Count anagrams having first character as a consonant and no pair of consonants or vowels placed adjacently
Last Updated :
18 Apr, 2023
Given a string S of length N, the task is to count the number of anagrams of S whose first character is a consonant and no pair of consonants or vowels are adjacent to each other.
Examples:
Input: S = “GADO”
Output: 4
Explanation:
The anagrams of string S satisfying the given conditions are GADO, GODA, DOGA, DAGO.
Therefore, the total number of such anagrams is 4.
Input: S = “AABCY”
Output: 6
Explanation:
The anagrams of the string S satisfying the given conditions are BACAY, BAYAC, CABAY, CAYAB, YABAC, YACAB.
Therefore, the total number of such anagrams is 6.
Naive Approach: The simplest approach is to generate all possible anagrams of the given string and count those anagrams that satisfy the given condition. Finally, print the count obtained.
C++
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool is_consonant(char c)
{
return (c != 'A' && c != 'E' && c != 'I' && c != 'O'
&& c != 'U');
}
int countAnagrams(string s)
{
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
int count = 0;
do {
bool check = true;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
if (!is_consonant(s[i])) {
check = false;
break;
}
}
else {
if (is_consonant(s[i])) {
check = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (check)
count++;
} while (next_permutation(s.begin(), s.end()));
return count;
}
int main()
{
string S = "GADO";
cout << countAnagrams(S) << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main
{
static boolean is_consonant(char c)
{
return (c != 'A' && c != 'E' && c != 'I' && c != 'O'
&& c != 'U');
}
static int countAnagrams(String s)
{
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(arr);
int count = 0;
do {
boolean check = true;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
if (!is_consonant(arr[i])) {
check = false;
break;
}
}
else {
if (is_consonant(arr[i])) {
check = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (check)
count++;
} while (nextPermutation(arr));
return count;
}
static boolean nextPermutation(char[] arr)
{
int n = arr.length;
int i = n - 2;
while (i >= 0 && arr[i] >= arr[i + 1]) {
i--;
}
if (i < 0) {
return false;
}
int j = n - 1;
while (arr[j] <= arr[i]) {
j--;
}
char temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
Arrays.sort(arr, i + 1, n);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String S = "GADO";
System.out.println(countAnagrams(S));
}
}
|
Python3
from itertools import permutations
def is_consonant(c):
return c not in "AEIOU"
def countAnagrams(s):
perms = permutations(s)
count = 0
for perm in perms:
check=1
for i in range(len(perm)):
if(i%2==0):
if(not is_consonant(perm[i])):
check=0
else:
if(is_consonant(perm[i])):
check=0
if(check==1):
count += 1
return count
if __name__ == '__main__':
S = "GADO"
print(countAnagrams(S))
|
Javascript
function isConsonant(c) {
return (c !== 'A' && c !== 'E' && c !== 'I' && c !== 'O' && c !== 'U');
}
function swap(str, i, j) {
const temp = str[i];
str = str.substring(0, i) + str[j] + str.substring(i+1);
str = str.substring(0, j) + temp + str.substring(j+1);
return str;
}
function generatePermutations(str, l, r, count) {
if (l === r) {
let check = true;
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
if (i % 2 === 0) {
if (!isConsonant(str[i])) {
check = false;
break;
}
} else {
if (isConsonant(str[i])) {
check = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (check) {
count[0]++;
}
} else {
for (let i = l; i <= r; i++) {
str = swap(str, l, i);
generatePermutations(str, l+1, r, count);
str = swap(str, l, i);
}
}
}
function countAnagrams(S) {
let count = [0];
generatePermutations(S, 0, S.length-1, count);
return count[0];
}
console.log(countAnagrams("GADO"));
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace ConsoleApp
{
class Program
{
static bool IsConsonant(char c)
{
return (c != 'A' && c != 'E' && c != 'I' && c != 'O'
&& c != 'U');
}
static int CountAnagrams(string s)
{
var permutations = GetPermutations(s);
int count = 0;
foreach (var permutation in permutations)
{
bool check = true;
for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
if (!IsConsonant(permutation[i]))
{
check = false;
break;
}
}
else
{
if (IsConsonant(permutation[i]))
{
check = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (check)
count++;
}
return count;
}
static List<string> GetPermutations(string s)
{
var permutations = new List<string>();
GetPermutationsHelper(s.ToCharArray(), 0, permutations);
return permutations;
}
static void GetPermutationsHelper(char[] s, int i, List<string> permutations)
{
if (i == s.Length - 1)
{
permutations.Add(new string(s));
}
else
{
for (int j = i; j < s.Length; j++)
{
Swap(s, i, j);
GetPermutationsHelper(s, i + 1, permutations);
Swap(s, i, j);
}
}
}
static void Swap(char[] s, int i, int j)
{
char temp = s[i];
s[i] = s[j];
s[j] = temp;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string S = "GADO";
Console.WriteLine(CountAnagrams(S));
}
}
}
|
Time Complexity: O(N!*N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Efficient Approach: The above approach can also be optimized based on the following observations:
- Strings that have an equal number of consonants and vowels satisfy the given condition.
- Strings having one more consonant than vowel also satisfy the given condition.
- Apart from these two conditions, the count of possible anagrams will always be 0.
- Now, the problem can be solved by using a combinatorial formula. Consider there are C1, C2…, CN consonants and V1, V2, …, VN vowels in the string S and
 and \sum C
and \sum C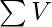 denote the total number of consonants and vowels respectively, then the answer would be:
denote the total number of consonants and vowels respectively, then the answer would be:
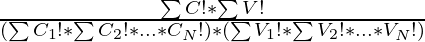
where,
Ci is the count of ith consonant.
Vi is the count of ith vowel.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Initialize a variable, say answer, to store the total count of anagrams.
- Store the frequency of each character of the string S in a HashMap count.
- Store the number of vowels and consonants in S in variables V and C respectively.
- If the value of V is not equal to C or C is not equal to (V + 1), then print 0. Otherwise, performing the following steps:
- Initialize denominator as 1.
- Traverse the string S using the variable i and update the denominator as denominator*((count[S[i]])!).
- Initialize numerator to V!*C!, and update the value of answer as numerator/denominator.
- After completing the above steps, print the value of the answer as the result.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define N 1000001
using namespace std;
void Precomputefact(unordered_map<ll, ll>& fac)
{
ll ans = 1;
for (ll i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
ans = (ans * i) % mod;
fac[i] = ans;
}
return;
}
bool isVowel(char a)
{
if (a == 'A' || a == 'E' || a == 'I' || a == 'O'
|| a == 'U')
return true;
else
return false;
}
void countAnagrams(string s, int n)
{
unordered_map<ll, ll> fac;
Precomputefact(fac);
unordered_map<char, ll> count;
int vo = 0, co = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
count[s[i]]++;
if (isVowel(s[i]))
vo++;
else
co++;
}
if ((co == vo + 1) || (co == vo)) {
ll deno = 1;
for (auto c : count) {
deno = (deno * fac[c.second]) % mod;
}
ll nume = fac[co] % mod;
nume = (nume * fac[vo]) % mod;
ll ans = nume / deno;
cout << ans;
}
else {
cout << 0;
}
}
int main()
{
string S = "GADO";
int l = S.size();
countAnagrams(S, l);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int mod = 1000000007;
static int N = 1000001;
static HashMap<Integer, Long> fac
= new HashMap<Integer, Long>();
static void precomputeFact()
{
long ans = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
ans = (ans * i) % mod;
fac.put(i, ans);
}
}
static boolean isVowel(char a)
{
return a == 'A' || a == 'E' || a == 'I' || a == 'O'
|| a == 'U';
}
static void countAnagrams(String s, int n)
{
precomputeFact();
HashMap<Character, Integer> count = new HashMap<>();
int vo = 0;
int co = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (count.containsKey(s.charAt(i))) {
count.put(s.charAt(i),
count.get(s.charAt(i)) + 1);
}
else {
count.put(s.charAt(i), 1);
}
if (isVowel(s.charAt(i))) {
vo++;
}
else {
co++;
}
}
if (co == vo + 1 || co == vo) {
long deno = 1;
for (var item : count.entrySet()) {
deno = (deno * fac.get(item.getValue()))
% mod;
}
long nume = fac.get(co) % mod;
nume = (nume * fac.get(vo)) % mod;
long ans = nume / deno;
System.out.println(ans);
}
else {
System.out.println(0);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String S = "GADO";
int l = S.length();
countAnagrams(S, l);
}
}
|
Python3
mod = 1000000007
N = 1000001
fac = {}
def Precomputefact():
global fac
ans = 1
for i in range(1,N+1,1):
ans = (ans * i) % mod
fac[i] = ans
return
def isVowel(a):
if (a == 'A' or a == 'E' or a == 'I' or a == 'O' or a == 'U'):
return True
else:
return False
def countAnagrams(s,n):
global fac
Precomputefact()
count = {}
vo = 0
co = 0
for i in range(n):
if s[i] in count:
count[s[i]] += 1
else:
count[s[i]] = 1
if (isVowel(s[i])):
vo += 1
else:
co += 1
if ((co == vo + 1) or (co == vo)):
deno = 1
for key,value in count.items():
deno = (deno * fac[value]) % mod
nume = fac[co] % mod
nume = (nume * fac[vo]) % mod
ans = nume // deno
print(ans)
else:
print(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
S = "GADO"
l = len(S)
countAnagrams(S, l)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
class GFG {
static int mod = 1000000007;
static int N = 1000001;
static Dictionary<int, long> fac
= new Dictionary<int, long>();
static void Precomputefact()
{
long ans = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
ans = (ans * i) % mod;
fac[i] = ans;
}
}
static bool IsVowel(char a)
{
return (a == 'A' || a == 'E' || a == 'I' || a == 'O'
|| a == 'U');
}
static void CountAnagrams(string s, int n)
{
Precomputefact();
Dictionary<char, int> count
= new Dictionary<char, int>();
int vo = 0;
int co = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (count.ContainsKey(s[i])) {
count[s[i]]++;
}
else {
count[s[i]] = 1;
}
if (IsVowel(s[i])) {
vo++;
}
else {
co++;
}
}
if (co == vo + 1 || co == vo) {
long deno = 1;
foreach(var item in count)
{
deno = (deno * fac[item.Value]) % mod;
}
long nume = fac[co] % mod;
nume = (nume * fac[vo]) % mod;
long ans = nume / deno;
Console.WriteLine(ans);
}
else
Console.WriteLine(0);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string S = "GADO";
int l = S.Length;
CountAnagrams(S, l);
}
}
|
Javascript
const mod = 1000000007;
const N = 1000001;
let fac = {};
function Precomputefact() {
let ans = 1;
for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
ans = (ans * i) % mod;
fac[i] = ans;
}
return;
}
function isVowel(a) {
if (a == "A" || a == "E" || a == "I" || a == "O" || a == "U") {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
function countAnagrams(s, n) {
Precomputefact();
let count = {};
let vo = 0;
let co = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i] in count) {
count[s[i]] += 1;
} else {
count[s[i]] = 1;
}
if (isVowel(s[i])) {
vo += 1;
} else {
co += 1;
}
}
if (co == vo + 1 || co == vo) {
let deno = 1;
for (let key of Object.keys(count)) {
deno = (deno * fac[count[key]]) % mod;
}
let nume = fac[co] % mod;
nume = (nume * fac[vo]) % mod;
let ans = Math.floor(nume / deno);
console.log(ans);
} else {
console.log(0);
}
}
let S = "GADO";
let l = S.length;
countAnagrams(S, l);
|
Time Complexity: O(N), The function Precomputefact() has a time complexity of O(N), as it iterates through all numbers from 1 to N and performs constant time operations.
The function countAnagrams() has a time complexity of O(N), as it iterates through all characters of the input string S and performs constant time operations.
The overall time complexity of the program is O(N), as the two functions are called one after the other.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), The function Precomputefact() stores all factorials up to N in an unordered_map, which has a space complexity of O(N).
The function countAnagrams() stores the frequencies of all characters in the input string S in an unordered_map, which has a space complexity of O(N).
The overall space complexity of the program is O(N), as the two unordered_maps are the only significant data structures used in the program.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...