Count integers in a range which are divisible by their euler totient value
Last Updated :
08 Apr, 2021
Given 2 integers L and R, the task is to find out the number of integers in the range [L, R] such that they are completely divisible by their Euler totient value.
Examples:
Input: L = 2, R = 3
Output: 1
*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula:
*** Error message:
Error: Nothing to show, formula is empty
(2) = 2 => 2 % *** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula:
*** Error message:
Error: Nothing to show, formula is empty
(2) = 0
*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula:
*** Error message:
Error: Nothing to show, formula is empty
(3) = 2 => 3 % *** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula:
*** Error message:
Error: Nothing to show, formula is empty
(3) = 1
Hence 2 satisfies the condition.
Input: L = 12, R = 21
Output: 3
Only 12, 16 and 18 satisfy the condition.
Approach: We know that the euler totient function of a number is given as follows:
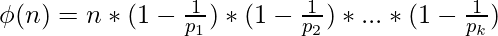
Rearranging the terms, we get:
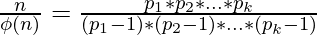
If we take a close look at the RHS, we observe that only 2 and 3 are the primes that satisfy n %
*** QuickLaTeX cannot compile formula:
*** Error message:
Error: Nothing to show, formula is empty
= 0. This is because for primes
p1 = 2 and p2 = 3, p1 – 1 = 1 and p2 – 1 = 2. Hence, only numbers of the form
2p3q where p >= 1 and q >= 0 need to be counted while lying in the range
[L, R].
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll power(ll a, ll n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
ll p = power(a, n / 2);
p = p * p;
if (n & 1)
p = p * a;
return p;
}
int countIntegers(ll l, ll r)
{
ll ans = 0, i = 1;
ll v = power(2, i);
while (v <= r) {
while (v <= r) {
if (v >= l)
ans++;
v = v * 3;
}
i++;
v = power(2, i);
}
if (l == 1)
ans++;
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ll l = 12, r = 21;
cout << countIntegers(l, r);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static long power(long a, long n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
long p = power(a, n / 2);
p = p * p;
if (n%2== 1)
p = p * a;
return p;
}
static int countIntegers(long l, long r)
{
long ans = 0, i = 1;
long v = power(2, i);
while (v <= r)
{
while (v <= r)
{
if (v >= l)
ans++;
v = v * 3;
}
i++;
v = power(2, i);
}
if (l == 1)
ans++;
return (int) ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long l = 12, r = 21;
System.out.println(countIntegers(l, r));
}
}
|
Python3
def power(a, n):
if n == 0:
return 1
p = power(a, n // 2)
p = p * p
if n & 1:
p = p * a
return p
def countIntegers(l, r):
ans, i = 0, 1
v = power(2, i)
while v <= r:
while v <= r:
if v >= l:
ans += 1
v = v * 3
i += 1
v = power(2, i)
if l == 1:
ans += 1
return ans
if __name__ == "__main__":
l, r = 12, 21
print(countIntegers(l, r))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static long power(long a, long n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
long p = power(a, n / 2);
p = p * p;
if (n % 2 == 1)
p = p * a;
return p;
}
static int countIntegers(long l, long r)
{
long ans = 0, i = 1;
long v = power(2, i);
while (v <= r)
{
while (v <= r)
{
if (v >= l)
ans++;
v = v * 3;
}
i++;
v = power(2, i);
}
if (l == 1)
ans++;
return (int) ans;
}
public static void Main()
{
long l = 12, r = 21;
Console.WriteLine(countIntegers(l, r));
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function power($a, $n)
{
if ($n == 0)
return 1;
$p = power($a, $n / 2);
$p = $p * $p;
if ($n & 1)
$p = $p * $a;
return $p;
}
function countIntegers($l, $r)
{
$ans = 0 ;
$i = 1;
$v = power(2, $i);
while ($v <= $r)
{
while ($v <= $r)
{
if ($v >= $l)
$ans++;
$v = $v * 3;
}
$i++;
$v = power(2, $i);
}
if ($l == 1)
$ans++;
return $ans;
}
$l = 12;
$r = 21;
echo countIntegers($l, $r);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function power(a , n) {
if (n == 0)
return 1;
var p = power(a, parseInt(n / 2));
p = p * p;
if (n % 2 == 1)
p = p * a;
return p;
}
function countIntegers(l , r) {
var ans = 0, i = 1;
var v = power(2, i);
while (v <= r) {
while (v <= r) {
if (v >= l)
ans++;
v = v * 3;
}
i++;
v = power(2, i);
}
if (l == 1)
ans++;
return parseInt( ans);
}
var l = 12, r = 21;
document.write(countIntegers(l, r));
</script>
|
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...