Count pairs of similar rectangles possible from a given array
Last Updated :
08 Apr, 2022
Given a 2D array A[][2] of size N (1 ? N ? 103), where A[i][0] and A[i][1] denotes the length and breadth of rectangle i respectively.
Two rectangle i and j where (i < j) are similar if the ratio of their length and breadth is equal
A[i][0] / A[i][1] = A[j][0] / A[j][1]
The task is to count the pair of rectangles that are nearly similar.
Examples:
Input : A[][2] = {{4, 8}, {15, 30}, {3, 6}, {10, 20}}
Output: 6
Explanation: Pairs of similar rectangles are (0, 1), {0, 2), (0, 3), (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3). For every rectangle, ratio of length : breadth is 1 : 2
Input : A[][2] = {{2, 3}, {4, 5}, {7, 8}}
Output: 0
Explanation: No pair of similar rectangles exists.
Method 1 (Simple Comparison Method)
Approach: Follow the steps to solve the problem
- Traverse the array.
- For every pair such that (i < j), check whether the rectangles are similar or not by checking if the condition A[i][0] / A[i][1] = A[j][0] / A[j][1] is satisfied or not.
- If found to be true, increment the count.
- Finally, print the count obtained.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int getCount(int rows,
int columns, int A[][2])
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < rows; j++) {
if (A[i][0] * 1LL * A[j][1]
== A[i][1] * 1LL * A[j][0]) {
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int A[][2]
= { { 4, 8 }, { 10, 20 }, { 15, 30 }, { 3, 6 } };
int columns = 2;
int rows = sizeof(A) / sizeof(A[0]);
cout << getCount(rows, columns, A);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int getCount(int rows, int columns,
int[][] A)
{
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < rows; j++)
{
if (A[i][0] * A[j][1] ==
A[i][1] * A[j][0])
{
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] A = { { 4, 8 }, { 10, 20 },
{ 15, 30 }, { 3, 6 } };
int columns = 2;
int rows = 4;
System.out.print(getCount(rows, columns, A));
}
}
|
Python3
def getCount(rows, columns, A):
res = 0
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(i + 1, rows, 1):
if (A[i][0] * A[j][1] ==
A[i][1] * A[j][0]):
res += 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
A = [ [ 4, 8 ], [ 10, 20 ],
[ 15, 30 ], [ 3, 6 ] ]
columns = 2
rows = len(A)
print(getCount(rows, columns, A))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static int getCount(int rows, int columns,
int[,] A)
{
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j < rows; j++)
{
if (A[i, 0] * A[j, 1] ==
A[i, 1] * A[j, 0])
{
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
static void Main()
{
int[,] A = { { 4, 8 }, { 10, 20 },
{ 15, 30 }, { 3, 6 } };
int columns = 2;
int rows = 4;
Console.Write(getCount(rows, columns, A));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function getCount(rows, columns, A)
{
var res = 0;
for(var i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
for(var j = i + 1; j < rows; j++)
{
if (A[i][0] * A[j][1] ==
A[i][1] * A[j][0])
{
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
var A = [ [ 4, 8 ], [ 10, 20 ],
[ 15, 30 ], [ 3, 6 ] ];
var columns = 2;
var rows = 4;
document.write(getCount(rows, columns, A));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Method 2 (Using HashMap)
Instead of comparing one rectangle’s ratio to another rectangle’s directly, we can store all the calculated ratios in the HashMap. Since HashMap has the access cost of O(1), that would allow a fast lookup for other rectangles with the same ratio and store them together. The number of pairs of similar rectangles can be derived from the number of rectangles with the same ratio using \frac{N \times (N – 1)}{2}. The reason one can use the mentioned equation to find the number of pairs of similar rectangles is that the number of pairs increases by 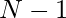 each time a rectangle with the same ratio is added.
each time a rectangle with the same ratio is added.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int getCount(int rows, int columns, int sides[][2])
{
int ans = 0;
unordered_map<double, int> umap;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
double ratio = (double)sides[i][0] / sides[i][1];
umap[ratio]++;
}
for (auto x : umap)
{
int value = x.second;
if (value > 1)
{
ans += (value * (value - 1)) / 2;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int sides[4][2] = {{4, 8}, {10, 20}, {15, 30}, {3, 6}};
int rows = 4;
int columns = 2;
cout << getCount(rows, columns, sides);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static int getCount(int rows, int columns,
int[][] sides)
{
int res = 0;
Map<Double, Integer> ratio
= new HashMap<Double, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
double rectRatio = (double) sides[i][0] /
sides[i][1];
if (ratio.get(rectRatio) == null) {
ratio.put(rectRatio, 0);
}
ratio.put(rectRatio, ratio.get(rectRatio) + 1);
}
for (double key : ratio.keySet()) {
int val = ratio.get(key);
if (val > 1) {
res += (val * (val - 1)) / 2;
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] A = {{4, 8}, {10, 20}, {15, 30}, {3, 6}};
int columns = 2;
int rows = 4;
System.out.println(getCount(rows, columns, A));
}
}
|
Python3
from collections import defaultdict
def getCount(rows, columns, sides):
ans = 0
umap = defaultdict(int)
for i in range(rows):
ratio = sides[i][0] / sides[i][1]
umap[ratio] += 1
for x in umap:
value = umap[x]
if (value > 1):
ans += (value * (value - 1)) / 2
return ans
if __name__ == "__main__":
sides = [[4, 8], [10, 20], [15, 30], [3, 6]]
rows = 4
columns = 2
print(int(getCount(rows, columns, sides)))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
public static int getCount(int rows, int columns,
int[, ] sides)
{
int res = 0;
Dictionary<double, int> ratio
= new Dictionary<double, int>();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
double rectRatio
= (double)sides[i, 0] / sides[i, 1];
if (!ratio.ContainsKey(rectRatio)) {
ratio[rectRatio] = 0;
}
ratio[rectRatio] = ratio[rectRatio] + 1;
}
foreach(KeyValuePair<double, int> p in ratio)
{
int val = p.Value;
if (val > 1) {
res += (val * (val - 1)) / 2;
}
}
return res;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[, ] A = {
{ 4, 8 }, { 10, 20 }, { 15, 30 }, { 3, 6 }
};
int columns = 2;
int rows = 4;
Console.WriteLine(getCount(rows, columns, A));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function getCount(rows, columns, sides)
{
let ans = 0;
let umap = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
let ratio = sides[i][0] / sides[i][1];
if(umap.has(ratio)){
umap.set(ratio,umap.get(ratio)+1);
}
else umap.set(ratio,1);
}
for (let [x,y] of umap)
{
let value = y;
if (value > 1)
{
ans += (value * (value - 1)) / 2;
}
}
return ans;
}
let sides = [[4, 8], [10, 20], [15, 30], [3, 6]];
let rows = 4;
let columns = 2;
document.write(getCount(rows, columns, sides));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...