Class 12 RD Sharma Solutions – Chapter 22 Differential Equations – Exercise 22.5 | Set 1
Last Updated :
21 Feb, 2021
Solve the following differential equations:
Question 1. (dy/dx) = x2 + x – (1/x)
Solution:
We have,
(dy/dx) = x2 + x – (1/x)
dy = [x2 + x – (1/x)]dx
On integrating both sides, we get
∫(dy) = ∫[x2 + x – (1/x)]dx
y = (x3/3) + (x2/2) – log(x) + c -(Here, ‘c’ is integration constant)
Question 2. (dy/dx) = x5 + x2 – (2/x)
Solution:
We have,
(dy/dx) = x5 + x2 – (2/x)
On integrating both sides, we get
∫(dy) = ∫[x5 + x2 – (2/x)]dx
y = (x6/6) + (x3/3) – 2log(x) + c -(Here, ‘c’ is integration constant)
Question 3. (dy/dx) + 2x = e3x
Solution:
We have,
(dy/dx) + 2x = e3x
(dy/dx) = -2x + e3x
dy = [-2x + e3x]dx
On integrating both sides, we get
∫dy = ∫[-2x + e3x]dx
y = (-2x2/2) + (e3x/3) + c
y = (-x2) + (e3x/3) + c -(Here, ‘c’ is integration constant)
Question 4. (x2 + 1)(dy/dx) = 1
Solution:
We have,
(x2 + 1)(dy/dx) = 1
dy = (1/x2 + 1)dx
On integrating both sides, we get
∫dy = ∫(dx/x2 + 1)
y = tan-1x + c -(Here, ‘c’ is integration constant)
Question 5. (dy/dx) = (1 – cosx)/(1 + cosx)
Solution:
We have,
(dy/dx) = (1 – cosx)/(1 + cosx)
(dy/dx) = (2sin2x/2)/(2cos2x/2)
dy/dx = tan2(x/2)
dy/dx = [sec2(x/2) – 1]
On integrating both sides, we get
∫dy = ∫[sec2(x/2) – 1]dx
y = [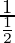 tan(x/2)] – x + c
tan(x/2)] – x + c
y = 2tan(x/2) – x + c -(Here, ‘c’ is integration constant)
Question 6. (x + 2)(dy/dx) = x2 + 3x + 7
Solution:
We have,
(x + 2)(dy/dx) = x2 + 3x + 7
(dy/dx) = (x2 + 3x + 7)/(x + 2)
(dy/dx) = (x2 + 3x + 2 + 5)/(x + 2)
(dy/dx) = [(x + 1)(x + 2) + 5]/(x + 2)
(dy/dx) = (x + 1) + 5/(x + 2)
dy = (x + 1)dx + 5dx/(x + 2)
On integrating both sides, we get
∫dy = ∫(x + 1)dx + 5∫dx/(x + 2)
y = x2/2 + x + 5log(x + 2) + c -(Here, ‘c’ is integration constant)
Question 7. (dy/dx) = tan-1x
Solution:
We have,
(dy/dx) = tan-1x
dy = tan-1xdx
On integrating both sides, we get
∫dy = ∫tan-1xdx
y = ∫1 × tan-1xdx
y = tan-1x∫1dx – ∫[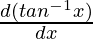 ∫1dx]dx
∫1dx]dx
y = xtan-1x – ∫\frac{x}{(1 + x2)}dx
y = xtan-1x – 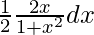
y = xtan-1x – (1/2)log(1 + x2) + c -(Here, ‘c’ is integration constant)
Question 8. (dy/dx) = logx
Solution:
We have,
(dy/dx) = logx
dy = logxdx
On integrating both sides, we get
∫dy = logx∫1dx – ∫[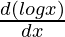 ∫1dx]dx
∫1dx]dx
y = xlogx – ∫[x/x]dx
y = xlogx – ∫dx
y = xlogx – x + c
y = x(logx – 1) + c -(Here, ‘c’ is integration constant)
Question 9. (1/x)(dy/dx) = tan-1x
Solution:
We have,
(1/x)(dy/dx) = tan-1x
dy = xtan-1x dx
On integrating both sides, we get
∫dy = ∫xtan-1x dx
y = tan-1x∫xdx – ∫[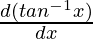 ∫xdx]dx
∫xdx]dx
y = (x2/2)tan-1x – 
y = (x2/2)tan-1x – (1/2)∫1- \frac{1}{(1 + x^2)}dx
y = (x2/2)tan-1x – (x/2) + (1/2)tan-1x + c
y = (1/2)(x2 + 1)tan-1x – (x/2) + c -(Here, ‘c’ is integration constant)
Question 10. (dy/dx) = cos3xsin2x + x√(2x + 1)
Solution:
We have,
(dy/dx) = cos3xsin2x + x√(2x + 1)
(dy/dx) = cosxcos2xsin2x + x√(2x + 1)
y = I1 + I2
I1 = cosxcos2xsin2xdx
On integrating both sides, we get
= ∫(1 – sin2x)sin2xcosxdx
Let, sinx = z
On differentiating both sides
cosxdx = dz
= ∫(1 – z2)z2dz
= z3/3 – z5/5 + c1
= sin3x/3 – sin5x/5 + c1
I2 = x√(2x + 1)dx
Let, (2x + 1) = u2
On differentiating both sides
2dx = 2udu
dx = udu
= [(u2 – 1)/2]u × udu
I2 = (1/2)(u4-u2)du
On integrating both sides, we get
= (1/2)[u5/5 – u3/3] + c2
= 1/10(2x + 1)5/2 – 1/6(2x + 1)3/2 + c2
y = I1 + I2
y = (sin3x/3) – (sin5x/5) + 1/10(2x + 1)5/2 – 1/6(2x + 1)3/2 + c
Question 11. (sinx + cosx)dy + (cosx – sinx)dx = 0
Solution:
We have,
(sinx + cosx)dy + (cosx – sinx)dx = 0
(dy/dx) = -[(cosx – sinx)/(sinx + cosx)]
Let, (sinx + cosx) = z
On differentiating both sides
(sinx + cosx)dx = dz
dy = (dz/z)
On integrating both sides, we get
∫dy = ∫(dz/z)
y = logz + c
y = log(sinx + cosx) + c
Question12. (dy/dx) – xsin2x = 1/(xlogx)
Solution:
We have,
(dy/dx) – xsin2x = 1/(xlogx)
dy = xsin2xdx + 1/(xlogx)dx
On integrating both sides, we get
y = ∫xsin2xdx + ∫dx/(xlogx)
y = I1 + I2
I1 = (1/2)(2sin2x)xdx
= (1/2)[(1 – cos2x)xdx]
= (1/2)(xdx – xcos2x)dx
On integrating both sides, we get
= 1/2[∫xdx – ∫xcos2x dx]
= 1/2(x2/2) – 1/2[x∫cos2x dx – ∫(1∫cos2x dx)]dx
= 1/2(x2/2) – (x/4)sin2x + ∫(1/4sin2x)dx
= 1/2(x2/2) – (x/4)sin2x + ((1/8)cos2x) + c1
I2 = 1/(xlogx)dx
Let, logx = z
On differentiating both sides, we get
(dx/x) = dz
= (dz/z)
= logz
= log(logx) + c2
y = I1 + I2
y = (x2/4) – (xsin2x/4) + (cos2x/8) + log(logx) + c
Question 13. (dy/dx) = x5tan-1(x3)
Solution:
We have,
(dy/dx) = x5tan-1(x3)
Let, x3 = z
On differentiating both sides, we get
3x2dx = dz
x2dx = dz/3
dy = (1/3)[ztan-1z]dz
On integrating both sides, we get
∫dy = (1/3)∫ztan-1z dz
y = (1/3)[tan – 1z ∫zdz – ∫{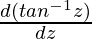 ∫zdz}dz]
∫zdz}dz]
y = (z2/6)tan-1z – 
y = (z2/6)tan-1z – (1/6)∫1 - \frac{1}{(1 + z^2)}dz
y = (z2/6)tan-1z – (1/6)∫dz – (1/6)∫dz/(1 + z2)
y = (z2/6)tan-1z – (z/6) – (1/6)tan-1z
y = (1/6)(z2 + 1)tan-1z – (z/6) + c
y = (1/6)[(x6 + 1)tan – 1(x3) – (x3)] + c
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...