C++ Program For Finding Length Of A Linked List
Last Updated :
05 Jan, 2023
Write a function to count the number of nodes in a given singly linked list.
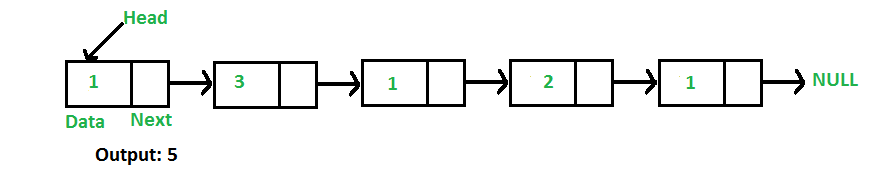
For example, the function should return 5 for linked list 1->3->1->2->1.
Iterative Solution:
1) Initialize count as 0
2) Initialize a node pointer, current = head.
3) Do following while current is not NULL
a) current = current -> next
b) count++;
4) Return count
Following is the Iterative implementation of the above algorithm to find the count of nodes in a given singly linked list.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node =new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int getCount(Node* head)
{
int count = 0;
Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL)
{
count++;
current = current->next;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout << "count of nodes is " <<
getCount(head);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
count of nodes is 5
Time Complexity: O(n), where n represents the length of the given linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), no extra space is required, so it is a constant.
Recursive Solution:
int getCount(head)
1) If head is NULL, return 0.
2) Else return 1 + getCount(head->next)
Following is the Recursive implementation of the above algorithm to find the count of nodes in a given singly linked list.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int getCount(Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return 1 + getCount(head->next);
}
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout << "Count of nodes is " <<
getCount(head);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
Count of nodes is 5
Time Complexity: O(n), where n represents the length of the given linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(n), for recursive stack where n represents the length of the given linked list.
Please refer complete article on Find Length of a Linked List (Iterative and Recursive) for more details!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...