Count pairs from 1 to N such that their Sum is divisible by their XOR
Last Updated :
26 Feb, 2023
Given a number 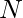 , the task is to count pairs (x, y) such that their sum (x+y) is divisible by their xor value (x^y) and the condition 1 ? x < y ? N holds true.
, the task is to count pairs (x, y) such that their sum (x+y) is divisible by their xor value (x^y) and the condition 1 ? x < y ? N holds true.
Examples:
Input: N = 3
Output: 3
Explanation:
(1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3) are the valid pairs
Input: N = 6
Output: 11
Approach:
- After taking the array as input, first we need to find out all the possible pairs in that array.
- So, find out the pairs from the array
- Then for each pair, check whether the sum of the pair is divisible by the xor value of the pair. If it is, then increase the required count by one.
- When all the pairs have been checked, return or print the count of such pair.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int countPairs(int n)
{
int count = 0;
for (int x = 1; x < n; x++) {
for (int y = x + 1; y <= n; y++) {
if ((y + x) % (y ^ x) == 0)
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
int n = 6;
cout << countPairs(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static int countPairs(int n)
{
int count = 0;
for (int x = 1; x < n; x++)
{
for (int y = x + 1; y <= n; y++)
{
if ((y + x) % (y ^ x) == 0)
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int n = 6;
System.out.println(countPairs(n));
}
}
|
Python3
def countPairs(n) :
count = 0;
for x in range(1, n) :
for y in range(x + 1, n + 1) :
if ((y + x) % (y ^ x) == 0) :
count += 1;
return count;
if __name__ == "__main__" :
n = 6;
print(countPairs(n));
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
static int countPairs(int n)
{
int count = 0;
for (int x = 1; x < n; x++)
{
for (int y = x + 1; y <= n; y++)
{
if ((y + x) % (y ^ x) == 0)
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 6;
Console.WriteLine(countPairs(n));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function countPairs(n)
{
let count = 0;
for (let x = 1; x < n; x++) {
for (let y = x + 1; y <= n; y++) {
if ((y + x) % (y ^ x) == 0)
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
let n = 6;
document.write(countPairs(n));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N2), as we are using nested loops to traverse N*N times.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as we are not using any extra space.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...