A consumer is said to be the king of the market; therefore, the earlier approach, Caveat Emptor (Let the buyer beware) has been changed to Caveat Venditor (Let the seller beware). It means that, because of the fast-growing competition in the market, some businesses are involved in unfair trade practices and exploit customers, from which the customers need protection. Hence, Consumer Protection is an act that provides adequate protection to the customers against any unfair trade practices, exploitative, and unscrupulous practices of the businesses (including manufacturers and service providers).
Consumer Rights
Even though businessmen know their social responsibilities towards society, many businessmen exploit the consumers by way of unfair trade practices, fraud, etc. Therefore, the government of India provides some rights to consumers under the Consumer Protection Act to protect their interests. These rights are Right to Safety, Right to Information, Right to make Choice, Right to be Heard, Right to Seek Redressal and Right to Consumer Education.
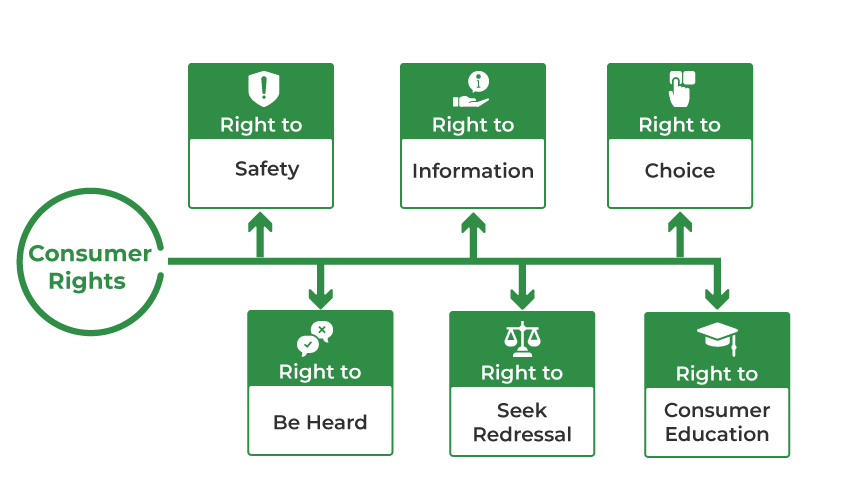
1. Right to Safety
Right to Safety states that a consumer has the right to be protected against the marketing of hazardous goods and services to their life and property. It is essential for consumers for their secure and safe life and consists of concern for the present requirement and long-term interests of the consumers. Sometimes, a manufacturing defect in the goods like gas cylinders, electrical appliances, etc., may cause loss to the consumer’s life, health, and property. Hence, the right to safety protects the customers from the sale of hazardous goods and services.
2. Right to Information
Right to Information states that a consumer has the right to be informed about the quantity, quality, purity, price, and standard of goods and services. The basic aim of this right is to protect consumers from any abusive and unfair trade practices. The right says that a producer must supply all the relevant information for consumers at a suitable place. Because of the right to information, the legal framework of India states that it is compulsory for the manufacturers to provide the relevant information on the package and label of the product.
3. Right to make Choice/Right to Choose/Right to be Assured
Right to Choose states that a consumer has the right to choose the goods and services of their choice or liking. In simple terms, it means that the consumers are given an assurance of ability, availability, and access to different products and services at a competitive price. A competitive price here means a fair price. The retailers, manufacturers, or traders cannot force the consumers to purchase a specific brand only, the consumers can choose any brand they find suitable from their point of view.
4. Right to be Heard/Right to Representation
Right to be Heard states that a consumer has the right to be heard or advocate his/her interest or represent himself/herself. In simple terms, if a consumer has been exploited by a business or has a complaint regarding a business, good, or service, then he/she has the right to be heard and assured that his/her interest would be taken into consideration. For the fulfilment of this right, it is essential for the companies to have a complaint cell, so they can attend to the complaints of customers. Besides, the Right to be Heard also includes the right to representation in the government and other bodies making policies related to consumer protection.
5. Right to Seek Redressal
Right to Seek Redressal states that a consumer has the right to seek redressal and get compensation against exploitation or any other unfair trade practices. In simple terms, this right aims at assuring justice to the consumer against exploitation. The compensation can be in form of money, replacement of goods, or repair of defective goods according to the satisfaction of the consumer. For the accomplishment of this right, the government has set up various redressal forums at the state level and national levels.
6. Right to Consumer Education
Right to Consumer Education states that a consumer has the right to acquire the required knowledge and skills to be an informed consumer. Literate consumers can easily attain required information, know their rights, and take actions, but illiterate consumers cannot. Therefore, this right assures that illiterate consumers can seek information regarding their rights, existing acts, and agencies set up for their protection. For the same reason, the government of India has made it compulsory to add consumer education to the school curriculum and various university courses. To make consumers aware of their rights, the government is also using media and putting its money to good use.
Consumers’ Responsibilities
In order to protect the interests of consumers, government and non-government organisations have made various efforts. But, these efforts can be helpful and can stop exploitation only when the consumers themselves will understand their responsibilities and move forward to safeguard their interests. Some of the responsibilities of consumers are as follows:
1. A consumer must exercise his/her right
The Consumer Protection Act grants various rights to the consumer, such as right to seek redressal, right to safety, right to be heard, right to choose, etc. But these rights can prove to be useful only when the consumer exercises these rights. In other words, a consumer must choose the product according to his/her taste and preferences, must file a complaint if the quality of the product is not satisfactory, and must be aware of his/her rights and exercise them when required.
2. A consumer must be cautious
It is the responsibility of the consumer not to blindly trust the words of the seller. He/she must first attain full information on the quantity, price, quality, standard, etc., of the product or service. By being cautious, the consumer can most of the time avoid exploitation or unfair practices.
3. A consumer must be quality-conscious
If the consumers stop compromising on the quality of products, then only the problems of adulterated products, duplicate products, and substandard products can be resolved. Therefore, while purchasing goods or services, a consumer must look for quality marks, like ISI marks, Agmark, etc.
Different marks indicating quality in different products are:
|
ISI
|
This mark is for consumer durable goods, electronic items, kitchen appliances, etc. |
 |
|
AGMARK
|
This mark is for agricultural commodities and live stock products. |
 |
BIS Mark (Hallmark)
|
This mark is for gold jewellery. |
 |
|
Woolmark
|
This mark signifies 100% pure wool. |
 |
|
ECO MARK
|
This mark is for environmental friendly products. |
 |
|
FPO Mark
|
This mark is for food products. |
 |
4. A consumer should file complaints for the redressal of genuine grievances
Usually, when a consumer receives a defective good or service, he/she tends to ignore the loss suffered. However, this attitude of the consumers of not filing a complaint encourages the businessmen to practise unfair trade practices to supply bad quality or defective goods and services. It is the responsibility of the consumer to file a complaint even when the loss is small. The awareness towards filing a complaint for any unfair practice will then make the seller conscious to supply good quality, non-defective goods and services. However, the consumers must complain with a genuine grievance and should not exaggerate the defect or loss of goods.
5. A consumer must insist on a cash memo
Consumers usually do not ask for a cash memo after making a purchase of goods and services, and the cash memo is compulsory as evidence of purchase while filing a complaint. A seller is bound to give a cash memo to the buyer even if he/she does not ask for it. However, a consumer must ask the seller for a cash memo to file a complaint and get compensation.
6. A consumer should not get carried away by advertisements
Advertisements of products or services tend to exaggerate their features and quality. While making a purchase for goods and services, a consumer must compare the actual use of that good with the use told or shown in the advertisement. And if there is any change in the actual use and described use or discrepancy, then the consumer must bring this to the notice of the sponsor of the advertisement, so they can stop the exaggerated qualities.
7. A consumer should use the products safely
Before using a product or service, a consumer has the responsibility to first read its user manual, learn about the risks associated with them, and use the goods safely.
8. A consumer must be honest
While making a deal with the seller, a consumer should be honest and not engage in any illegal trade, and should also discourage black marketing, hoarding, etc.
9. Save Environment
A consumer is also responsible for keeping the environment safe. He/she can do so by avoiding contributing to pollution, waste, and littering.
10. Form Consumer Organisation
Consumers should also form consumer organisations or societies to play an active role in the education and protection of their interests.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...