CSS :scope pseudo-class
Last Updated :
30 Aug, 2022
A scope element forms a context for a block of styles. That element provides a reference point for selectors to be matched against. A scope element is defined using the scoped attribute. Styles declared with scoped attributes will be applied to all elements inside its parent element.
Syntax:
:scope
Example 1:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<title>GeeksforGeeks</title>
<body>
<h1 style="text-align: center;
color: green;" id="paragra">
Welcome to GeeksforGeeks.
It's a Computer Science portal.
</h1>
<p style="color: #000; text-align: center;" id="opt">
</p>
<script>
let para =
document.getElementById("paragra");
let opt =
document.getElementById("opt");
if (para.matches(":scope")) {
opt.innerText =
"Yeah!!, we are under scope GeeksforGeeks";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:
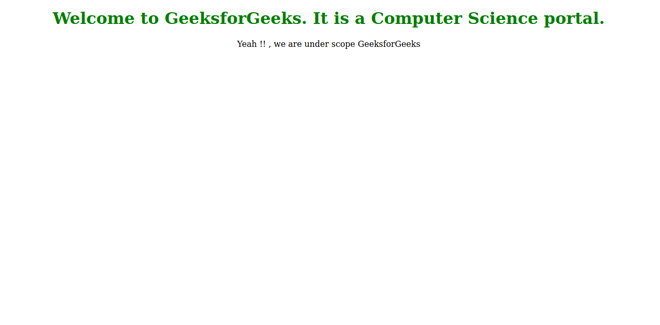
Example 2:
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>GeeeksforGeeks</title>
<style>
#contains {
margin: 5% auto;
max-width: 500px;
background-color: #eeeeee;
}
section {
padding: 60px;
}
:scope {
background-color: #3cd33c;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="contains">
<section>
<p>
Inside the scope,
<span style="color: green;">
GeeksforGeeks
</span>
</p>
</section>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:
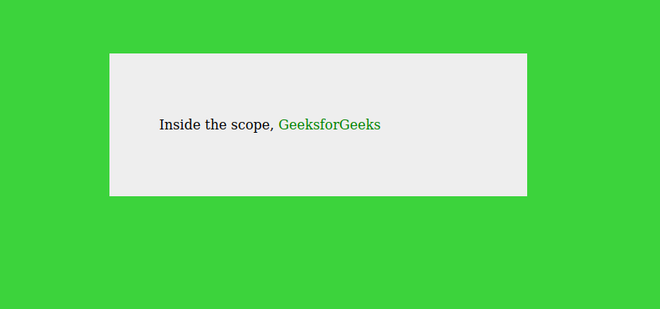
Browser Support:
- Google Chrome 27+
- Edge 79+
- Firefox 32+
- Opera 15+
- Safari 7+
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...