Convert Binary Tree to Doubly Linked List by keeping track of visited node
Last Updated :
21 Apr, 2024
Given a Binary Tree, The task is to convert it to a Doubly Linked List keeping the same order.
- The left and right pointers in nodes are to be used as previous and next pointers respectively in converted DLL.
- The order of nodes in DLL must be the same as in Inorder for the given Binary Tree.
- The first node of Inorder traversal (leftmost node in BT) must be the head node of the DLL.
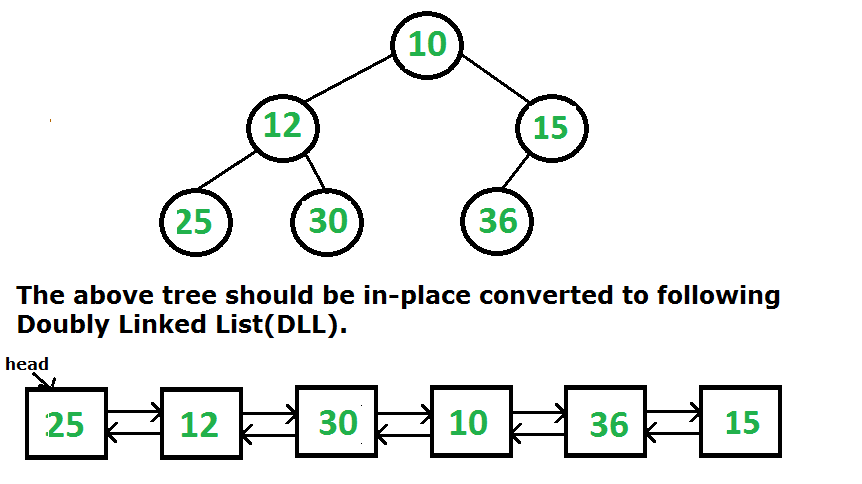
The following two different solutions have been discussed for this problem.
Convert a given Binary Tree to a Doubly Linked List | Set 1
Convert a given Binary Tree to a Doubly Linked List | Set 2
Approach: Below is the idea to solve the problem:
The idea is to do in-order traversal of the binary tree. While doing inorder traversal, keep track of the previously visited node in a variable, say prev. For every visited node, make it next to the prev and set previous of this node as prev.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// A C++ program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to
// DLL
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, and left and right pointers
*/
struct node {
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
// A simple recursive function to convert a given Binary
// tree to Doubly Linked List root --> Root of Binary Tree
// head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly linked
// list
void BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(node* root, node** head)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is
// static so that the same value is accessible in all
// recursive calls
static node* prev = NULL;
// Recursively convert left subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root->left, head);
// Now convert this node
if (prev == NULL)
*head = root;
else {
root->left = prev;
prev->right = root;
}
prev = root;
// Finally convert right subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root->right, head);
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* new_node = new node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = new_node->right = NULL;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->right;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(25);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
// Convert to DLL
node* head = NULL;
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root, &head);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Sania Kumari Gupta (kriSania804)
// A C program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to DLL
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* A binary tree node has data, and left and right pointers
*/
typedef struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
} node;
// A simple recursive function to convert a given Binary
// tree to Doubly Linked List root --> Root of Binary Tree
// head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly linked
// list
void BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(node* root, node** head)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is
// static so that the same value is accessible in all
// recursive calls
static node* prev = NULL;
// Recursively convert left subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root->left, head);
// Now convert this node
if (prev == NULL)
*head = root;
else {
root->left = prev;
prev->right = root;
}
prev = root;
// Finally convert right subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root->right, head);
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* new_node = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = new_node->right = NULL;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->right;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(25);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
// Convert to DLL
node* head = NULL;
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root, &head);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Sania Kumari Gupta (kriSania804)
// A Java program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to DLL
// A binary tree node has data, left pointers and right pointers
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
// head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly linked list
Node head;
// Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is
// static so that the same value is accessible in all recursive
// calls
static Node prev = null;
// A simple recursive function to convert a given Binary tree
// to Doubly Linked List
// root --> Root of Binary Tree
void BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(Node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
// Recursively convert left subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.left);
// Now convert this node
if (prev == null)
head = root;
else
{
root.left = prev;
prev.right = root;
}
prev = root;
// Finally convert right subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.right);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null)
{
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.right;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(25);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
// convert to DLL
tree.BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(tree.root);
// Print the converted List
tree.printList(tree.head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal(mayank_24)
# Python program for conversion of
# binary tree to doubly linked list.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.right = None
self.data = val
self.left = None
# Global variable used in convert
prev = None
def BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root):
# Base case
if root is None:
return root
# Recursively convert left subtree
head = BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.left);
# Since we are going to change prev,
# we need to use global keyword
global prev
# If prev is empty, then this is the
# first node of DLL
if prev is None :
head = root
else:
root.left = prev
prev.right = root
# Update prev
prev = root;
# Recursively convert right subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.right);
return head
def print_dll(head):
# Function to print nodes in given
# doubly linked list
while head is not None:
print(head.data, end=" ")
head = head.right
# Driver program to test above functions
# Let us create the tree as
# shown in above diagram
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(10)
root.left = Node(12)
root.right = Node(15)
root.left.left = Node(25)
root.left.right = Node(30)
root.right.left = Node(36)
head = BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root)
# Print the converted list
print_dll(head)
# This code is contributed by codesankalp (SANKALP)
// A C# program for in-place conversion
// of Binary Tree to DLL
using System;
// A binary tree node has data, left
// pointers and right pointers
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG
{
public Node root;
// head --> Pointer to head node of
// created doubly linked list
public Node head;
// Initialize previously visited node
// as NULL. This is static so that the
// same value is accessible in all
// recursive calls
public static Node prev = null;
// A simple recursive function to
// convert a given Binary tree
// to Doubly Linked List
// root --> Root of Binary Tree
public virtual void BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(Node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
{
return;
}
// Recursively convert left subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.left);
// Now convert this node
if (prev == null)
{
head = root;
}
else
{
root.left = prev;
prev.right = root;
}
prev = root;
// Finally convert right subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.right);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a
given doubly linked list */
public virtual void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null)
{
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.right;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Let us create the tree as
// shown in above diagram
GFG tree = new GFG();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(25);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(30);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(36);
// convert to DLL
tree.BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(tree.root);
// Print the converted List
tree.printList(tree.head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
// A binary tree node has data, left pointers and right pointers
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
var root;
// head --> Pointer to head node of created doubly linked list
var head;
// Initialize previously visited node as NULL. This is
// so that the same value is accessible in all recursive
// calls
var prev = null;
// A simple recursive function to convert a given Binary tree
// to Doubly Linked List
// root --> Root of Binary Tree
function BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
// Recursively convert left subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.left);
// Now convert this node
if (prev == null)
head = root;
else
{
root.left = prev;
prev.right = root;
}
prev = root;
// Finally convert right subtree
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root.right);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
function printList(node)
{
while (node != null)
{
console.log(node.data + " ");
node = node.right;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
// Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram
root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(12);
root.right = new Node(15);
root.left.left = new Node(25);
root.left.right = new Node(30);
root.right.left = new Node(36);
// convert to DLL
BinaryTree2DoubleLinkedList(root);
// Print the converted List
printList(head);
// This code contributed by umadevi9616
Note: The use of static variables like above is not a recommended practice, here static is used for simplicity. Imagine if the same function is called for two or more trees. The old value of prev would be used in the next call for a different tree. To avoid such problems, we can use a double-pointer or a reference to a pointer.
Time Complexity: O(N), The above program does a simple inorder traversal, so time complexity is O(N) where N is the number of nodes in a given Binary tree.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), For recursion call stack.
Convert a given Binary Tree to Doubly Linked List iteratively using Stack data structure:
Do iterative inorder traversal and maintain a prev pointer to point the last visited node then point current node’s perv to prev and prev’s next to current node.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// A C++ program for in-place conversion of Binary Tree to
// DLL
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, and left and right pointers
*/
struct node {
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
node * bToDLL(node *root)
{
stack<pair<node*, int>> s;
s.push({root, 0});
vector<int> res;
bool flag = true;
node* head = NULL;
node* prev = NULL;
while(!s.empty()) {
auto x = s.top();
node* t = x.first;
int state = x.second;
s.pop();
if(state == 3 or t == NULL) continue;
s.push({t, state+1});
if(state == 0) s.push({t->left, 0});
else if(state == 1) {
if(prev) prev->right = t;
t->left = prev;
prev = t;
if(flag) {
head = t;
flag = false;
}
}
else if(state == 2) s.push({t->right, 0});
}
return head;
}
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
node* newNode(int data)
{
node* new_node = new node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->left = new_node->right = NULL;
return (new_node);
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
void printList(node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->right;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(12);
root->right = newNode(15);
root->left->left = newNode(25);
root->left->right = newNode(30);
root->right->left = newNode(36);
// Convert to DLL
node* head = bToDLL(root);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
return 0;
}
import java.util.Stack;
class Node {
int data;
Node left;
Node right;
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
public class Main {
static Node bToDLL(Node root) {
Stack<Pair<Node, Integer>> s = new Stack<>();
s.push(new Pair<>(root, 0));
boolean flag = true;
Node head = null;
Node prev = null;
while (!s.empty()) {
Pair<Node, Integer> x = s.pop();
Node t = x.getKey();
int state = x.getValue();
if (state == 3 || t == null) {
continue;
}
s.push(new Pair<>(t, state + 1));
if (state == 0) {
s.push(new Pair<>(t.left, 0));
} else if (state == 1) {
if (prev != null) {
prev.right = t;
}
t.left = prev;
prev = t;
if (flag) {
head = t;
flag = false;
}
} else if (state == 2) {
s.push(new Pair<>(t.right, 0));
}
}
return head;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list */
static void printList(Node head) {
while (head != null) {
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(12);
root.right = new Node(15);
root.left.left = new Node(25);
root.left.right = new Node(30);
root.right.left = new Node(36);
// Convert to DLL
Node head = bToDLL(root);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
}
}
class Pair<K, V> {
private K key;
private V value;
public Pair(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
}
// This code is contributed by aadityamaharshi21.
def bToDLL(root):
s = []
s.append([root, 0])
res = []
flag = True
head = None
prev = None
while len(s) > 0:
x = s.pop()
t = x[0]
state = x[1]
if state == 3 or t == None: continue
s.append([t, state+1])
if state == 0: s.append([t.left, 0])
elif state == 1:
if prev != None: prev.right = t
t.left = prev
prev = t
if flag:
head = t
flag = False
elif state == 2: s.append([t.right, 0])
return head
# This code is contributed by Tapeshdua420.
// C# code implementation for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
/* Helper function that allocates a new node with the
given data and NULL left and right pointers. */
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
public class GFG {
static Node bToDLL(Node root)
{
Stack<KeyValuePair<Node, int> > s
= new Stack<KeyValuePair<Node, int> >();
s.Push(new KeyValuePair<Node, int>(root, 0));
bool flag = true;
Node head = null;
Node prev = null;
while (s.Count != 0) {
KeyValuePair<Node, int> x = s.Pop();
Node t = x.Key;
int state = x.Value;
if (state == 3 || t == null) {
continue;
}
s.Push(
new KeyValuePair<Node, int>(t, state + 1));
if (state == 0) {
s.Push(
new KeyValuePair<Node, int>(t.left, 0));
}
else if (state == 1) {
if (prev != null) {
prev.right = t;
}
t.left = prev;
prev = t;
if (flag) {
head = t;
flag = false;
}
}
else if (state == 2) {
s.Push(new KeyValuePair<Node, int>(t.right,
0));
}
}
return head;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
*/
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null) {
System.Console.Write(head.data + " ");
head = head.right;
}
}
static public void Main()
{
// Code
// Let us create the tree shown in above diagram
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(12);
root.right = new Node(15);
root.left.left = new Node(25);
root.left.right = new Node(30);
root.right.left = new Node(36);
// Convert to DLL
Node head = bToDLL(root);
// Print the converted list
printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by lokesh.
// JavaScript code for above approach
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function bToDLL(root) {
let s = [];
s.push([root, 0]);
let res = [];
let flag = true;
let head = null;
let prev = null;
while (s.length > 0) {
let [t, state] = s.pop();
if (state === 3 || t === null) continue;
s.push([t, state + 1]);
if (state === 0) s.push([t.left, 0]);
else if (state === 1) {
if (prev) prev.right = t;
t.left = prev;
prev = t;
if (flag) {
head = t;
flag = false;
}
} else if (state === 2) s.push([t.right, 0]);
}
return head;
}
function newNode(data) {
let new_node = new Node(data);
return new_node;
}
function printList(node) {
while (node !== null) {
console.log(node.data);
node = node.right;
}
}
let root = newNode(10);
root.left = newNode(12);
root.right = newNode(15);
root.left.left = newNode(25);
root.left.right = newNode(30);
root.right.left = newNode(36);
let head = bToDLL(root);
printList(head);
// This code is contributed by adityamaharshi21
Time complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Convert a given Binary Tree to Doubly Linked List iteratively using Morris Traversal:
The idea is to keep track of previous node while doing Inorder tree traversal using Morris Traversal. This removes the need for a recursion call stack or a stack thus reducing space complexity
C++
#include <iostream>
// Structure for a binary tree node
struct Node {
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
// Constructor
Node(int val) : data(val), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
// Function to convert binary tree to doubly linked list
Node* bToDLL(Node* root) {
// Initialization
Node* curr = root;
Node* prev = nullptr; // Used to keep track of prev node
Node* final_head = nullptr; // Used to return the final head
// Traverse the tree
while (curr) {
// If no left child
if (!curr->left) {
// If final_head is not set, set it to current node
if (!final_head) {
prev = curr;
final_head = curr;
} else {
// Set next of prev as curr and prev of curr as prev
prev->right = curr;
curr->left = prev;
}
// Set the new prev node
prev = curr;
curr = curr->right;
} else {
// If left child exists
Node* pre = curr->left;
while (pre->right && pre->right != curr) {
pre = pre->right;
}
if (!pre->right) {
pre->right = curr;
curr = curr->left;
} else {
curr = pre->right;
// Set next of prev as curr and prev of curr as prev
prev->right = curr;
curr->left = prev;
// Set the new prev node
prev = curr;
curr = curr->right;
}
}
}
return final_head; // Return the final head of the linked list
}
// Function to print nodes in the doubly linked list
void print_dll(Node* head) {
while (head != nullptr) {
std::cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->right;
}
}
// Driver code
int main() {
// Create the binary tree
Node* root = new Node(10);
root->left = new Node(12);
root->right = new Node(15);
root->left->left = new Node(25);
root->left->right = new Node(30);
root->right->left = new Node(36);
// Convert the binary tree to doubly linked list
Node* head = bToDLL(root);
// Print the converted list
print_dll(head);
return 0;
}
// Definition of Node class representing a tree node
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item) {
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
// Class to convert a binary tree to a doubly linked list
public class BinaryTreeToDLL {
// Function to convert a binary tree to a doubly linked list
static Node bToDLL(Node root) {
Node curr = root;
Node prev = null; // Used to keep track of prev node
Node finalHead = null; // Used to return the final head
// Traverse the binary tree
while (curr != null) {
// If current node has no left child
if (curr.left == null) {
// If finalHead is not set, set it to current node
if (finalHead == null) {
prev = curr;
finalHead = curr;
} else {
// Connect previous node's right to current node
prev.right = curr;
// Connect current node's left to previous node
curr.left = prev;
}
// Move prev pointer to current node
prev = curr;
// Move current pointer to its right child
curr = curr.right;
} else {
// If current node has left child, find its inorder predecessor
Node pre = curr.left;
while (pre.right != null && pre.right != curr) {
pre = pre.right;
}
if (pre.right == null) {
// If inorder predecessor's right is not connected, connect it to current node
pre.right = curr;
// Move current pointer to its left child
curr = curr.left;
} else {
// If inorder predecessor's right is connected,
// connect current node to previous node and move pointers
curr = pre.right;
prev.right = curr;
curr.left = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
// Return the final head of the doubly linked list
return finalHead;
}
// Function to print the doubly linked list
static void printDLL(Node head) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
// Concatenate nodes data into a single line
while (head != null) {
result.append(head.data).append(" ");
head = head.right;
}
System.out.println("Elements are: " + result.toString().trim());
}
// Driver code to test above functions
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Create the tree as shown in the diagram
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(12);
root.right = new Node(15);
root.left.left = new Node(25);
root.left.right = new Node(30);
root.right.left = new Node(36);
// Convert the binary tree to doubly linked list
Node head = bToDLL(root);
// Print the converted list
printDLL(head);
}
}
# Python program for conversion of
# binary tree to doubly linked list.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.right = None
self.data = val
self.left = None
def bToDLL(root):
# do Code here
curr = root
prev = None #Used to keep track of prev node
final_head = None #used to return the final head
while curr:
if not curr.left:
if not final_head:
prev = curr
final_head = curr
else:
#set next of prev as curr and prev of curr as prev
prev.right = curr
curr.left = prev
#set the new prev node
prev = curr
curr = curr.right
else:
pre = curr.left
while pre.right and pre.right != curr:
pre = pre.right
if not pre.right:
pre.right = curr
curr = curr.left
else:
curr = pre.right
#set next of prev as curr and prev of curr as prev
prev.right = curr
curr.left = prev
#set the new prev node
prev = curr
curr = curr.right
return final_head
def print_dll(head):
# Function to print nodes in given
# doubly linked list
while head is not None:
print(head.data, end=" ")
head = head.right
# Driver program to test above functions
# Let us create the tree as
# shown in above diagram
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(10)
root.left = Node(12)
root.right = Node(15)
root.left.left = Node(25)
root.left.right = Node(30)
root.right.left = Node(36)
head = bToDLL(root)
# Print the converted list
print_dll(head)
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function bToDLL(root) {
let curr = root;
let prev = null; // Used to keep track of prev node
let final_head = null; // Used to return the final head
while (curr) {
if (!curr.left) {
if (!final_head) {
prev = curr;
final_head = curr;
} else {
prev.right = curr;
curr.left = prev;
}
prev = curr;
curr = curr.right;
} else {
let pre = curr.left;
while (pre.right && pre.right !== curr) {
pre = pre.right;
}
if (!pre.right) {
pre.right = curr;
curr = curr.left;
} else {
curr = pre.right;
prev.right = curr;
curr.left = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
return final_head;
}
function printDLL(head) {
let result = "";
// Function to concatenate nodes data into a single line
while (head !== null) {
result += head.data + " ";
head = head.right;
}
console.log(result.trim());
}
// Driver program to test above functions
// Let us create the tree as shown in above diagram
let root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(12);
root.right = new Node(15);
root.left.left = new Node(25);
root.left.right = new Node(30);
root.right.left = new Node(36);
let head = bToDLL(root);
// Print the converted list
printDLL(head);
Time complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...