Counting even integers in modified Sequence
Last Updated :
02 Oct, 2023
Given an integer array A of size N, and Q queries. In each query, you are given an integer X. Create a new sequence X^A[i], say sequence B. For each query find the number of even integers in the modified sequence for a given value of X.
Examples:
Input: A = {15, 6, 100, 8, 23, 45, 7, 101, 90}, N = 9, Q = 4, X = {3, 7, 10, 60}
Output: {5, 5, 4, 4}
Explanation: For first query, 3 XOR 15 = 12, 3 XOR 23 = 20, 3 XOR 45 = 46, 3 XOR 7 = 4 and 3 XOR 101 = 102. So total 5 even numbers. Similarly for the rest of the Q queries for X array.
Input: A = {55, 90, 100101}, N = 3, Q = 2, X = {10006, 54401}
Output: {1, 2}
Naive Approach: To solve the problem follow the below idea:
The idea is to generate the new sequence B for each query and store it. Now, traverse through the new sequence and count the number of even numbers.
Below are the steps for the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int calculate(vector<int> A, int N, int X)
{
int evenCount = 0;
for (int i : A) {
int B = i ^ X;
if (B & 1) {
continue;
}
else {
evenCount++;
}
}
return evenCount;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> A = { 15, 6, 100, 8, 23, 45, 7, 101, 90 };
int N = 9;
int Q = 4;
vector<int> X = { 3, 7, 10, 60 };
for (int i : X) {
cout << calculate(A, N, i) << " ";
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int calculate(ArrayList<Integer> A, int N, int X)
{
int evenCount = 0;
for (int i : A) {
int B = i ^ X;
if ((B & 1) == 1) {
continue;
}
else {
evenCount++;
}
}
return evenCount;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<Integer> A
= new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(
15, 6, 100, 8, 23, 45, 7, 101, 90));
int N = 9;
int Q = 4;
ArrayList<Integer> X = new ArrayList<Integer>(
Arrays.asList(3, 7, 10, 60));
for (int i : X) {
System.out.print(calculate(A, N, i) + " ");
}
}
}
|
Python3
def calculate(A, N, X):
evenCount = 0
for i in A:
B = i ^ X
if B & 1:
continue
else:
evenCount += 1
return evenCount
if __name__ == '__main__':
A = [15, 6, 100, 8, 23, 45, 7, 101, 90]
N = 9
Q = 4
X = [3, 7, 10, 60]
for i in X:
print(calculate(A, N, i), end=" ")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
static int Calculate(List<int> A, int N, int X)
{
int evenCount = 0;
foreach (int i in A)
{
int B = i ^ X;
if ((B & 1) != 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
evenCount++;
}
}
return evenCount;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> A = new List<int> { 15, 6, 100, 8, 23, 45, 7, 101, 90 };
int N = 9;
List<int> X = new List<int> { 3, 7, 10, 60 };
foreach (int i in X)
{
Console.Write(Calculate(A, N, i) + " ");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
function calculate(A, N, X) {
let evenCount = 0;
for (let i of A) {
let B = i ^ X;
if (B & 1) {
continue;
}
else {
evenCount++;
}
}
return evenCount;
}
let A = [15, 6, 100, 8, 23, 45, 7, 101, 90];
let N = 9;
let Q = 4;
let X = [3, 7, 10, 60];
let output = "";
for (let i of X) {
output += calculate(A, N, i) + " ";
}
console.log(output.trim());
|
Time Complexity: O(Q*N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Efficient Approach: To solve the problem follow the below idea:
XOR of A and B produces a set bit when both bits are different and produces an unset bit when both bits are the same. A number can be even only if its LSB is unset. In binary representation, only the LSB contributes to the odd number addition as all other numbers are multiples of 2. Thus we have to find numbers where LSB(X) ^ LSB(A[i]) = 0 i.e. unset. It can happen only when both LSB bits are the same. Thus if the value of X is odd then odd numbers in A will produce even numbers and similarly, if the value of X is even then the even numbers will produce an even value in the new sequence.
Below are the steps for the above approach:
- Initialize a variable evenCount = 0.
- Traverse the array A[] and for each element,
- Check if it is even by doing bitwise AND with 1, increment the value of evenCount.
- Return the evenCount variable and store it in a variable evenC.
- Traverse the query array X[] and for each query,
- Check if it is odd by doing bitwise AND with 1, return the number of odd elements, N – evenC.
- Else, return evenC.
Below is the code for the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int findEven(vector<int> A, int N)
{
int evenCount = 0;
for (int i : A) {
if (!(i & 1)) {
evenCount++;
}
}
return evenCount;
}
int calculate(int evenC, int N, int X)
{
if (X & 1) {
return N - evenC;
}
else {
return evenC;
}
}
int main()
{
vector<int> A = { 15, 6, 100, 8, 23, 45, 7, 101, 90 };
int N = 9;
int Q = 4;
vector<int> X = { 3, 7, 10, 60 };
int evenC = findEven(A, N);
for (int i : X) {
cout << calculate(evenC, N, i) << " ";
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Main {
public static int findEven(List<Integer> A, int N) {
int evenCount = 0;
for (int i : A) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
evenCount++;
}
}
return evenCount;
}
public static int calculate(int evenC, int N, int X) {
if (X % 2 == 1) {
return N - evenC;
}
else {
return evenC;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> A = new ArrayList<>();
A.add(15);
A.add(6);
A.add(100);
A.add(8);
A.add(23);
A.add(45);
A.add(7);
A.add(101);
A.add(90);
int N = 9;
int Q = 4;
List<Integer> X = new ArrayList<>();
X.add(3);
X.add(7);
X.add(10);
X.add(60);
int evenC = findEven(A, N);
for (int i : X) {
System.out.print(calculate(evenC, N, i) + " ");
}
}
}
|
Python3
def findEven(A):
evenCount = 0
for i in A:
if i % 2 == 0:
evenCount += 1
return evenCount
def calculate(evenC, N, X):
if X % 2 != 0:
return N - evenC
else:
return evenC
A = [15, 6, 100, 8, 23, 45, 7, 101, 90]
N = 9
Q = 4
X = [3, 7, 10, 60]
evenC = findEven(A)
for i in X:
print(calculate(evenC, N, i), end=' ')
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
static int FindEven(List<int> A)
{
int evenCount = 0;
foreach(int i in A)
{
if ((i & 1) == 0) {
evenCount++;
}
}
return evenCount;
}
static int Calculate(int evenC, int N, int X)
{
if ((X & 1) != 0) {
return N - evenC;
}
else {
return evenC;
}
}
static public void Main()
{
List<int> A = new List<int>{ 15, 6, 100, 8, 23,
45, 7, 101, 90 };
int N = 9;
List<int> X = new List<int>{ 3, 7, 10, 60 };
int evenC = FindEven(A);
foreach(int i in X)
{
Console.Write(Calculate(evenC, N, i) + " ");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
function findEven(arr) {
let evenCount = 0;
for (let i of arr) {
if (i % 2 === 0) {
evenCount++;
}
}
return evenCount;
}
function calculate(evenCount, N, X) {
if (X % 2 !== 0) {
return N - evenCount;
} else {
return evenCount;
}
}
function main() {
const A = [15, 6, 100, 8, 23, 45, 7, 101, 90];
const N = 9;
const Q = 4;
const X = [3, 7, 10, 60];
const evenC = findEven(A);
const results = [];
for (let i of X) {
results.push(calculate(evenC, N, i));
}
console.log(results.join(' '));
}
main();
|
Time Complexity: 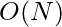
Auxiliary Space: 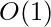
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...