C++ Program To Find Transpose of a Matrix
Last Updated :
21 Jun, 2023
Transpose of a matrix is obtained by changing rows to columns and columns to rows. In other words, the transpose of A[][] is obtained by changing A[i][j] to A[j][i].
Example:
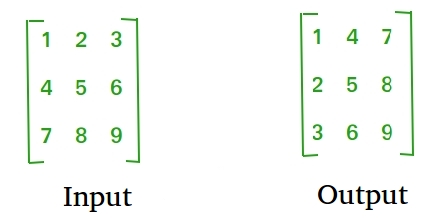
1. For Square Matrix
The below program finds the transpose of A[][] and stores the result in B[][], we can change N for a different dimension.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
void transpose(int A[][N],
int B[][N])
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
B[i][j] = A[j][i];
}
int main()
{
int A[N][N] = {{1, 1, 1, 1},
{2, 2, 2, 2},
{3, 3, 3, 3},
{4, 4, 4, 4}};
int B[N][N], i, j;
transpose(A, B);
cout << "Result matrix is \n";
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < N; j++)
cout << " " << B[i][j];
cout <<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
|
Output
Result matrix is
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
The complexity of the above method
Time Complexity: O(N*N) as two nested loops are running.
Space Complexity: O(N*N) as 2d array is created to store transpose.
2. For Rectangular Matrix
The below program finds the transpose of A[][] and stores the result in B[][].
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define M 3
#define N 4
void transpose(int A[][N], int B[][M])
{
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
for(j = 0; j < M; j++)
B[i][j] = A[j][i];
}
int main()
{
int A[M][N] = {{1, 1, 1, 1},
{2, 2, 2, 2},
{3, 3, 3, 3}};
int B[N][M], i, j;
transpose(A, B);
cout << "Result matrix is \n";
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < M; j++)
cout << " " << B[i][j];
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
|
Output
Result matrix is
1 2 3
1 2 3
1 2 3
1 2 3
The complexity of the above method
Time Complexity: O(N*M) as two nested loops are running.
Space Complexity: O(N*M) as 2d array is created to store transpose.
3. In-Place for Square Matrix
Below is the implementation of the method:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
void transpose(int A[][N])
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++)
swap(A[i][j], A[j][i]);
}
int main()
{
int A[N][N] = {{1, 1, 1, 1},
{2, 2, 2, 2},
{3, 3, 3, 3},
{4, 4, 4, 4}};
transpose(A);
printf("Modified matrix is \n");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
printf("%d ", A[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
|
Output
Modified matrix is
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4
The complexity of the above method
Time complexity: O(n)
- Transpose has a time complexity of O(n + m), where n is the number of columns and m is the number of non-zero elements in the matrix.
- The computational time for transposing of a matrix using an identity matrix as a reference matrix is O(m*n).
- Suppose, if the given matrix is a square matrix, the running time will be O(n2).
Auxiliary space: O(1).
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...