Count the values greater than X in the modified array
Last Updated :
29 Dec, 2022
Given an array Arr of positive integers and a value X. The task is to find the number of values that is greater than or equal to X.
But the twist is that the values of the array are kept changing after every operation. There are two possibilities:
- If the current value is picked then all the remaining values in the array will be decreased by 1.
- If the current value is not picked then all the remaining values in the array will be increased by 1.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {10, 5, 5, 4, 9}, X = 10
Output: 2
Explanation:
Arr = {10, 5, 5, 4, 9}, pos = 0
10 is picked
Arr = {10, 4, 4, 3, 8}, pos = 1
4 is not picked
Arr = {10, 4, 5, 4, 9}, pos = 2
5 is not picked
Arr = {10, 4, 5, 5, 10}, pos = 3
5 is not picked
Arr = {10, 4, 5, 5, 11}, pos = 4
11 is picked
Hence two elements are picked.
Input: arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}, X = 4
Output: 1
Naive Approach: The idea is to iterate through every value in an array and check whether the ith value is greater, lesser, or equal than required value X. If the ith value is less than required value then increase the value from (i+1)th to end of the array by 1 else If the ith value is greater or equal than required value X then decrease the value by 1 from (i+1)th to end of the array.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[],
int x, int n)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
int main()
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x, n);
cout << countValue;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr, int x)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int[] arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
System.out.println(countValue);
}
}
|
Python3
def increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x):
TotalValue = 0
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] < x:
for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)):
arr[j] += 1
else:
TotalValue += 1
for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)):
if arr[j] == 0:
continue
arr[j] -= 1
return TotalValue
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = 4
arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
countValue =\
increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x)
print(countValue)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr, int x)
{
int TotalValue = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
TotalValue += 1;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.Length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int[] arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
Console.WriteLine(countValue);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x)
{
let TotalValue = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < x)
{
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
arr[j] += 1;
}
}
else
{
TotalValue += 1;
for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++)
{
if (arr[j] == 0)
{
continue;
}
else
{
arr[j] -= 1;
}
}
}
}
return TotalValue;
}
let x = 4;
let arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
let countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
document.write(countValue);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: 
Auxiliary Space: O(1), no extra space is required, so it is a constant.
Efficient Approach:
- This problem can further be optimized to
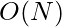 .
. - Here the main idea is to check by how much this index value should change.
- This can be done by using a temporary variable, here it is currentStatus that will keep the net effect on the current index by the previous decisions.
- The effect will be added to the value of that index and that will tell us the updated original value of the array.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int increaseDecreaseValue(vector<int> arr, int x)
{
int currentStatus = 0;
int totalValue = 0;
int i;
int len = arr.size();
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else {
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
int main()
{
int x = 4;
vector<int> arr = { 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 };
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
cout << (countValue);
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int arr[], int x)
{
int currentStatus = 0;
int totalValue = 0;
int i;
int len = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int x = 4;
int arr[] = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
System.out.println(countValue);
}
}
|
Python3
def increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x):
currentStatus = 0
totalValue = 0
for i in arr:
if i + currentStatus < x:
currentStatus += 1
else:
currentStatus -= 1
totalValue += 1
return totalValue
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = 4
arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x)
print(countValue)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int increaseDecreaseValue(int []arr,
int x)
{
int currentStatus = 0;
int totalValue = 0;
int i;
int len = arr.Length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
static public void Main ()
{
int x = 4;
int []arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
int countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
Console.Write(countValue);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x)
{
let currentStatus = 0;
let totalValue = 0;
let i;
let len = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < len ; i++ )
{
if (arr[i] + currentStatus < x)
currentStatus += 1;
else
{
currentStatus -= 1;
totalValue += 1;
}
}
return totalValue;
}
let x = 4;
let arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
let countValue = increaseDecreaseValue(arr, x);
document.write(countValue);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: 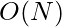
Auxiliary Space: O(1), no extra space is required, so it is a constant.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...