume the existence of file “demo.txt”.
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
byte[] buf = { 71, 69, 69, 75, 83 };
FileOutputStream outputStream
= new FileOutputStream("c:\\demo.txt");
DataOutputStream dataOutputStr
= new DataOutputStream(outputStream);
for (byte b : buf) {
dataOutputStr.writeChar(b);
}
dataOutputStr.flush();
FileInputStream inputStream
= new FileInputStream("c:\\demo.txt");
DataInputStream dataInputStr
= new DataInputStream(inputStream);
while (dataInputStr.available() > 0) {
System.out.print(
dataInputStr.readChar());
}
}
}
|
Output:
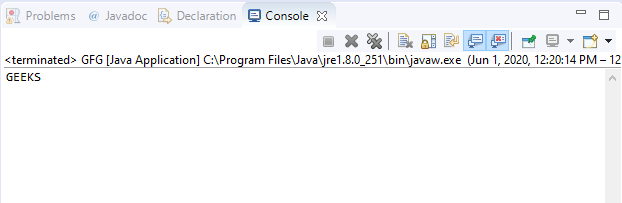
Program 2: Assume the existence of file “demo.txt”.
import java.io.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
byte[] buf = { 71, 69, 69, 75, 83,
70, 79, 82, 71, 69,
69, 75, 83 };
FileOutputStream outputStream
= new FileOutputStream("c:\\demo.txt");
DataOutputStream dataOutputStr
= new DataOutputStream(outputStream);
for (byte b : buf) {
dataOutputStr.writeChar(b);
}
dataOutputStr.flush();
FileInputStream inputStream
= new FileInputStream("c:\\demo.txt");
DataInputStream dataInputStr
= new DataInputStream(inputStream);
while (dataInputStr.available() > 0) {
System.out.print(
dataInputStr.readChar());
}
}
}
|
Output:
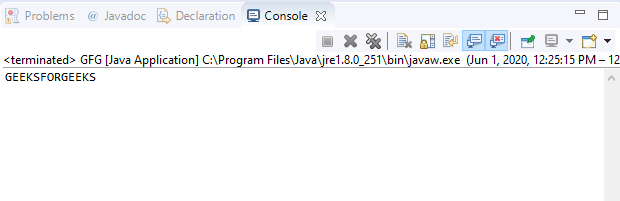
References:
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/10/docs/api/java/io/DataInputStream.html#readChar()
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...