Law of Conservation of Mass: The law of conservation of mass states that the mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This implies, in a closed system the mass of the elements involved initially in a chemical reaction is equal to the mass of the product obtained by the reaction.
Hence, for any type of chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants and the products involved is conserved. This concept of mass conservation is widely used in chemistry and other fields like mechanics, dynamics, etc.
In this article, we will about the Law of Conservation of Mass, its Definition, Formula, Examples, and Solved Examples and FAQs.
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?
According to the law of conservation of mass, mass is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction. For example, when coal is burned, the carbon atom in it changes into carbon dioxide. The carbon atom changes from a solid to a gas, yet its mass remains constant.
Law of Conservation of Mass
The Law of Conservation of mass states that mass in an isolated system is neither created nor destroyed by chemical reactions or physical transformations.
The image discussed below shows that the mass of the reactant is always equal to the mass of the product and thus verifies the law of conservation of mass.
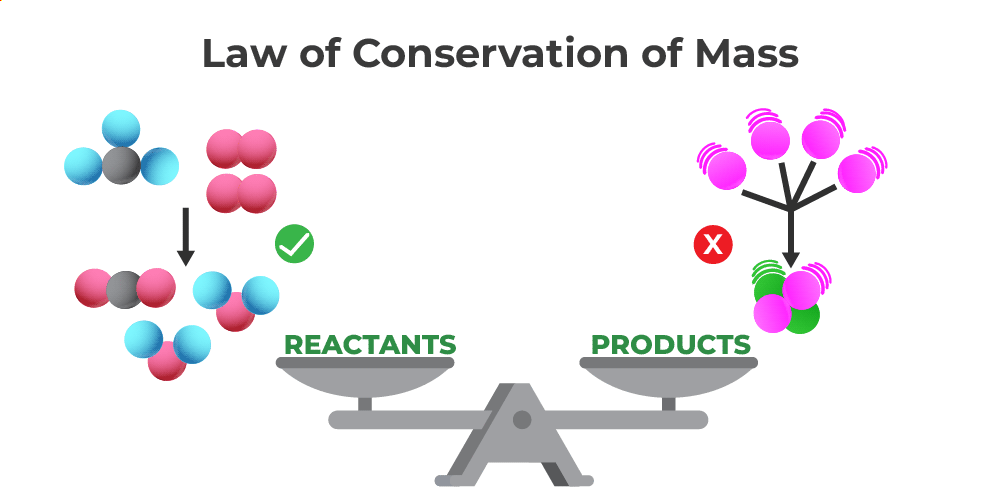
Law of Conservation of Mass
Similarly, according to the law of conservation of energy, energy cannot be created or destroyed.
A system that is isolated from its surroundings is one that does not interact with it. As a result, no matter what changes or chemical reactions occur in that isolated system, the mass will remain constant; even if the final state may differ from the initial state, there can be no more or less mass than before the change or reaction.
The understanding that substances do not actually disappear as a result of a reaction, despite what might appear to be the case, but rather change into another material of equal mass, was made possible by the law of conservation of mass, which was essential to the development of chemistry.
For example, kinetic energy is converted to potential energy when a toy vehicle is rolled down a ramp and collides with a wall.
In simple words, the law of conservation of mass can be stated as,
Mass of Reactants = Mass of Products
However, in fluid mechanics and continuum mechanics, the law of conservation of mass can be represented as follows using the differential form of the continuity equation:
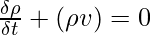
where,
ρ is the density,
t is the time,
v is the velocity, and
∇ is the divergence.
When Matter Undergoes a Physical Change
When the matter undergoes a physical change the law of conservation of the mass holds true. This can be understood with the help of the example given below.
Place a small amount of ice which is just frozen water in a flask. The flask is now being gently heated to melt the ice into the water after being appropriately weighted and overfilled.
Ice → (Heat) → Water

When the flask is weighed once more, it is clear that the weight has not changed because the ice’s mass has not changed as a result of the physical transformation.
When Matter Undergoes a Chemical Change
When the matter undergoes a chemical change the law of conservation of the mass holds true. This can be understood with the help of the example given below.
Take one mole of sodium hydroxide(NaOH) and one mole of hydrochloric acid(HCl) and allow them to react in a test tube, after the reaction, you will notice that one mole of Sodium chloride (NaCl) and one mole of water (H2O) is formed. which establishes the law of conservation of mass.

Examples on Law of Conservation of Mass
Various examples which confirm the Law of Conservation of Mass are,
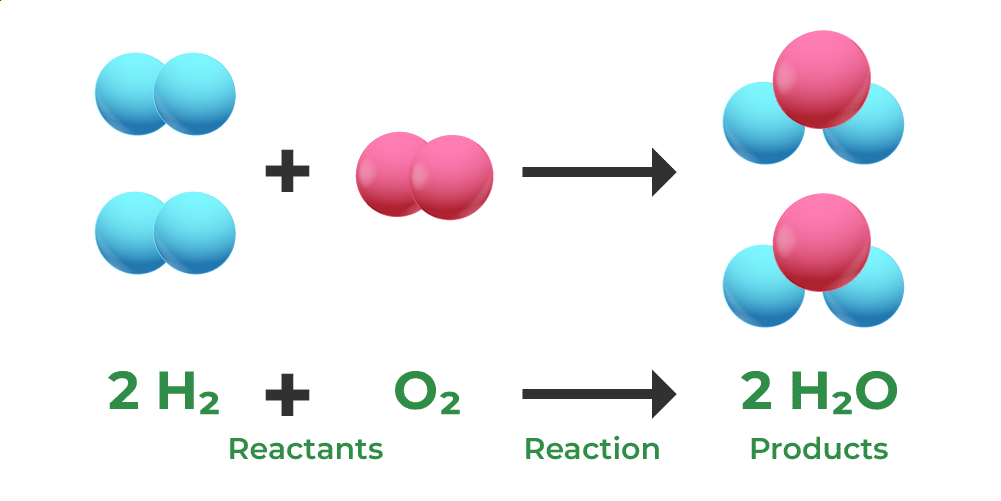
Formation of Water
Water is formed by the combination of Hydrogen and Oxygen. A water molecule is created when hydrogen and oxygen combine in a 2:1 ratio to generate two moles of the molecule. That is, One molecule of water, with the chemical formula H2O, has a molecular weight of 10. This is formed by the elements hydrogen having a molecular weight of 2 along with oxygen with a molecular weight equivalent to 8. Therefore, the mass is conserved.
Formation of Carbon Dioxide
Here we used 12 g of carbon and 32 g of oxygen as chemical compounds. After performing the reaction the amount of carbon –dioxide produced as the product will be 44g which is equivalent to the summation of the amount of carbon and oxygen used.
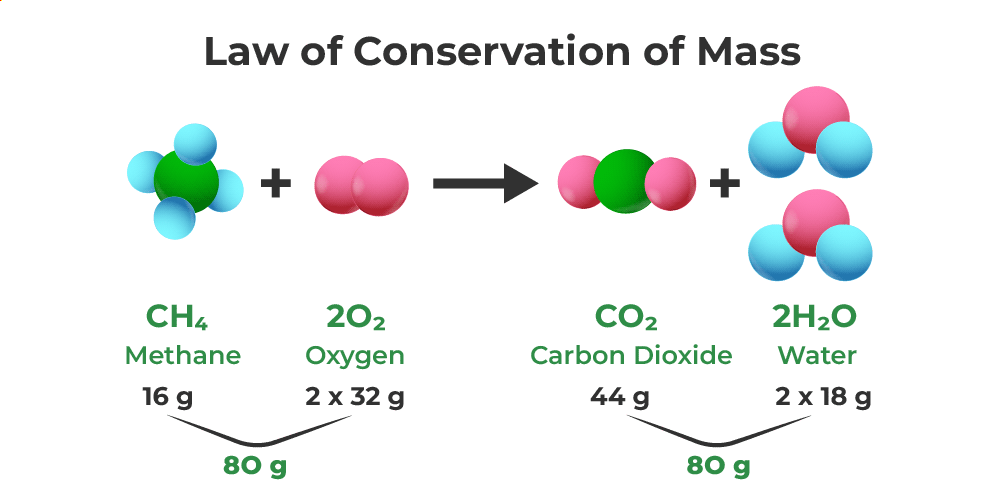
Limitation of Law of Conservation of Mass
A nuclear reaction produces an imbalance between the mass of the reactants and the mass of the products because some of the mass is transformed into energy.
Hence, the total mass is therefore not conserved.
People Also View:
Law of Conservation of Mass Class 9
For a class 9 level understanding, the Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental principle in science that tells us how mass behaves during chemical reactions. This law is very important in science, especially in chemistry. It helps chemists:
- Understand and predict the outcomes of chemical reactions.
- Balance chemical equations, ensuring that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
- Conserve resources in industrial processes by making sure no material is wasted.
Law of Conservation of Mass Examples
Example 1: If heating 12.0 grams of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) produces 6.4 g of carbon dioxide (CO2) and 5.6 g of calcium oxide (CaO), show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass.
Solution:
We know that,
Mass of the reactants = Mass of the products
12.0g of CaCO3 = 6.4g of CO2 + 5.6g of CaO
12.0g of reactant = 12.0g of products
Because the mass of the reactant is equal to the mass of the products, the observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass.
Example 2: Sodium carbonate reacts with ethanoic acid to form sodium ethanoate, carbon dioxide, and water. In an experiment, 5.3g of Sodium carbonate reacted with 6g of ethanoic acid to form 8.2g of sodium ethanoate, 2.2g of carbon dioxide, and 0.9g of water. Show that this data verifies the law of conservation of mass.
Solution:
We know,
Sodium Carbonate + Ethanoic Acid = Sodium Ethanoate + Carbon Dioxide + Water.
Substituting the masses of the compounds we have,
5.3g + 6g = 8.2g + 2.2g + 0.9g = 11.3g
Hence, the conservation of mass is verified.
Example 3: What happens when 4.2 g of KClO3 is heated to give 1.92 g of Oxygen and 2.96 g of KCl as the product? How this reaction follows the Law of Conservation of Mass?
Answer:
The reaction for the given case is given as,
KClO3 ⇢ KCl + 3/2 O2
Here, the total mass involved from the reactant side is equal to 4.2 g.
And the total mass involved from the product side is equal to 1.92 g + 2.96 g = 4.98 g.
Hence, the mass of the reactant < mass of the products involved in the reaction.
Thus, the given case doesn’t follow Law of Conservation of Mass.
Summary – Law of Conservation of Mass
The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, articulating that mass cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system during chemical or physical transformations. Essentially, it means that the total mass before and after a reaction remains unchanged. This principle was pivotal in advancing chemistry, revealing that substances transform rather than vanish. The law applies to both physical changes, like ice melting into water without mass alteration, and chemical changes, such as the reaction between sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid to produce sodium chloride and water, where the mass of the products equals the mass of the reactants. It’s symbolized in equations as the mass of reactants equaling the mass of products. However, it’s noted that during nuclear reactions, this law does not hold because mass can be converted into energy, demonstrating a limitation of the law in certain scenarios.
FAQs on Law of Conservation of Mass
State the Law of Conservation of Mass.
According to the law of conservation of mass, mass is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction. For example, when coal is burned, the carbon atom in it changes into carbon dioxide. The carbon atom changes from a solid to a gas, yet its mass remains constant.
Who gave the Law of Conservation of Mass?
The Law of Conservation of Mass was given by the French chemist Antoine Lavoisier in 1789.
Why is there no change in mass during chemical reactions?
Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed. Hence atoms in a chemical reaction only change their bond and position while transforming from reactant to product and hence the total mass of the chemical reaction is conserved and there is no change in mass during the chemical reaction.
What are some real-life examples of the law of conservation of mass?
Some real-life examples of the law of conservation of mass are:
- Bonfire or Campfire – In a bonfire or a campfire the mass of the wood burned in the presence of air is equal to the mass of the ashes left, the carbon dioxide released, and water vapor obtained.
- Melted Ice – When a piece of ice is melted, then the liquid or water obtained through it weight equals.
Is law of conservation of mass and matter the same?
Yes, the Law of Conservation of Mass and the Law of Conservation of Matter essentially refer to the same scientific principle, although the terms “mass” and “matter” have slightly different meanings.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...