Classification of Mobile Communication
Last Updated :
24 Jan, 2022
The Era of technology has revolutionized communication with the introduction of mobile and wireless communication. Mobile communication system may be defined as a communication system that allows people to communicate without utilizing any physical link, disregarding, location, time, and distance. The idea of wireless communication was set forth by Marconi in 1985 with the invention of Wireless Telegraph.
Classification of Mobile Communication :
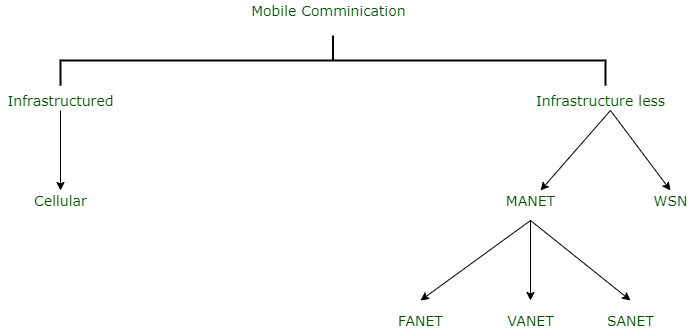
1. Infrastructured Mobile Communication :
In this type of communication, service provider needs to lay out the infrastructure to establish a network for communication, hence network is dependent upon infrastructure.
Example :
Cellular Communication :
Cellular communication is categorized as infrastructured as it involves use of Base trans-receiver System (BTS) for communication. The BTS uses two categories of antenna to make communication, viz :
- Vertical Antenna :
It is also known as RF antenna or GSM antenna. It works on radio frequency i.e in MHz and is responsible for sending and receiving signals.
- Drum Antenna :
It is also known as microwave antenna. It is responsible for creating connecting link between BTS. It works on Microwaves, having a frequency in GHz.
2. Infrastructure-less Mobile Communication :
This category of communication has eliminated the need of infrastructure for communication, hence making mobile communication cost-effective, BTS independent and more efficient. It is categorized as :
- Mobile Adhoc Network (MANET) :
Mobile Adhoc network is an improvised network which is established when need arises. Once the job is done, the network is terminated. MANET is used in military organisation for communication purpose during war like emergency. There are several fields in MANET which are under research.
MANET is used in various fields and is categorized into following types :
- (i) FANET :
FANET stands for Flying Adhoc Network. It is used in multi Unmanned Air Vehicles (UAV) systems to solve the problems arising from infrastructure-based communication systems, which restricts the capabilities of multi UAV systems. Using FANET, a cluster of UAVs is connected over adhoc network, forming a team and increasing capability of UAVs in various fields.
- (ii) VANET :
VANET stands for Vehicular Adhoc Network. It is another subset of MANET employed in vehicles in order to enable inter-vehicular communication. VANET provides assistance with traffic monitoring, collision avoidance, safety enhancement etc, however this field is still in research and has not been implemented completely.
- (iii) SANET :
SANET stands for Smartphone Adhoc Network. In this, adhoc networking is used between smartphones for cellular communication, eliminating use of BTS.
- Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) :
Wireless Sensor Network is an infrastructure-less network that employs sensing devices i.e. sensors to analyze and collect data and transmit it to remote servers. These sensors are smart, small in size and cost-effective, and are linked wirelessly for hassle free and remote communication. WSN is mostly used in remote environment monitoring systems wherein sensors analyze and record the physical and chemical factors of environment including temperature, pressure, pollutants, sound etc and transmit the data to a prime centralized location. It is also used in tracking targets. Another use of WSN is in tracking the amount of pollutants in water bodies.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...