Comparison between Height Balanced Tree and Weight Balanced Tree
Last Updated :
27 Dec, 2021
What is Height Balanced Tree?
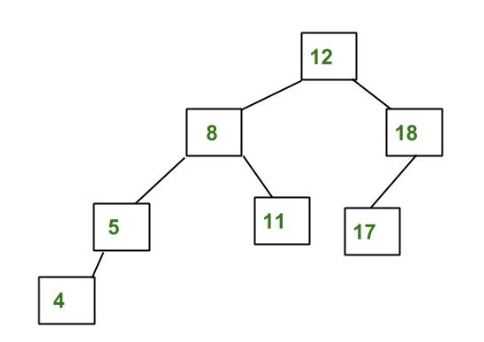
Self-Balancing binary search trees are the height-balanced binary tree is one for which at every node, the absolute value of the difference in heights of the left and right subtree is no larger than one. An empty tree is height-balanced. A non-empty binary tree T is balanced if:
- The left subtree of T is balanced.
- The right subtree of T is balanced.
- The difference between the heights of the left subtree and the right subtree is not more than 1.
Note:
Every complete binary tree is height-balanced.
Example:
Red Black Tree, Splay Tree, and an AVL Tree is height-balanced binary search tree.
What is Weight Balanced Binary Tree?
A weight-balanced tree is a binary tree in which for each node the number of nodes in the left subtree is at least half and at most twice the number of nodes in the right subtree. It is a binary tree that is balanced based on the knowledge of the probabilities of searching for each individual node. In each sub-tree, the node with the highest weight appears at the root thereby resulting in more efficient searching performance. The nodes which are most likely to be searched/accessed have the lowest search time.
Example:
Huffman Tree.

In the above diagram, the letters represent the node values and the numbers represent node weights.
Why different definitions of balanced
Binary Search Tree (BST) was invented to make searching a more efficient process, than searching in an unordered array. However, when the BST is unbalanced then that case searching was inefficient. For efficient searching, it is advisable to keep the tree balanced. But it is difficult and inefficient to keep a BST balanced as the values are added and deleted frequently. Thus, a way was invented to keep the BST balanced by adding more information to each node or by allowing a node to have more than two children. Some of the examples of such invented trees were AVL Tree, 2-3 Tree, B-Tree, Red-Black Tree, etc.
Comparison of Height Balanced and Weight Balanced Tree
A height-balanced tree improves the worst-case lookup time (for a binary tree, it will always be bounded by log2(n)), at the expense of making the typical case roughly one lookup less (approximately half of the nodes will be at the maximum depth).
If your weight is related to frequency-of-lookup, a weight-balanced tree will improve the average lookup time, at the expense of making the worst-case higher (more frequently requested items have a higher weight, and will thus tend to be in shallower trees, with the cost being deeper trees for less-frequently-requested items).
| S No. |
Height Balanced Tree |
Weight Balanced Tree |
| 1 |
It is the binary tree that is balanced based on the height of the subtrees. |
It is the binary tree that is balanced based on the weight on the edges of the tree. |
| 2 |
In a height-balanced tree, the absolute difference of height of the left subtree and the right subtree should be minimum. |
In weight balanced tree, the absolute difference between the weight of the left subtree and the right subtree should be minimum. |
| 3 |
It will improve the worst-case lookup time at the expense of making a typical case roughly one lookup less |
It will improve the average lookup time at the expense of making the worst-case higher. |
| 4 |
The restructuring operation on a node with n descendants happens every 2-O(lg n) operation. |
The restructuring operation on a node with n descendants happens every O(1/n) operation. |
Which one is best?
The best way to determine which is the best binary search tree out of the two is to measure the performance of the two trees. This can be done in the following steps:
- Gather representative query traffic.
- Build a test rig where one can count the tree operations.
- Replay the canned queries against both a height-balanced and a weight-balanced tree.
As a general rule, a height-balanced tree would work better the more even the request frequencies are across the data set, and the more skewed it is, the more advantage one can get from a weight-balanced tree.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...