C++ Program For Pointing Arbit Pointer To Greatest Value Right Side Node In A Linked List
Last Updated :
03 May, 2023
Given singly linked list with every node having an additional “arbitrary” pointer that currently points to NULL. We need to make the “arbitrary” pointer to the greatest value node in a linked list on its right side.
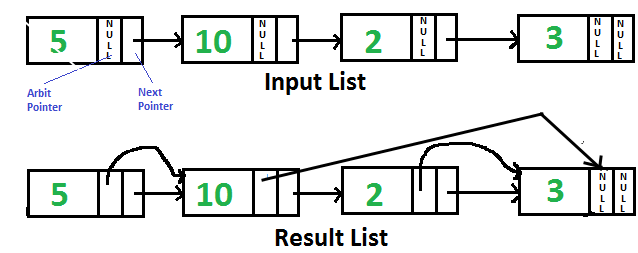
A Simple Solution is to traverse all nodes one by one. For every node, find the node which has the greatest value on the right side and change the next pointer. The Time Complexity of this solution is O(n2).
An Efficient Solution can work in O(n) time. Below are the steps.
- Reverse the given linked list.
- Start traversing the linked list and store the maximum value node encountered so far. Make arbit of every node to point to max. If the data in the current node is more than the max node so far, update max.
- Reverse modified linked list and return head.
Following is the implementation of the above steps.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* next, *arbit;
};
Node* reverse(Node *head)
{
Node *prev = NULL,
*current = head, *next;
while (current != NULL)
{
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
return prev;
}
Node* populateArbit(Node *head)
{
head = reverse(head);
Node *max = head;
Node *temp = head->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
temp->arbit = max;
if (max->data < temp->data)
max = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
return reverse(head);
}
void printNextArbitPointers(Node *node)
{
printf("Node Next Pointer Arbit Pointer");
while (node!=NULL)
{
cout << node->data <<
" ";
if (node->next)
cout << node->next->data <<
" ";
else cout << "NULL" << " ";
if (node->arbit)
cout << node->arbit->data;
else cout << "NULL";
cout << endl;
node = node->next;
}
}
Node *newNode(int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
int main()
{
Node *head = newNode(5);
head->next = newNode(10);
head->next->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next->next = newNode(3);
head = populateArbit(head);
printf("Resultant Linked List is: ");
printNextArbitPointers(head);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
Resultant Linked List is:
Node Next Pointer Arbit Pointer
5 10 10
10 2 3
2 3 3
3 NULL NULL
Time complexity: O(n)
Space complexity: O(1)
Recursive Solution:
We can recursively reach the last node and traverse the linked list from the end. The recursive solution doesn’t require reversing of the linked list. We can also use a stack in place of recursion to temporarily hold nodes. Thanks to Santosh Kumar Mishra for providing this solution.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *next, *arbit;
};
void populateArbit(Node* head)
{
static Node* maxNode;
if (head == NULL)
return;
if (head->next == NULL) {
maxNode = head;
return;
}
populateArbit(head->next);
head->arbit = maxNode;
if (head->data > maxNode->data)
maxNode = head;
return;
}
void printNextArbitPointers(Node* node)
{
printf("Node Next Pointer Arbit Pointer");
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
if (node->next)
cout << node->next->data << " ";
else
cout << "NULL"
<< " ";
if (node->arbit)
cout << node->arbit->data;
else
cout << "NULL";
cout << endl;
node = node->next;
}
}
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(5);
head->next = newNode(10);
head->next->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next->next = newNode(3);
populateArbit(head);
printf("Resultant Linked List is: ");
printNextArbitPointers(head);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
Resultant Linked List is:
Node Next Pointer Arbit Pointer
5 10 10
10 2 3
2 3 3
3 NULL NULL
Time complexity: O(n) where n is no of nodes in a linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1) since using constant space for variables
Please refer complete article on Point arbit pointer to greatest value right side node in a linked list for more details!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...