Count unique paths with given sum in an N-ary Tree
Last Updated :
13 Apr, 2023
Given an integer X and integer N, the task is to find the number of unique paths starting from the root in N-ary tree such that the sum of all these paths is equal to X. The N-ary tree satisfies the following conditions:
- All the nodes have N children and the weight of each edge is distinct and lies in the range [1, N].
- The tree is extended up to infinity.
Examples:
Input: N = 3, X = 2
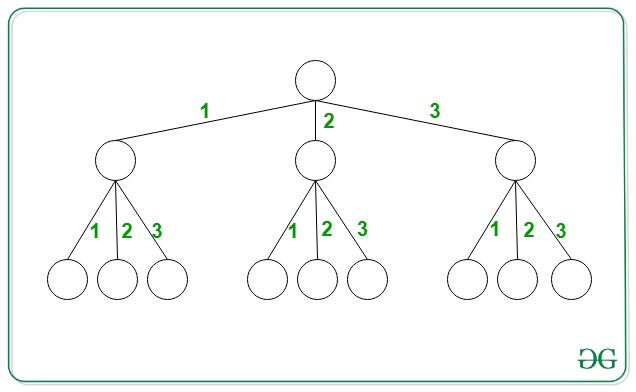
Output: 2
Explanation: the two paths having path sum equal to 2 are {1, 1} and {2}.
Input: N = 3, X = 6
Output: 24
Naive Approach: The simplest approach is to recursively find all possible ways to obtain path sum equal to X and print the count obtained.
Time Complexity: O(N * X)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Efficient Approach: To optimize the above approach, the idea is to use Dynamic Programming. Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Initialize a dp[] array which for every ith index, stores the count of paths adding up to i.
- For every vertex, iterate form strong>1 to min(X, N), i.e. all possible values of its children and find the number of paths possible with given sum from each node considered.
- Add all the paths made using the edges 1 to N and check if count is already computed or not. If already computed, return the value. Otherwise, recursively count the number of paths with sum equal to current value by considering all possible ways to extend the tree from the current vertex.
- Update the dp[] array and return the count obtained.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
ll findTotalPath(int X, int n,
vector<int>& dp)
{
if (X == 0) {
return 1;
}
ll ans = 0;
if (dp[X] != -1) {
return dp[X];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= min(X, n); ++i) {
ans += findTotalPath(
X - i, n, dp)
% mod;
ans %= mod;
}
return dp[X] = ans;
}
int main()
{
int n = 3, X = 2;
vector<int> dp(X + 1, -1);
cout << findTotalPath(X, n, dp);
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
static int findTotalPath(int X, int n,
ArrayList<Integer> dp)
{
if (X == 0)
{
return 1;
}
int ans = 0;
if (dp.get(X) != -1)
{
return dp.get(X);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= Math.min(X, n); ++i)
{
ans += findTotalPath(X - i, n, dp) % mod;
ans %= mod;
}
dp.set(X, ans);
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 3, X = 2;
ArrayList<Integer> dp = new ArrayList<Integer>(
Collections.nCopies(X + 1, -1));
System.out.print(findTotalPath(X, n, dp));
}
}
|
Python3
mod = int(1e9 + 7)
def findTotalPath(X, n, dp):
if (X == 0):
return 1
ans = 0
if (dp[X] != -1):
return dp[X]
for i in range(1, min(X, n) + 1):
ans = ans + findTotalPath(X - i, n, dp) % mod;
ans %= mod;
dp[X] = ans
return ans
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 3
X = 2
dp = [-1] * (X + 1)
print(findTotalPath(X, n, dp))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
static int findTotalPath(int X, int n, int[] dp)
{
if (X == 0)
{
return 1;
}
int ans = 0;
if (dp[X] != -1)
{
return dp[X];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= Math.Min(X, n); ++i)
{
ans += findTotalPath(X - i, n, dp) % mod;
ans %= mod;
}
dp[X] = ans;
return ans;
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 3, X = 2;
int[] dp = new int[X + 1];
Array.Fill(dp, -1);
Console.WriteLine(findTotalPath(X, n, dp));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var mod = 1000000007;
function findTotalPath(X, n, dp)
{
if (X == 0) {
return 1;
}
var ans = 0;
if (dp[X] != -1) {
return dp[X];
}
for (var i = 1; i <= Math.min(X, n); ++i) {
ans += findTotalPath(
X - i, n, dp)
% mod;
ans %= mod;
}
return dp[X] = ans;
}
var n = 3, X = 2;
var dp = Array(X + 1).fill(-1);
document.write( findTotalPath(X, n, dp));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(min (N, X))
Auxiliary Space: O(X)
Another approach : Using DP Tabulation method ( Iterative approach )
The approach to solve this problem is same but DP tabulation(bottom-up) method is better then Dp + memoization(top-down) because memoization method needs extra stack space of recursion calls.
Steps to solve this problem :
- Create a Dp array to store the solution of the subproblems.
- Initialize the Dp with base cases
- Fill up the Dp iteratively and get the current value from previous computation.
- Return the final solution stored in dp[X].
Implementation :
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
ll findTotalPath(int X, int n)
{
vector<int> dp(X + 1);
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= X; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= min(i, n); ++j) {
dp[i] += dp[i - j];
dp[i] %= mod;
}
}
return dp[X];
}
int main()
{
int n = 3, X = 2;
cout << findTotalPath(X, n);
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static long findTotalPath(int X, int n) {
int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
int[] dp = new int[X + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= X; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= Math.min(i, n); ++j) {
dp[i] += dp[i - j];
dp[i] %= mod;
}
}
return dp[X];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 3, X = 2;
System.out.println(findTotalPath(X, n));
}
}
|
Python3
def findTotalPath(X, n):
dp = [0] * (X + 1)
dp[0] = 1
for i in range(1, X + 1):
for j in range(1, min(i, n) + 1):
dp[i] += dp[i - j]
dp[i] %= int(1e9 + 7)
return dp[X]
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 3
X = 2
print(findTotalPath(X, n))
|
Javascript
function findTotalPath(X, n)
{
const mod = 1e9 + 7;
const dp = new Array(X + 1).fill(0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (let i = 1; i <= X; ++i) {
for (let j = 1; j <= Math.min(i, n); ++j) {
dp[i] += dp[i - j];
dp[i] %= mod;
}
}
return dp[X];
}
const n = 3, X = 2;
console.log(findTotalPath(X, n));
|
C#
using System;
public class Program
{
public static int mod = (int)1e9 + 7;
public static long FindTotalPath(int X, int n)
{
int[] dp = new int[X + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= X; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= Math.Min(i, n); ++j)
{
dp[i] += dp[i - j];
dp[i] %= mod;
}
}
return dp[X];
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 3, X = 2;
Console.WriteLine(FindTotalPath(X, n));
}
}
|
Output:
2
Time Complexity: O( X * min (N, X))
Auxiliary Space: O(X)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...