COBOL – Basic Syntax
Last Updated :
04 Mar, 2022
Cobol is a high-level language, which has its own compiler. The COBOL compiler translates the COBOL program into an object program, which is finally executed. A Syntax refers to the rules and regulations for writing any statement in a programming language. It is related to the grammar and structure of the language.
Program Syntax Rules of COBOL:
- COBOL syntax is very easy.
- These are not case-sensitive.
- A COBOL consists of more than 300 reserved words.
- It lacks a big-size standard library, as it has only 43 statements, 87 functions, and just one class.
COBOL Character Set:
Cobol is based on an EBCDIC character set which has the following:
- English alphabets (both lowercase and uppercase).
- Number 0-9.
- Few special characters. E.g Space, comma, $,quote, etc.
COBOL Coding Sheet:
The below table describes the code layout, for writing working executable COBOL code.
Columns Number with a record length of 80 bytes:
| S.No |
Column specification |
Short Description |
Description |
| 1. |
1-6 |
Sequence Number |
it is used to identify each line of the source program, can contain any character in the system character set |
| 2. |
7 |
Reserved for special character |
it is an indicator area used for specifying.
- * ⇒ Comment
- – ⇒ Continuation
- / ⇒ Form Feed
|
| 3. |
8-11 |
Area A |
Cobol divisions, sections, paragraphs being written in columns 8-11 |
| 4. |
12-72 |
Area B |
Space for Writing Cobol Statements |
| 5. |
73-80 |
System generated Number |
For programmer use |
Let’s take an example and understand how to COBOL syntax and program works:
Example:
Cobol
IDENTIFICATION DIVISION.
PROGRAM-ID. YOUR-PROGRAM-NAME.
DATA DIVISION.
FILE SECTION.
WORKING-STORAGE SECTION.
01 NUM1 PIC 9(4) VALUE 1458.
01 MESSAGE PIC X(11) VALUE 'HELLO WORLD'.
PROCEDURE DIVISION.
MAIN-PROCEDURE.
**********This is a comment in Cobol***************
DISPLAY NUM1.
DISPLAY MESSAGE.
STOP RUN.
END PROGRAM YOUR-PROGRAM-NAME.
|
Output:
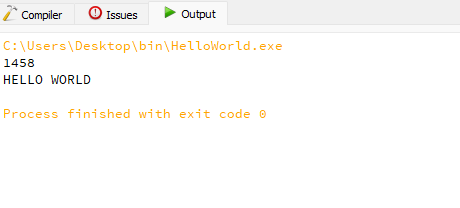
COBOL Code Explanation:
- In the COBOL program(YOUR-PROGRAM-NAME) NUM1 is a Numeric literal with a predefined default value of 1458.
- MESSAGE is an Alphanumeric literal with the predefined value of ‘HELLO WORLD’.
- DISPLAY keyword is used to print the Default value for both the Variables(NUM1, MESSAGE) used inside the program.
- There are 4 divisions inside every Cobol program.
- To compile a COBOL program through JCL we a have popularly used utility known as IGYWCL. Refer to JCL for compiling the COBOL.
- After the code is compiled it creates a Load Module. A Load Module is the non-human readable file, a low-level machine-readable file.
- To execute the Program in a mainframe environment we have to give the Program ID in the above example, YOUR-PROGRAM-NAME is the program-id and path of load library. Refer to RUN JCL.
JCL for compiling the COBOL:
//JOBNAME JOB ACCTNO,NAME,MSGCLASS=1
//S001 EXEC IGYWCL
//COBOL.SYSIN DD DSN = LOCATION_OF_CODE,DISP= SHR
//COBOL.SYSLIB DD DSN = COPYBOOK_LOCATION,DISP = SHR
//LKED.SYSMOD DD DSN = LOADLIB_PATH(YOUR-PROGRAM-NAME),DISP=SHR
RUN JCL – For running program:
//JOBNAME JOB ACCTNO,NAME,MSGCLASS=1
//* JCL TO RUN COBOL PROGRAM*
//STEP01 EXEC PGM= YOUR-PROGRAM-NAME
//STPLIB DD DSN = LOADLIB_PATH,DISP=SHR
//SYSOUT DD SYSOUT = *
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...