Concatenating CSV files using Pandas module
Last Updated :
02 Dec, 2020
Using pandas we can perform various operations on CSV files such as appending, updating, concatenating, etc. In this article, we are going to concatenate two CSV files using pandas module.
Suppose we have one .csv file named Employee.csv which contains some records and it is as below:

Employee.csv
There is another .csv file named Updated.csv which contains new records as well as few records from Employee.csv file but with updated information. The file is given below:

Updated.csv
We can see that the first five records in Updated.csv are new and the rest have updated information. For instance, the salaries of Louis and Diane are changed, email_id of Joe is different and so on.
The aim of this article is to add new records and update the information of existing records from Updated.csv file into Employee.csv.
Note: No two employees can have same emp_id.
Approach: Whenever it comes down to manipulate data using python we make use of Dataframes. The below approach has been used.
- Read Employee.csv and create a dataframe, say, employee_df..
- Similarly, read Updated.csv and from a dataframe, say, updated_df.
- Concatenate updated_df to employee_df and remove duplicates using emp_id as primary key.
- Create a new .csv file named Updated_Employees.csv containing all the old, new as well as updated records.
Example 1:
Python3
import pandas as pd
employee_df = pd.read_csv('Employee.csv')
print(employee_df)
updated_df = pd.read_csv('Updated.csv')
print(updated_df)
final_dataframe = pd.concat([employee_df, updated_df]).drop_duplicates(
subset='emp_id', keep='last').reset_index(drop=True)
print(final_dataframe)
final_dataframe.to_csv(
'Updated_Employees.csv', index=False)
|
Output:

employee_df

updated_df

final_dataframe
Below is the image of Updated_Employee.csv has been provided.

Updated_Employees.csv
Example:
Below are the two CSV files which are going to be concatenated:

gfg3.csv

gfg2.csv
Now executing the below program to concatenate the above CSV files.
Python3
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.read_csv('gfg1.csv')
print('\ngfg1.csv:\n', df1)
df2 = pd.read_csv('gfg2.csv')
print('\ngfg2.csv:\n', df2)
final_df = pd.concat([df1, df2]).drop_duplicates(
subset='ORGANIZATION').reset_index(drop=True)
print('\ngfg3.csv:\n', final_df)
final_df.to_csv(
'gfg3.csv', index=False)
|
Output:
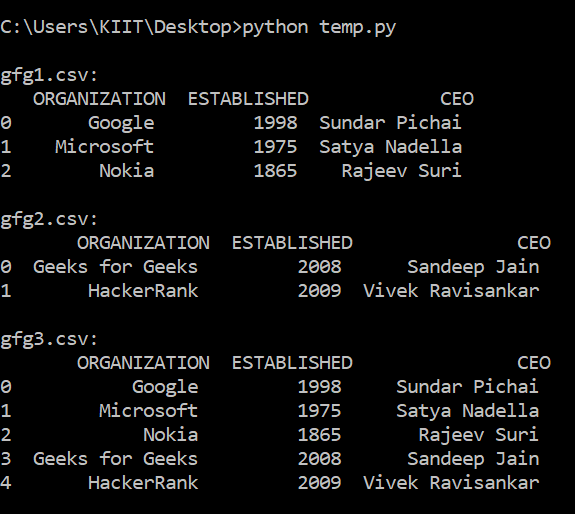
Below is the image of gfg3.csv:

gfg3.csv
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...