Computer Forensics Techniques
Last Updated :
24 Feb, 2022
Prerequisite: Introduction of Computer Forensics
In the early 80s PCs became more popular and easily accessible to the general population, this also led to the increased use of computers in all fields and criminal activities were no exception to this. The word “forensics” means the use of science and technology to investigate and establish facts in criminal or civil courts of law. Forensics is the process of using scientific knowledge for analyzing and presenting evidence to the court.
Computer forensics is a branch of digital forensic science concerned with evidence found in computers and digital storage media, it is defined as the discipline that combines elements of law and computer science to collect and analyze data from wireless communications, computer systems, networks, and storage devices in a way that is permissible as evidence by the court. Because computer forensics is a new discipline, there are not many standard rules or practices for it, there is little standardization and consistency across the industry and courts.
Types of Computer Forensics:
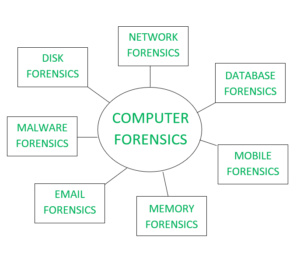
There are multiple types of computer forensics depending on the field in which digital investigation is needed. The fields are:
- Network forensics
- Email forensics
- Malware forensics
- Memory forensics
- Mobile Phone forensics
- Database forensics
- Disk forensics
For more detail please refer Cyber Forensics article.
Techniques used in Computer Forensic:
Computer forensics investigation normally follows the typical digital forensics procedure which is the acquisition, examination, analysis, and reporting. These investigations are mostly performed on static data (disk images) rather than live data or live systems, though in early computer forensics days the investigators used to work on live data due to the lack of tools.
Various kinds of techniques are used in computer forensics investigation such as:
- Cross-drive analysis: Cross-drive analysis (CDA) is a technique that allows an investigator to quickly identify and correlate information from multiple data sources or information across multiple drives. Existing approaches include multi-drive correlation using text searches, e.g., email addresses, SSNs, message IDs, or credit card numbers.
- Live analysis: It is used to examine the computers from within the OS using various forensics and sysadmin tools to get the information from the device. In forensic analysis, the collection of volatile data is very important like the installed software packages, hardware information, etc. this approach is useful in the case where the investigator is dealing with encrypted files. If the device is still active and running when it’s handed to the investigator, the investigator should collect all the volatile information from the device such as user login history, which TCP and UDP ports are open, what services are currently in use, and running, etc.
- Deleted files recovery: It is a technique that is used to recover deleted files. The deleted data can be recovered or craved out using forensic tools such as CrashPlan, OnTrack EasyRecovery, Wise Data Recovery, etc.
- Stochastic forensics: It is a method to forensically re-establish the digital activities that have insufficient digital artifacts, thus analyzing emerging patterns resulting from the stochastic nature of modern-day computers.
- Steganography: Steganography is a technique of hiding the secret information inside or on top of something, that something can be anything from an image to any type o file. Computer forensics investigators can counter this by looking and comparing the hash value of the altered file and original file, the hash value will be different for both files even though they might appear identical on visual inspection.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...