Commercial Paper : Features and Types
Last Updated :
19 Jan, 2024
What is Commercial Paper?
A Commercial Paper (CP) is a short-period 90 to 364 day, unsecured promissory note that is issued by a company to raise funds (usually for the inventories, finance, and temporary liabilities). It is issued by one organization (Primary Dealers (PD) and All-India Financial Institutions (FIs) in India) to another organisation, insurance businesses, pension funds, and banks. The money raised by commercial paper is often huge. Due to the fact that this loan is entirely unsecured, the CP may only be issued by companies with a solid credit rating.

The Reserve Bank of India controls the issuance of Commercial Paper. The RBI first issued commercial paper to the Indian money market on March 27, 1989. Based on the points given below, commercial Paper was first recommended by the Vaghul Working Group:
- The registration of commercial papers should only be permitted for companies with a net worth of at least ₹5 cores and an excellent dividend payment record.
- The CAS discipline ought to be adopted by the market. The total quantum that can be upgraded in a year, the paper amount, and market access should all be managed by the RBI.
- Other than the smallest note size, there are no restrictions on the market for commercial paper. However, the amount of one issue and each lot cannot be less than ₹1 crore and ₹5 lakhs, respectively.
- The net worth of the company using commercial paper should be at least ₹5 crores, a maximum debt ratio of 105, a debt serving ratio of around 2, and a minimum current ratio of 1033. Besides, it should also be recorded on the stock exchange.
- The commercial paper can be made at a discounted rate to the face value or in interest terms.
Features of Commercial Paper
- Commercial paper is a short-term money market asset that consists of a promissory note with a pre-determined maturity.
- It is a certificate that represents an unsecured business loan with a short maturity date.
- It is possible to issue commercial paper in interest-bearing form, although it is often issued at a discount rate to face value.
- The issuer promises to pay the buyer a defined sum at some point in the future but pledges no assets to support that commitment, just his liquidity and established earning potential.
- A company can issue commercial paper directly to investors or via banks or merchant banks. Commercial paper cannot be converted into stock in the issuing firm since it is non-convertible.
- As it is not backed by collateral, it is classified as unsecured debt. Investors make investments based on the company’s financial strength and capacity to generate revenue.
Types of Commercial Paper
- Draft: There are three persons involved in this type of commercial paper: the drawer, the drawee, and the payee. A draft is a written order from one person the drawer to another person the drawee to pay the specified amount of money to a third party the payee.
- Note: Promissory Notes is the most popular type of commercial paper. The maker and the payee are the two parties involved in this transaction. The issuer or entity drawing the Commercial Paper as written confirmation of paying the specified amount to the payee upon maturity is known as the maker.
- Cheque: Compared to typical Commercial Papers, this is a different kind of instrument with a separate set of rules and restrictions. A cheque is a particular kind of draft and in this case, the bank is the drawee.
- Certificate of Deposit: A bank will issue this type of commercial paper and by doing so, it will accept the deposit made by the depositor. This instrument is a special kind of promissory note and carries all the information about the deposit, including the interest rate, maturity date, and maturity amount.
- Secured Commercial Papers: These commercial papers are assured by other financial assets and are also known as Asset-Backed Commercial Papers (ABCP).
- Unsecured Commercial Papers: These are the traditional commercial papers that are allotted without any security.
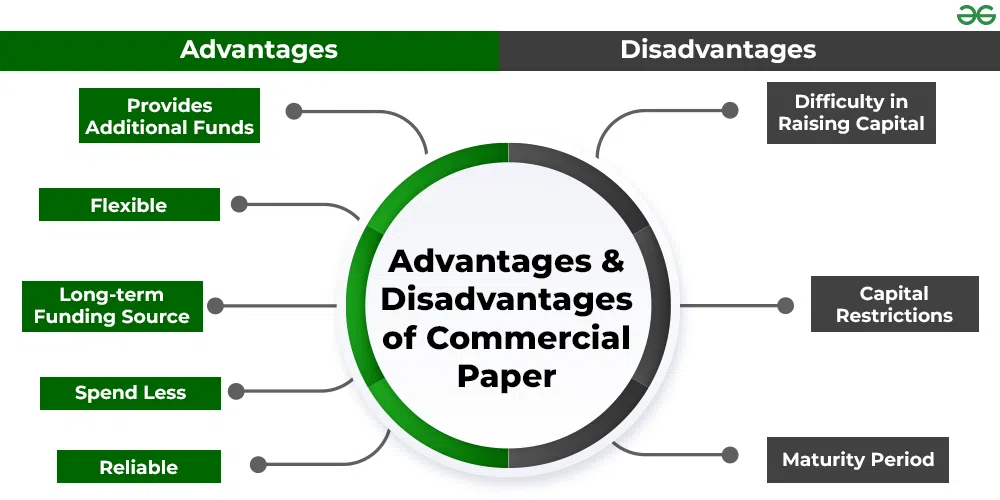
Advantages and Disadvantages of Commercial Paper: The advantages of commercial paper include flexibility, reliability, additional funds, etc., and its disadvantages include capital restriction, maturity period, etc.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...