C++ Program For Binary Search
Last Updated :
07 Aug, 2023
In this article, we will learn about the Binary Search algorithm and how to implement it in a C++ program.
Binary Search is a search algorithm that is faster than the linear search algorithm. Binary Search is used to search the position of the target element in a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search space in half. Binary search eliminates half portion of the array with each comparison. It works in a time complexity of O(log n) where n is the number of elements in the array.
How does Binary Search works?
The idea is to compare the middle element with the target value, if the middle element is equal to the target value, the index of the middle element is the position of the target value.
If the target value is smaller than the middle element, the target value is searched in the left half of the current space and If the target value is greater than the middle element, the target value is searched in the right half of the current space. This is done until the target element is found if the element is present in the array.
Examples
Input: arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 50, 60, 80, 110, 130, 140, 170}, x = 110
Output: 6
Explanation: Element x is present at index 6.
Input: arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 110, 120, 130, 170}, x = 175
Output: -1
Explanation: Element x is not present in arr[].
Illustration of Binary Search Algorithm
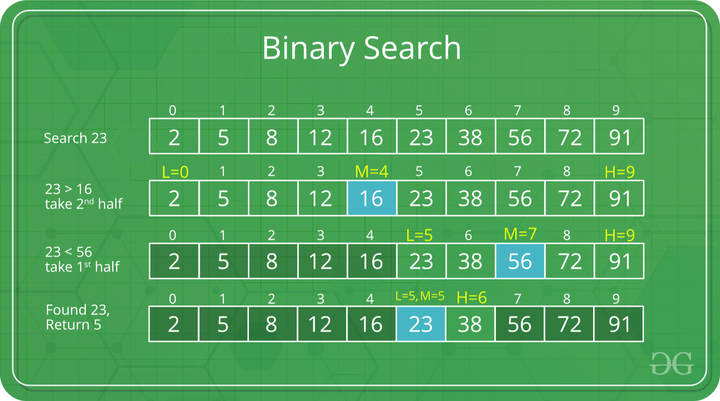
Example of Binary Search Algorithm
The middle index of the array can be calculated as:
int mid = low + (high – low)/2;
Binary Search Program in C++ (Recursive)
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int binarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int x)
{
if (high >= low) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (arr[mid] > x)
return binarySearch(arr, low, mid - 1, x);
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, high, x);
}
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1)
? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
|
Output
Element is present at index 3
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity : O(log n)
- Auxiliary Space : O(log n)
Binary Search Program in C++ (Iterative)
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int binarySearch(int arr[], int low, int high, int x)
{
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (arr[mid] < x)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);
(result == -1)
? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
|
Output
Element is present at index 3
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity : O(log n)
- Auxiliary Space : O(1)
Please refer complete article on Binary Search for a better understanding.
Related Articles
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...