Construct a graph using N vertices whose shortest distance between K pair of vertices is 2
Last Updated :
18 Aug, 2021
Given two positive integers N and K, the task is to construct a simple and connected graph consisting of N vertices with the length of each edge as 1 unit, such that the shortest distance between exactly K pairs of vertices is 2. If it is not possible to construct the graph, then print -1. Otherwise, print the edges of the graph.
Examples:
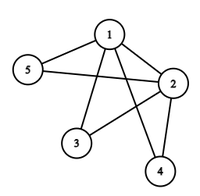
Input: N = 5, K = 3
Output: { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3}, { 1, 4 }, { 1, 5 }, { 2, 3 }, { 2, 4 }, { 2, 5 } }
Explanation:
The distance between the pairs of vertices { (3, 4), (4, 5), (3, 5) } is 2.
Input: N = 5, K = 8
Output: -1
Approach: Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Since the graph is simple and connected, Therefore, the maximum possible count of edges, say Max is ((N – 1) * (N – 2)) / 2.
- If K is greater than Max, then print -1.
- Initialize an array, say edges[], to store the edges of the graph.
- Otherwise, first connect all the vertices with 1 and store it in edges[], then connect all the pairs of vertices (i, j) such that i >= 2 and j > i and store it in edges[].
- Finally, print the first ((N – 1) + Max – K ) elements of edges[] array.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void constGraphWithCon(int N, int K)
{
int Max = ((N - 1) * (N - 2)) / 2;
if (K > Max) {
cout << -1 << endl;
return;
}
vector<pair<int, int> > ans;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= N; j++) {
ans.emplace_back(make_pair(i, j));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < (N - 1) + Max - K; i++) {
cout << ans[i].first << " "
<< ans[i].second << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
int N = 5, K = 3;
constGraphWithCon(N, K);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
void constGraphWithCon(int N, int K)
{
int Max = ((N - 1) * (N - 2)) / 2;
if (K > Max) {
printf("-1");
return;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= N; j++) {
printf("%d %d\n", i, j);
count++;
if (count == N * (N - 1) / 2 - K)
break;
}
if (count == N * (N - 1) / 2 - K)
break;
}
}
int main()
{
int N = 5, K = 3;
constGraphWithCon(N, K);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static void constGraphWithCon(int N, int K)
{
int Max = ((N - 1) * (N - 2)) / 2;
if (K > Max)
{
System.out.print(-1 + "\n");
return;
}
Vector<pair> ans = new Vector<>();
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j <= N; j++)
{
ans.add(new pair(i, j));
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < (N - 1) + Max - K; i++)
{
System.out.print(ans.get(i).first + " " +
ans.get(i).second +"\n");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 5, K = 3;
constGraphWithCon(N, K);
}
}
|
Python3
def constGraphWithCon(N, K):
Max = ((N - 1) * (N - 2)) // 2
if (K > Max):
print(-1)
return
ans = []
for i in range(1, N):
for j in range(i + 1, N + 1):
ans.append([i, j])
for i in range(0, (N - 1) + Max - K):
print(ans[i][0], ans[i][1], sep = " ")
if __name__ == '__main__':
N = 5
K = 3
constGraphWithCon(N, K)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG{
class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static void constGraphWithCon(int N, int K)
{
int Max = ((N - 1) * (N - 2)) / 2;
if (K > Max)
{
Console.Write(-1 + "\n");
return;
}
List<pair> ans = new List<pair>();
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
for(int j = i + 1; j <= N; j++)
{
ans.Add(new pair(i, j));
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < (N - 1) + Max - K; i++)
{
Console.Write(ans[i].first + " " +
ans[i].second +"\n");
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 5, K = 3;
constGraphWithCon(N, K);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class pair
{
constructor(first, second)
{
this[0] = first;
this[1] = second;
}
}
function constGraphWithCon(N, K)
{
var Max = ((N - 1) * (N - 2)) / 2;
if (K > Max)
{
document.write(-1 + "<br>");
return;
}
var ans = [];
for(var i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
for(var j = i + 1; j <= N; j++)
{
ans.push([i, j]);
}
}
for(var i = 0; i < (N - 1) + Max - K; i++)
{
document.write(ans[i][0] + " " +
ans[i][1] +"<br>");
}
}
var N = 5, K = 3;
constGraphWithCon(N, K);
</script>
|
Output:
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 5
2 3
2 4
2 5
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N2)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...