CSS font-variant-position Property
Last Updated :
08 Jun, 2023
The font-variant-position of CSS is used to alter the position of the font as a superscript, subscript, or normal font. These are positioned relative to the baseline of the font, which remains unchanged.
Syntax:
font-variant-position: normal | sub | super
Property values:
- Normal: Normal deactivates superscript and subscript glyphs. If not present any super or sub than the font style will be to the baseline.
- Super: Super activates superscript and alternate glyphs.
- Sub: Sub activates subscript and alternate glyphs.
Syntax:
font-variant-position: normal
Example: In this example, we are using font-variant-position: normal property.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,
initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS font-variant-position Property</title>
</head>
<style>
em {
font-style: unset;
}
.font {
font-variant-position: normal;
}
</style>
<body>
<em>
(geeksforgeeks)
<em class="font">
2
</em>
</em>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:
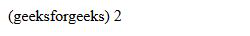
Example: In this example, we are using font-variant-position: super property.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,
initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS font-variant-position Property</title>
</head>
<style>
.font {
font-variant-position: super;
}
</style>
<body>
<em>
(geeksforgeeks)
<em class="font">
2
</em>
</em>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

Example: In this example, we are using font-variant-position: sub property.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,
initial-scale=1.0">
<title>CSS font-variant-position Property</title>
</head>
<style>
.font {
font-variant-position: sub;
}
</style>
<body>
<em>
H
<em class="font">
2
</em>
O
<em class="font">
2
</em>
</em>
</body>
</html>
|
Output:

Supported Browsers:
- Mozilla Firefox 34
- Safari 9.1
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...