Count of subarrays whose sum is a perfect square
Last Updated :
24 Nov, 2021
Given an array arr[] with positive and negative elements, the task is to count all subarrays whose sum is a perfect square.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {2, 3, -5, 6, -7, 4};
Output: 5
Explanation:
Subarrays {2, 3, -5}, {-5, 6}, {3, -5, 6}, {3, -5, 6, -7, 4} and {4} with sum is 0, 1, 4, 1 and 4 respectively have perfect square sum.
Input: arr[] = {3, -6, 4, -2, 7};
Output: 3
Explanation: {3, -6, 4}, {4}, {4, -2, 7} are the subarrays with perfect square sum.
Naive Approach:
A simple solution would be to generate all possible subarrays. While traversing, keep track of the subarray sum. Keep a count of all subarrays whose sum is a perfect square.
Efficient Solution: The idea is to use a prefix sum array to solve the given problem.
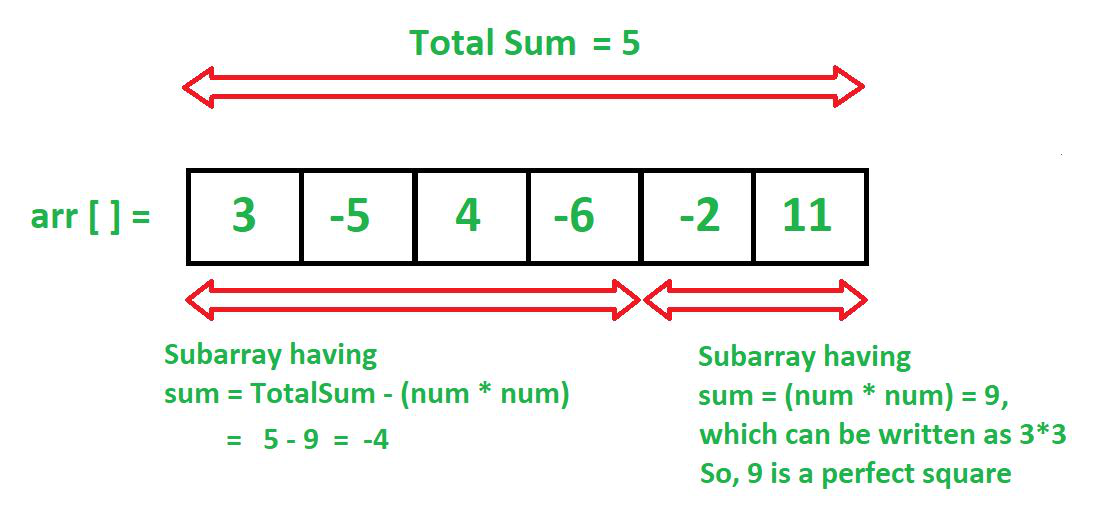
- Create a prefixSum array and store it’s prefix sum.
- Traverse the prefixSum array and identify it’s minimum value i.e (prefixMin).
- Now, create an unordered map that can be used to store the frequency of current prefixSum, while traversing the prefixSum array.
- Initialize the 0th key-index of the map with value 1, as 0 is a perfect square.
- Traverse the prefixSum array with a nested loop.
- For each prefixSum element, the nested loop is going to find the mapKey = (prefixSum[i] – j*j), if available in the map index.
- If (prefixSum[i] – j*j) is already available in the map, we update our counter with the index value of (prefixSum[i] – j*j).
- The idea is to check the current prefixSum value with all the squares (j*j) till the difference reaches prefixMin.
- Now, increment the map with index of the current prefixSum by 1 with every iteration of the outer loop.
- The underlying concept is that we keep searching from (prefixSum[i] – j*j ) because, if one part is the array is (prefixSum[i] – j*j ), then the other part of the array would be (j*j) i.e a perfect square sum.
- You can see in the above diagram that the totalSum is actually the prefixSum, which is used for that purpose.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define lli long long int
lli countSubarrays(int arr[],
int n)
{
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
int prefixSum[n];
int prefixMin = 0;
prefixSum[0] = arr[0];
prefixMin = min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1]
+ arr[i];
prefixMin = min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[i]);
}
lli countSubs = 0;
mp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0;
prefixSum[i] - j * j >= prefixMin;
j++) {
if (mp.find(prefixSum[i] - j * j)
!= mp.end())
countSubs += mp[prefixSum[i]
- j * j];
}
mp[prefixSum[i]]++;
}
return countSubs;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, -5,
6, -7, 4 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
lli ans = countSubarrays(arr, n);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static long countSubarrays(int arr[],
int n)
{
HashMap<Integer,
Integer> mp = new HashMap<Integer,
Integer>();
int []prefixSum = new int[n];
int prefixMin = 0;
prefixSum[0] = arr[0];
prefixMin = Math.min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] + arr[i];
prefixMin = Math.min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[i]);
}
long countSubs = 0;
mp.put(0, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0;
prefixSum[i] - j *
j >= prefixMin; j++)
{
if (mp.containsKey(prefixSum[i] - j * j))
countSubs += mp.get(prefixSum[i] -
j * j);
}
if(mp.containsKey(prefixSum[i]))
{
mp.put(prefixSum[i],
mp.get(prefixSum[i]) + 1);
}
else
{
mp.put(prefixSum[i], 1);
}
}
return countSubs;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {2, 3, -5,
6, -7, 4};
int n = arr.length;
long ans = countSubarrays(arr, n);
System.out.print(ans);
}
}
|
Python3
from collections import defaultdict
def countSubarrays(arr, n):
mp = defaultdict(lambda:0)
prefixSum = [0] * n
prefixMin = 0
prefixSum[0] = arr[0]
prefixMin = min(prefixMin, prefixSum[0])
for i in range(1, n):
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] + arr[i]
prefixMin = min(prefixMin, prefixSum[i])
countSubs = 0
mp[0] = 1
for i in range(n):
j = 0
while prefixSum[i] - j * j >= prefixMin:
if prefixSum[i] - j * j in mp:
countSubs += mp[prefixSum[i] - j * j]
j += 1
mp[prefixSum[i]] += 1
return countSubs
arr = [ 2, 3, -5, 6, -7, 4 ]
n = len(arr)
ans = countSubarrays(arr, n)
print(ans)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static long countSubarrays(int []arr,
int n)
{
Dictionary<int,
int> mp =
new Dictionary<int,
int>();
int []prefixSum = new int[n];
int prefixMin = 0;
prefixSum[0] = arr[0];
prefixMin = Math.Min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] +
arr[i];
prefixMin = Math.Min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[i]);
}
long countSubs = 0;
mp.Add(0, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; prefixSum[i] - j *
j >= prefixMin; j++)
{
if (mp.ContainsKey(prefixSum[i] -
j * j))
countSubs += mp[prefixSum[i] -
j * j];
}
if(mp.ContainsKey(prefixSum[i]))
{
mp[prefixSum[i]]++;
}
else
{
mp.Add(prefixSum[i], 1);
}
}
return countSubs;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = {2, 3, -5,
6, -7, 4};
int n = arr.Length;
long ans = countSubarrays(arr, n);
Console.Write(ans);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function countSubarrays(arr, n)
{
let mp = new Map();
let prefixSum = Array.from({length: n}, (_, i) => 0);
let prefixMin = 0;
prefixSum[0] = arr[0];
prefixMin = Math.min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[0]);
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1] + arr[i];
prefixMin = Math.min(prefixMin,
prefixSum[i]);
}
let countSubs = 0;
mp.set(0, 1);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (let j = 0;
prefixSum[i] - j *
j >= prefixMin; j++)
{
if (mp.has(prefixSum[i] - j * j))
countSubs += mp.get(prefixSum[i] -
j * j);
}
if(mp.has(prefixSum[i]))
{
mp.set(prefixSum[i],
mp.get(prefixSum[i]) + 1);
}
else
{
mp.set(prefixSum[i], 1);
}
}
return countSubs;
}
let arr = [2, 3, -5,
6, -7, 4];
let n = arr.length;
let ans = countSubarrays(arr, n);
document.write(ans);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N * sqrt(K))
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...