Count number of times each Edge appears in all possible paths of a given Tree
Last Updated :
07 Sep, 2021
Given an Undirected Connected Graph in the form of a tree consisting of N nodes and (N – 1) edges, the task for each edge is to count the number of times it appears across all possible paths in the Tree.
Examples:
Input:

Output: 3 4 3
Explanation:
All possible paths of a given tree are {(1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4)}
Edge 1 occurs in the paths {(1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4)}. Therefore, the frequency of the edge is 3.
Edge 2 occurs in the paths {(1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 4)}. Therefore, the frequency of the edge is 4.
Edge 3 occurs in the paths {(1, 4), (2, 4), (3, 4)}. Therefore, the frequency of the edge is 3.
Input:

Output: 4 6 4 4
Explanation:
Edge 1 occurs in the paths {(1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5)}. Therefore, the frequency of the edge is 4
Edge 2 occurs in the paths {(1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5)}. Therefore, the frequency of the edge is 6
Edge 3 occurs in the paths {(1, 4), (2, 4), (3, 4), (4, 5)}. Therefore, the frequency of the edge is 4
Edge 4 occurs in the paths {(1, 5), (2, 5), (3, 5), (4, 5)}. Therefore, the frequency of the edge is 4
Naive Approach: The simplest approach is to generate all possible paths from each node of the given graph and store the count of edges occurring in these paths by a HashMap. Finally, print the frequencies of each edge.
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Efficient Approach: To optimize the above approach, the following observation needs to be made:
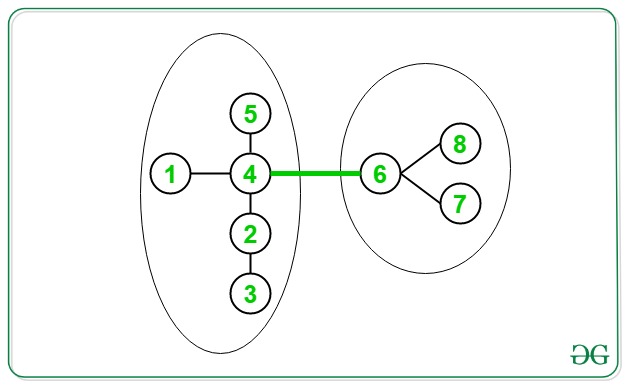
The green-colored edge will appear in all the paths that connect any vertex from the subtree on its left to any vertex from the subtree on its right.
Therefore, the number of paths in which the edge occurs = Product of the count of nodes in the two subtrees = 5 * 3 = 15.
Follow the steps below in order to solve the problem:
- Root the tree at any random vertex, say 1.
- Perform DFS at Root. Using DFS calculate the subtree size connected to the edges.
- The frequency of each edge connected to subtree is (subtree size) * (N – subtree size).
- Store the value calculated above for each node in a HashMap. Finally, after complete the traversal of the tree, traverse the HashMap to print the result.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int N;
struct Node {
int node;
int edgeLabel;
};
vector<Node> adj[100005];
vector<int> freq;
int dfs(int u = 1, int p = 1)
{
int sz = 1;
for (auto a : adj[u]) {
if (a.node != p) {
int val = dfs(a.node, u);
freq[a.edgeLabel]
= val * (N - val);
sz += val;
}
}
return sz;
}
void addEdge(int u, int v, int label)
{
adj[u].push_back({ v, label });
adj[v].push_back({ u, label });
}
void printFrequencies()
{
freq = vector<int>(N);
dfs();
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
cout << freq[i] << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
N = 4;
addEdge(1, 2, 1);
addEdge(2, 3, 2);
addEdge(3, 4, 3);
printFrequencies();
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int N;
static class Node
{
int node;
int edgeLabel;
public Node(int node, int edgeLabel)
{
super();
this.node = node;
this.edgeLabel = edgeLabel;
}
};
static Vector<Node> []adj = new Vector[100005];
static int []freq;
static int dfs(int u , int p)
{
int sz = 1;
for (Node a : adj[u])
{
if (a.node != p)
{
int val = dfs(a.node, u);
freq[a.edgeLabel] = val * (N - val);
sz += val;
}
}
return sz;
}
static void addEdge(int u, int v, int label)
{
adj[u].add(new Node( v, label ));
adj[v].add(new Node( u, label));
}
static void printFrequencies()
{
freq = new int[N];
dfs(1, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
System.out.print(freq[i] + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
N = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector<Node>();
addEdge(1, 2, 1);
addEdge(2, 3, 2);
addEdge(3, 4, 3);
printFrequencies();
}
}
|
Python3
N = 4
class Node:
def __init__(self, v, label):
self.node = v
self.edgeLabel = label
adj = []
for i in range(100005):
adj.append([])
freq = [0] * N
def dfs(u = 1, p = 1):
global N
sz = 1
for a in adj[u]:
if a.node != p:
val = dfs(a.node, u)
freq[a.edgeLabel] = val * (N - val)
sz += val
return sz
def addEdge(u, v, label):
adj[u].append(Node(v, label))
adj[v].append(Node(u, label))
def printFrequencies():
global N
dfs()
for i in range(1, N):
print(freq[i], end = " ")
N = 4
addEdge(1, 2, 1)
addEdge(2, 3, 2)
addEdge(3, 4, 3)
printFrequencies()
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int N;
public class Node
{
public int node;
public int edgeLabel;
public Node(int node,
int edgeLabel)
{
this.node = node;
this.edgeLabel = edgeLabel;
}
};
static List<Node> []adj =
new List<Node>[100005];
static int []freq;
static int dfs(int u, int p)
{
int sz = 1;
foreach (Node a in adj[u])
{
if (a.node != p)
{
int val = dfs(a.node, u);
freq[a.edgeLabel] = val * (N - val);
sz += val;
}
}
return sz;
}
static void addEdge(int u, int v,
int label)
{
adj[u].Add(new Node(v, label));
adj[v].Add(new Node(u, label));
}
static void printFrequencies()
{
freq = new int[N];
dfs(1, 1);
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
Console.Write(freq[i] + " ");
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
N = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List<Node>();
addEdge(1, 2, 1);
addEdge(2, 3, 2);
addEdge(3, 4, 3);
printFrequencies();
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let N;
class Node
{
constructor(node, edgeLabel) {
this.node = node;
this.edgeLabel = edgeLabel;
}
}
let adj = new Array(100005);
let freq;
function dfs(u, p)
{
let sz = 1;
for (let a = 0; a < adj[u].length; a++)
{
if (adj[u][a].node != p)
{
let val = dfs(adj[u][a].node, u);
freq[adj[u][a].edgeLabel] = val * (N - val);
sz += val;
}
}
return sz;
}
function addEdge(u, v, label)
{
adj[u].push(new Node( v, label ));
adj[v].push(new Node( u, label));
}
function printFrequencies()
{
freq = new Array(N);
dfs(1, 1);
for (let i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
document.write(freq[i] + " ");
}
}
N = 4;
for (let i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = [];
addEdge(1, 2, 1);
addEdge(2, 3, 2);
addEdge(3, 4, 3);
printFrequencies();
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...