Cloud Stakeholders as per NIST
Last Updated :
03 Apr, 2024
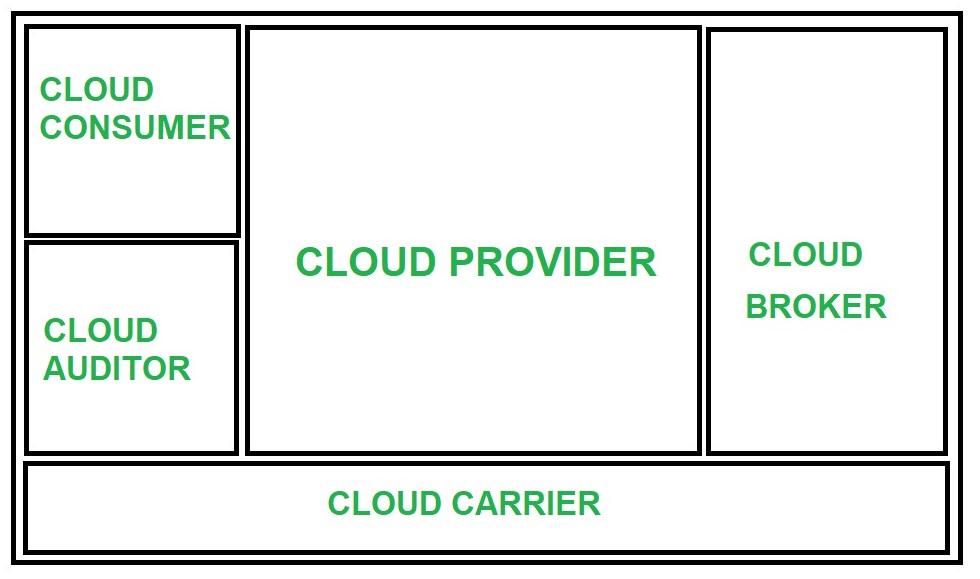
NIST Cloud Computing reference architecture defines five major performers:
- Cloud Provider
- Cloud Carrier
- Cloud Broker
- Cloud Auditor
- Cloud Consumer
Each performer is an object (a person or an organization) that contributes to a transaction or method and/or performs tasks in Cloud computing. There are five major actors defined in the NIST cloud computing reference architecture, which are described below:
1. Cloud Service Providers: A group or object that delivers cloud services to cloud consumers or end-users. It offers various components of cloud computing. Cloud computing consumers purchase a growing variety of cloud services from cloud service providers. There are various categories of cloud-based services mentioned below:
- IaaS Providers: In this model, the cloud service providers offer infrastructure components that would exist in an on-premises data center. These components consist of servers, networking, and storage as well as the virtualization layer.
- SaaS Providers: In Software as a Service (SaaS), vendors provide a wide sequence of business technologies, such as Human resources management (HRM) software, customer relationship management (CRM) software, all of which the SaaS vendor hosts and provides services through the internet.
- PaaS Providers: In Platform as a Service (PaaS), vendors offer cloud infrastructure and services that can access to perform many functions. In PaaS, services and products are mostly utilized in software development. PaaS providers offer more services than IaaS providers. PaaS providers provide operating system and middleware along with application stack, to the underlying infrastructure.
2. Cloud Carrier: The mediator who provides offers connectivity and transport of cloud services within cloud service providers and cloud consumers. It allows access to the services of the cloud through Internet networks, telecommunication, and other access devices. Network and telecom carriers or a transport agent can provide distribution. A consistent level of services is provided when cloud providers set up Service Level Agreements (SLA) with a cloud carrier. In general, Carrier may be required to offer dedicated and encrypted connections.
3. Cloud Broker: An organization or a unit that manages the performance, use, and delivery of cloud services by enhancing specific capability and offers value-added services to cloud consumers. It combines and integrates various services into one or more new services. They provide service arbitrage which allows flexibility and opportunistic choices. There are major three services offered by a cloud broker:
- Service Intermediation.
- Service Aggregation.
- Service Arbitrage.
4. Cloud Auditor: An entity that can conduct independent assessment of cloud services, security, performance, and information system operations of the cloud implementations. The services that are provided by Cloud Service Providers (CSP) can be evaluated by service auditors in terms of privacy impact, security control, and performance, etc. Cloud Auditor can make an assessment of the security controls in the information system to determine the extent to which the controls are implemented correctly, operating as planned and constructing the desired outcome with respect to meeting the security necessities for the system. There are three major roles of Cloud Auditor which are mentioned below:
- Security Audit.
- Privacy Impact Audit.
- Performance Audit.
5. Cloud Consumer: A cloud consumer is the end-user who browses or utilizes the services provided by Cloud Service Providers (CSP), sets up service contracts with the cloud provider. The cloud consumer pays per use of the service provisioned. Measured services utilized by the consumer. In this, a set of organizations having mutual regulatory constraints performs a security and risk assessment for each use case of Cloud migrations and deployments.
Cloud consumers use Service-Level Agreement (SLAs) to specify the technical performance requirements to be fulfilled by a cloud provider. SLAs can cover terms concerning the quality of service, security, and remedies for performance failures. A cloud provider may also list in the SLAs a set of limitations or boundaries, and obligations that cloud consumers must accept. In a mature market environment, a cloud consumer can freely pick a cloud provider with better pricing and more favourable terms. Typically, a cloud provider’s public pricing policy and SLAs are non-negotiable, although a cloud consumer who assumes to have substantial usage might be able to negotiate for better contracts.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...