Count the number of intervals in which a given value lies
Last Updated :
08 Jul, 2022
Given a 2D-array of 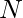 integer intervals
integer intervals ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com [L, R]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-02b987d90267ffc9f0832876c6ce81d3_l3.png) and a value
and a value 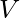 . For every interval [li, ri], the task is to check if V lies in between li and ri, both inclusive. The task is to print the count of intervals that satisfies this.
. For every interval [li, ri], the task is to check if V lies in between li and ri, both inclusive. The task is to print the count of intervals that satisfies this.
Note: 1<=li<= ri
Examples:
Input: arr[][] = {{1, 10}, {5, 10}, {15, 25}, {7, 12}, {20, 25}}, V = 7
Output: 3
For V = 7, it lies in the intervals [1, 10], [5, 10] and [7, 12]. So, the count of intervals V lies in is 3.
Input: arr[][] = {{3, 7}, {2, 2}, {2, 8}, {7, 11}}, V = 2
Output: 2
For V = 2, it lies in the intervals [2, 2] and [2, 8]. So, the count of intervals V lies in is 2.
Method-1: Traverse the entire array checking for every interval [li, ri], if V lies in the interval or not. If it does, then increment the count.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int countIntervals(int arr[][2], int V, int N)
{
int count = 0;
int li, ri;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
li = arr[i][0];
ri = arr[i][1];
if (V >= li && V <= ri)
count++;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
int arr[][2] = { { 1, 10 }, { 5, 10 },{ 15, 25 }, { 7, 12 }, { 20, 25 } };
int V = 7;
int N = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout<<(countIntervals(arr, V, N))<<endl;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG {
static int countIntervals(int[][] arr, int V, int N)
{
int count = 0;
int li, ri;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
li = arr[i][0];
ri = arr[i][1];
if (V >= li && V <= ri)
count++;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int[][] arr = { { 1, 10 }, { 5, 10 },
{ 15, 25 }, { 7, 12 }, { 20, 25 } };
int V = 7;
int N = arr.length;
System.out.println(countIntervals(arr, V, N));
}
}
|
Python3
def countIntervals(arr, V, N) :
count = 0
for i in range(N) :
li = arr[i][0]
ri = arr[i][1]
if (V >= li and V <= ri) :
count += 1
return count;
if __name__ == "__main__" :
arr = [ [ 1, 10 ], [ 5, 10 ],
[ 15, 25 ], [ 7, 12 ],
[ 20, 25 ] ]
V = 7
N = len(arr)
print((countIntervals(arr, V, N)))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int countIntervals(int[,] arr, int V, int N)
{
int count = 0;
int li, ri;
for (int i = 0; i < N ; i++)
{
li = arr[i, 0];
ri = arr[i, 1];
if (V >= li && V <= ri)
count++;
}
return count;
}
public static void Main()
{
int[,] arr = new int[,]{ { 1, 10 }, { 5, 10 },
{ 15, 25 }, { 7, 12 }, { 20, 25 } };
int V = 7;
int N = arr.GetLength(0);
Console.WriteLine(countIntervals(arr, V, N));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function countIntervals($arr, $V, $N)
{
$count = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $N; $i++)
{
$li = $arr[$i][0];
$ri = $arr[$i][1];
if ($V >= $li && $V <= $ri)
$count++;
}
return $count;
}
$arr = array(array(1, 10),
array(5, 10),
array(15, 25),
array(7, 12),
array(20, 25));
$V = 7;
$N = sizeof($arr);
echo countIntervals($arr, $V, $N);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function countIntervals(arr, V, N)
{
let count = 0;
let li, ri;
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
li = arr[i][0];
ri = arr[i][1];
if (V >= li && V <= ri)
count++;
}
return count;
}
let arr = [ [ 1, 10 ], [ 5, 10 ],
[ 15, 25 ], [ 7, 12 ], [ 20, 25 ] ];
let V = 7;
let N = arr.length;
document.write(countIntervals(arr, V, N));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Method-2(Efficient for queries): Use a frequency array that keeps track of how many of the given intervals an element lies in.
- For every interval [L, R], put freq[L] as freq[L] + 1 and freq[R+1] as freq[R + 1] – 1 indicating start and end of the interval.
- Keep track of the overall minimum and maximum of the intervals.
- Starting from minimum to maximum construct the frequency array from its previous element i.e.,
freq[i] = freq[i] + freq[i – 1]. - Required count of intervals is then given by freq[V].
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_VAL = 200000;
int countIntervals(int arr[][2], int V, int N)
{
int min = INT_MAX;
int max = INT_MIN;
int li, ri;
int freq[MAX_VAL];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
li = arr[i][0];
freq[li] = freq[li] + 1;
ri = arr[i][1];
freq[ri + 1] = freq[ri + 1] - 1;
if (li < min)
min = li;
if (ri > max)
max = ri;
}
for (int i = min; i <= max; i++)
freq[i] = freq[i] + freq[i - 1];
return freq[V];
}
int main()
{
int arr[5][2] = { { 1, 10 }, { 5, 10 },
{ 15, 25 }, { 7, 12 },
{ 20, 25 } };
int V = 7;
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << (countIntervals(arr, V, N));
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG {
static final int MAX_VAL = 200000;
static int countIntervals(int[][] arr, int V, int N)
{
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int li, ri;
int[] freq = new int[MAX_VAL];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
li = arr[i][0];
freq[li] = freq[li] + 1;
ri = arr[i][1];
freq[ri + 1] = freq[ri + 1] - 1;
if (li < min)
min = li;
if (ri > max)
max = ri;
}
for (int i = min; i <= max; i++)
freq[i] = freq[i] + freq[i - 1];
return freq[V];
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int[][] arr = { { 1, 10 }, { 5, 10 },
{ 15, 25 }, { 7, 12 }, { 20, 25 } };
int V = 7;
int N = arr.length;
System.out.println(countIntervals(arr, V, N));
}
}
|
Python3
MAX_VAL = 200000
def countIntervals(arr, V, N):
minimum = float("inf")
maximum = 0
freq = [0] * (MAX_VAL)
for i in range(0, N):
li = arr[i][0]
freq[li] = freq[li] + 1
ri = arr[i][1]
freq[ri + 1] = freq[ri + 1] - 1
if li < minimum:
minimum = li
if ri > maximum:
maximum = ri
for i in range(minimum, maximum + 1):
freq[i] = freq[i] + freq[i - 1]
return freq[V]
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [[1, 10], [5, 10], [15, 25],
[7, 12], [20, 25]]
V = 7
N = len(arr)
print(countIntervals(arr, V, N))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int MAX_VAL = 200000;
static int countIntervals(int[,] arr, int V, int N)
{
int min = int.MaxValue, max = int.MinValue;
int li, ri;
int[] freq = new int[MAX_VAL];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
li = arr[i,0];
freq[li] = freq[li] + 1;
ri = arr[i,1];
freq[ri + 1] = freq[ri + 1] - 1;
if (li < min)
min = li;
if (ri > max)
max = ri;
}
for (int i = min; i <= max; i++)
freq[i] = freq[i] + freq[i - 1];
return freq[V];
}
public static void Main()
{
int[,] arr = new int[,]{ { 1, 10 }, { 5, 10 },
{ 15, 25 }, { 7, 12 }, { 20, 25 } };
int V = 7;
int N = arr.Length/arr.Rank;
Console.WriteLine(countIntervals(arr, V, N));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
$MAX_VAL = 200000;
function countIntervals($arr, $V, $N)
{
global $MAX_VAL;
$min = PHP_INT_MAX;
$max = 0;
$li = 0;
$ri = 0;
$freq = array_fill(0, $MAX_VAL, 0);
for ($i = 0; $i < $N; $i++)
{
$li = $arr[$i][0];
$freq[$li] = $freq[$li] + 1;
$ri = $arr[$i][1];
$freq[$ri + 1] = $freq[$ri + 1] - 1;
if ($li < $min)
$min = $li;
if ($ri > $max)
$max = $ri;
}
for ($i = $min; $i <= $max; $i++)
$freq[$i] = $freq[$i] + $freq[$i - 1];
return $freq[$V];
}
$arr = array(array( 1, 10 ),
array( 5, 10 ),
array( 15, 25 ),
array( 7, 12 ),
array( 20, 25 ));
$V = 7;
$N = count($arr);
echo (countIntervals($arr, $V, $N));
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
let MAX_VAL = 200000;
function countIntervals(arr, V, N)
{
let min = Number.MAX_VALUE, max = Number.MIN_VALUE;
let li, ri;
let freq = new Array(MAX_VAL);
freq.fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
li = arr[i][0];
freq[li] = freq[li] + 1;
ri = arr[i][1];
freq[ri + 1] = freq[ri + 1] - 1;
if (li < min)
min = li;
if (ri > max)
max = ri;
}
for (let i = min; i <= max; i++)
freq[i] = freq[i] + freq[i - 1];
return freq[V];
}
let arr = [ [ 1, 10 ], [ 5, 10 ],
[ 15, 25 ], [ 7, 12 ], [ 20, 25 ] ];
let V = 7;
let N = arr.length;
document.write(countIntervals(arr, V, N));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(MAX)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...