Question 1. Using binomial theorem, write down the expressions of the following:
(i) (2x + 3y)5
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
(2x + 3y)5 = 5C0 (2x)5 (3y)0 + 5C1 (2x)4 (3y)1 + 5C2 (2x)3 (3y)2 + 5C3 (2x)2 (3y)3 + 5C4 (2x)1 (3y)4 + 5C5 (2x)0 (3y)5
= 32x5 + 5 (16x4) (3y) + 10 (8x3) (9y)2 + 10 (4x)2 (27y)3 + 5 (2x) (81y4) + 243 y5
= 32x5 + 240x4 y + 720x3y2 + 1080x2y3 + 810xy4 + 243y5
(ii) (2x – 3y)4
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
(2x – 3y)4 = 4C0 (2x)4 (3y)0 – 4C1 (2x)3 (3y)1 + 4C2 (2x)2 (3y)2 – 4C3 (2x)1 (3y)3 + 4C4 (2x)0 (3y)4
= 16x4 – 4 (8x3) (3y) + 6 (4x2) (9y2) – 4 (2x) (27y3) + 81y4
= 16x4 – 96x3y + 216x2y2 – 216xy3 + 81y4
(iii) (x – 1/x)6
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
(x – 1/x)6 = 6C0 x6 (1/x)0 – 6C1 x5 (1/x)1 + 6C2 x4 (1/x)2 – 6C3 x3 (1/x)3 + 6C4 x2 (1/x)4 – 6C5 x1 (1/x)5 + 6C6 (1/x)6
= x6 – 6x5 (1/x) + 15x4 (1/x2) – 20 x3 (1/x3) + 15x2 (1/x4) – 6x (1/x5) + 1/x6
= x6 – 6x4 + 15x2 – 20 + 15/x2 – 6/x4 + 1/x6
(iv) (1 – 3x)7
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
(1 – 3x)7 = 7C0 (3x)0 – 7C1 (3x)1 + 7C2 (3x)2 – 7C3 (3x)3 + 7C4 (3x)4 – 7C5 (3x)5 + 7C6 (3x)6 – 7C7 (3x)7
= 1 – 7 (3x) + 21 (9x)2 – 35 (27x3) + 35 (81x4) – 21 (243x5) + 7 (729x6) – 2187(x7)
= 1 – 21x + 189x2 – 945x3 + 2835x4 – 5103x5 + 5103x6 – 2187x7
(v) (ax – b/x)6
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
(ax – b/x)^6 = 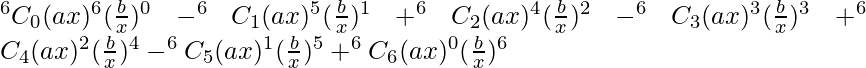
= 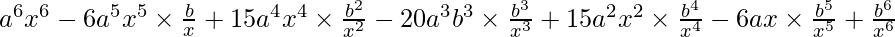
= 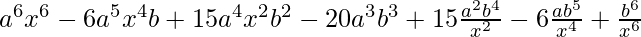
(vi) 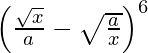
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,

= 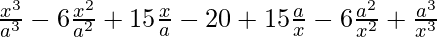
(vii) ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \left( \sqrt[3]{x} - \sqrt[3]{a} \right)^6](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0595efec6736fe18f6d2e87d28ef3007_l3.png)
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \left( \sqrt[3]{x} - \sqrt[3]{a} \right)^6 = ^{6}{}{C}_0 (\sqrt[3]{x} )^6 (\sqrt[3]{a} )^0 -^{6}{}{C}_1 (\sqrt[3]{x} )^5 (\sqrt[3]{a} )^1 +^{6}{}{C}_2 (\sqrt[3]{x} )^4 (\sqrt[3]{a} )^2 -^{6}{}{C}_3 (\sqrt[3]{x} )^3 (\sqrt[3]{a} )^3 +^{6}{}{C}_4 (\sqrt[3]{x} )^2 (\sqrt[3]{a} )^4 -^{6}{}{C}_5 (\sqrt[3]{x} )^1 (\sqrt[3]{a} )^5 + ^{6}{}{C}_6 (\sqrt[3]{x} )^0 (\sqrt[3]{a} )^6](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-de18aa60648259abb36fdbf5d0866dec_l3.png)
= 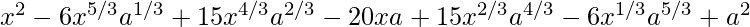
(viii) (1 + 2x – 3x2)5
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
(1 + 2x – 3x2)5 = 5C0 (1 + 2x)5 (3x2)0 – 5C1 (1 + 2x)4 (3x2)1 + 5C2 (1 + 2x)3 (3x2)2 – 5C3 (1 + 2x)2 (3x2)3 + 5C4 (1 + 2x)1 (3x2)4 – 5C5 (1 + 2x)0 (3x2)5
= (1 + 2x)5 – 5(1 + 2x)4 (3x2) + 10 (1 + 2x)3 (9x4) – 10 (1 + 2x)2 (27x6) + 5 (1 + 2x) (81x8) – 243x10
= 5C0 (2x)0 + 5C1 (2x)1 + 5C2 (2x)2 + 5C3 (2x)3 + 5C4 (2x)4 + 5C5 (2x)5 – 15x2 [4C0 (2x)0 + 4C1 (2x)1 + 4C2 (2x)2 + 4C3 (2x)3 + 4C4 (2x)4] + 90x4 [1 + 8x3 + 6x + 12x2] – 270x6(1 + 4x2 + 4x) + 405x8 + 810x9 – 243x10
= 1 + 10x + 40x2 + 80x3 + 80x4 + 32x5 – 15x2 – 120x3 – 3604 – 480x5 – 240x6 + 90x4 + 720x7 + 540x5 + 1080x6 – 270x6 – 1080x8 – 1080x7 + 405x8 + 810x9 – 243x10
= 1 + 10x + 25x2 – 40x3 – 190x4 + 92x5 + 570x6 – 360x7 – 675x8 + 810x9 – 243x10
(ix) 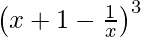
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
(x + 1 – 1/x)3 = 3C0 (x + 1)3 (1/x)0 – 3C1(x + 1)2(1/x)1 + 3C2(x + 1)1(1/x)2 – 3C3 (x + 1)0 (1/x)3
= 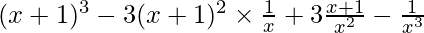
= 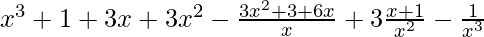
= 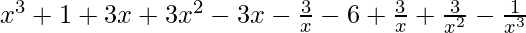
= 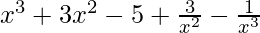
(x) (1 – 2x + 3x2)3
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
(1 – 2x + 3 x2)3 = 3C0 (1 – 2x)3 + 3C1 (1 – 2x)2 (3x2) + 3C2 (1 – 2x)(3x2)2 + 3C3 (3x2)3
= (1 – 2x)3 + 9x2 (1 – 2x)2 + 27x4 (1 – 2x) + 27x6
= 1 – 8x3 + 12x2 – 6x + 9x2 (1 + 4x2 – 4x) + 27x4 – 54x5 + 27x6
= 1 – 8x3 + 12x2 – 6x + 9x2 + 36x4 – 36x3 + 27x4 – 54x5 + 27x6
= 1 – 6x + 21x2 – 44x3 + 63x4 – 54x5 + 27x6
Question 2. Evaluate the following:
(i) 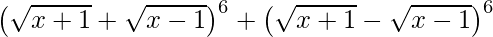
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
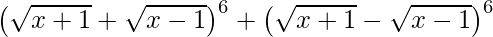 =
= ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com 2[ ^{6}{}{C}_0 (\sqrt{x + 1} )^6 (\sqrt{x - 1} )^0 + ^{6}{}{C}_2 (\sqrt{x + 1} )^4 (\sqrt{x - 1} )^2 +^{6}{}{C}_4 (\sqrt{x + 1} )^2 (\sqrt{x - 1} )^4 + ^{6}{}{C}_6 (\sqrt{x + 1} )^0 (\sqrt{x - 1} )^6 ]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ec7297ec095720948ee84f73721fc9f1_l3.png)
= 2 [(x + 1)3 + 15(x + 1)2 (x – 1) + 15(x + 1)(x – 1 )2 + (x – 1 )3]
= 2 [x3 + 1 + 3x + 3 x2 + 15( x2 + 2x + 1)(x – 1) + 15(x + 1)( x2 + 1 – 2x) + x3 – 1 + 3x – 3 x2]
= 2 [2 x3 + 6x + 15 x3 – 15 x2 + 30 x2 – 30x + 15x – 15 + 15 x3 + 15 x2 – 30 x2 – 30x + 15x + 15]
= 2 [32 x3 – 24x]
= 16x [4x2 – 3]
(ii) 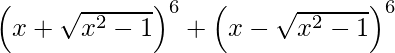
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (x + \sqrt{x^2 - 1} )^6 + (x - \sqrt{x^2 - 1} )^6 = 2[ ^ {6}{}{C}_0 x^6 (\sqrt{x^2 - 1} )^0 +^{6}{}{C}_2 x^4 (\sqrt{x^2 - 1} )^2 +^{6}{}{C}_4 x^2 (\sqrt{x^2 - 1} )^4 + ^{6}{}{C}_6 x^0 (\sqrt{x^2 - 1} )^6 ]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-69d57ac98243e15175f6cf4cfc03285c_l3.png)
= 2 [x6 + 15 x4 ( x2 – 1) + 15 x2 ( x2 – 1 )2 + ( x2 – 1 )3]
= 2 [x6 + 15 x6 – 15 x4 + 15 x2 ( x4 – 2 x2 + 1) + ( x6 – 1 + 3 x2 – 3 x4)]
= 2 [x6 + 15 x6 – 15 x4 + 15 x6 – 30 x4 + 15 x2 + x6 – 1 + 3 x2 – 3 x4]
= 64 x6 – 96 x4 + 36 x2 – 2
(iii) 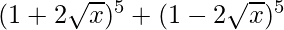
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
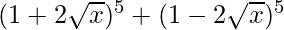 = 2 [5C0 (2√x)0 + 5C2 (2√x)2 + 5C4 (2√x)4]
= 2 [5C0 (2√x)0 + 5C2 (2√x)2 + 5C4 (2√x)4]
= 2 [1 + 10 (4x) + 5 (16x2)]
= 2 [1 + 40x + 80x2]
(iv) 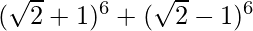
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
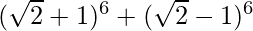 = 2 [6C0 (√2)6 + 6C2 (√2)4 + 6C4 (√2)2 + 6C6 (√2)0]
= 2 [6C0 (√2)6 + 6C2 (√2)4 + 6C4 (√2)2 + 6C6 (√2)0]
= 2 [8 + 15 (4) + 15 (2) + 1]
= 2 [99]
= 198
(v) 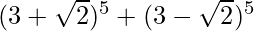
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
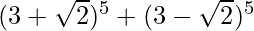 = 2 [5C1 (34) (√2)1 + 5C3 (32) (√2)3 + 5C5 (30) (√2)5]
= 2 [5C1 (34) (√2)1 + 5C3 (32) (√2)3 + 5C5 (30) (√2)5]
= 2 [5 (81) (√2) + 10 (9) (2√2) + 4√2]
= 2√2 (405 + 180 + 4)
= 1178√2
(vi) 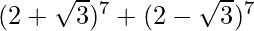
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
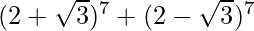 = 2 [7C0 (27) (√3)0 + 7C2 (25) (√3)2 + 7C4 (23) (√3)4 + 7C6 (21) (√3)6]
= 2 [7C0 (27) (√3)0 + 7C2 (25) (√3)2 + 7C4 (23) (√3)4 + 7C6 (21) (√3)6]
= 2 [128 + 21 (32)(3) + 35(8)(9) + 7(2)(27)]
= 2 [128 + 2016 + 2520 + 378]
= 2 [5042]
= 10084
(vii) 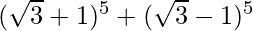
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
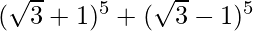 = 2 [5C1 (√3)4 + 5C3 (√3)2 + 5C5 (√3)0]
= 2 [5C1 (√3)4 + 5C3 (√3)2 + 5C5 (√3)0]
= 2 [5 (9) + 10 (3) + 1]
= 2 [76]
= 152
(viii) (0.99)5 + (1.01)5
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
(0.99)5 + (1.01)5 = (1 – 0.01)5 + (1 + 0.01)5
= 2 [5C0 (0.01)0 + 5C2 (0.01)2 + 5C4 (0.01)4]
= 2 [1 + 10 (0.0001) + 5 (0.00000001)]
= 2 [1.00100005]
= 2.0020001
(ix) 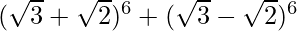
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
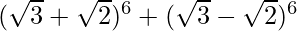 = 2 [6C1 (√3)5 (√2)1 + 6C3 (√3)3 (√2)3 + 6C5 (√3)1 (√2)5]
= 2 [6C1 (√3)5 (√2)1 + 6C3 (√3)3 (√2)3 + 6C5 (√3)1 (√2)5]
= 2 [6 (9√3) (√2) + 20 (3√3) (2√2) + 6 (√3) (4√2)]
= 2 [√6 (54 + 120 + 24)]
= 396 √6
(x) 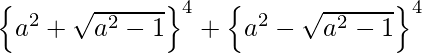
Solution:
Using binomial theorem, we have,
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \left\{ a^2 + \sqrt{a^2 - 1} \right\}^4 + \left\{ a^2 - \sqrt{a^2 - 1} \right\}^4 = 2[ ^{4}{}{C}_0 ( a^2 )^4 (\sqrt{a^2 - 1} )^0 +^{4}{}{C}_2 ( a^2 )^2 (\sqrt{a^2 - 1} )^2 + ^{4}{}{C}_4 ( a^2 )^0 (\sqrt{a^2 - 1} )^4 ]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7ee17f903a56814624aa76b8bba5a1ec_l3.png)
= 2[ a8 + 6 a4 (a2 – 1) + ( a2 – 1 )2]
= 2[a8 + 6 a6 – 6 a4 + a4 + 1 – 2 a2]
= 2 a8 + 12 a6 – 10 a4 – 4 a2 + 2
Question 3. Find (a + b)4 – (a – b)4. Hence, evaluate (√3 + √2)4 – (√3 – √2)4.
Solution:
We are given,
(a + b)4 – (a – b)4 = 2 [4C1 a3b1 + 4C3 a1b3]
= 2 [4a3b + 4ab3]
= 8 (a3b + ab3)
Now,
(√3 + √2)4 – (√3 – √2)4 = 8 (a3b + ab3)
= 8 [(√3)3 (√2) + (√3) (√2)3]
= 8 [(3√6) + (2√6)]
= 8 (5√6)
= 40√6
Question 4. Find (x + 1)6 + (x – 1)6. Hence, or otherwise evaluate (√2 + 1)6 + (√2 – 1)6.
Solution:
We are given,
(x + 1)6 + (x – 1)6 = 2 [6C0 x6 + 6C2 x4 + 6C4 x2 + 6C6 x0]
= 2 [x6 + 15x4 + 15x2 + 1]
Now,
(√2 + 1)6 + (√2 – 1)6
So consider, x = √2 then we get,
(√2 + 1)6 + (√2 – 1)6 = 2 [x6 + 15x4 + 15x2 + 1]
= 2 [(√2)6 + 15 (√2)4 + 15 (√2)2 + 1]
= 2 [8 + 15 (4) + 15 (2) + 1]
= 2 [8 + 60 + 30 + 1]
= 198
Question 5. Using binomial theorem evaluate each of the following:
(i) (96)3
Solution:
On expressing the given expression as two different entities and applying the binomial theorem, we get,
(96)3 = (100 – 4)3
= 3C0 (100)3 (4)0 – 3C1 (100)2 (4)1 + 3C2 (100)1 (4)2 – 3C3 (100)0 (4)3
= 1000000 – 120000 + 4800 – 64
= 884736
(ii) (102)5
Solution:
On expressing the given expression as two different entities and applying the binomial theorem, we get,
(102)5 = (100 + 2)5
= 5C0 (100)5 (2)0 + 5C1 (100)4 (2)1 + 5C2 (100)3 (2)2 + 5C3 (100)2 (2)3 + 5C4 (100)1 (2)4 + 5C5 (100)0 (2)5
= 10000000000 + 1000000000 + 40000000 + 800000 + 8000 + 32
= 11040808032
(iii) (101)4
Solution:
On expressing the given expression as two different entities and applying the binomial theorem, we get,
(101)4 = (100 + 1)4
= 4C0 (100)4 + 4C1 (100)3 + 4C2 (100)2 + 4C3 (100)1 + 4C4 (100)0
= 100000000 + 4000000 + 60000 + 400 + 1
= 104060401
(iv) (98)5
Solution:
On expressing the given expression as two different entities and applying the binomial theorem, we get,
(98)5 = (100 – 2)5
= 5C0 (100)5 (2)0 – 5C1 (100)4 (2)1 + 5C2 (100)3 (2)2 – 5C3 (100)2 (2)3 + 5C4 (100)1 (2)4 – 5C5 (100)0 (2)5
= 10000000000 – 1000000000 + 40000000 – 800000 + 8000 – 32
= 9039207968
Question 6. Using binomial theorem, prove that 23n – 7n – 1 is divisible by 49, where n ∈ N.
Solution:
We are given,
23n – 7n – 1 = 8n – 7n – 1
= (1 + 7)n – 7n – 1
= nC0 + nC1 (7)1 + nC2 (7)2 + nC3 (7)3 + nC4 (7)2 + nC5 (7)1 + .… + nCn (7)n – 7n – 1
= 1 + 7n + 72 [ nC2 + nC3 (71) + nC4 (72) + … + nCn (7)n-2] – 7n – 1
= 49 [ nC2 + nC3 (71) + nC4 (72) + … + nCn (7)n-2] , which is divisible by 49.
Therefore, 23n – 1 – 7n is divisible by 49.
Hence proved.
Question 7. Using the binomial theorem, prove that 32n+2 – 8n – 9 is divisible by 64, where n ∈ N.
Solution:
We are given,
32n+2 – 8n – 9 = 32(n+1) – 8n – 9
= 9n+1 – 8n – 9
= (1 + 8)n+1 – 8n – 9
= n+1C0 + n+1C1 (8)1 + n+1C2 (8)2 + n+1C3 (8)3 + n+1C4 (8)2 + n+1C5 (8)1 + .… + n+1Cn+1 (8)n+1 – 8n – 9
= 1 + 8(n+1) + 82 [ n+1C2 + n+1C3 (81) + n+1C4 (82) + … + n+1Cn+1 (8)n-1] – 8n – 9
= 8n + 9 + 64 [ n+1C2 + n+1C3 (81) + n+1C4 (82) + … + n+1Cn+1 (8)n-1] – 8n – 9
= 64 [ n+1C2 + n+1C3 (81) + n+1C4 (82) + … + n+1Cn+1 (8)n-1], which is divisible by 64.
Therefore, 32n+2 – 8n – 9 is divisible by 64.
Hence proved.
Question 8. If n is a positive integer, prove that 33n – 26n – 1 is divisible by 676.
Solution:
We are given,
33n – 26n – 1 = (33)n – 26n – 1
= 27n – 26n – 1
= (1 + 26)n – 26n – 1
= nC0 + nC1 (26)1 + nC2 (26)2 + nC3 (26)3 + nC4 (26)2 + nC5 (26)1 + .… + nCn (26)n – 26n – 1
= 1 + 26n + 262 [ nC2 + nC3 (261) + nC4 (262) + … + nCn (26)n-2] – 26n – 1
= 676 [ nC2 + nC3 (261) + nC4 (262) + … + nCn (26)n-2] , which is divisible by 676.
Therefore, 33n – 26n – 1 is divisible by 676.
Hence proved.
Question 9. Using binomial theorem, indicate which is larger (1.1)10000 or 1000.
Solution:
We have,
(1.1)10000 = (1 + 0.1)10000
= 10000C0 + 10000C1 (0.1)1 + 10000C2 (0.1)2 + .… + 10000C10000 (0.1)10000
= 1 + (10000) (0.1) + other positive terms
= 1 + 1000 + other positive terms
= 1001 + other positive terms
Therefore, (1.1)10000 is larger than 1000.
Question 10. Using binomial theorem, determine which number is larger, (1.2)4000 or 800?
Solution:
We have,
(1.2)4000 = (1 + 0.2)4000
= 4000C0 + 4000C1 (0.2)1 + 4000C2 (0.2)2 + .… + 4000C4000 (0.2)4000
= 1 + (4000) (0.2) + other positive terms
= 1 + 800 + other positive terms
= 801 + other positive terms
Therefore, (1.2)4000 is larger than 800.
Question 11. Find the value of (1.01)10 + (1−0.01)10 correct to 7 places of decimal.
Solution:
We have,
(1.01)10 + (1−0.01)10 = (1+0.01)10 + (1−0.01)10
= 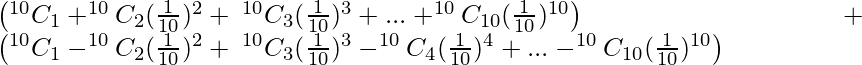
= 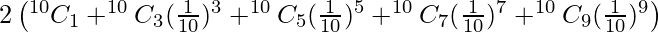
= 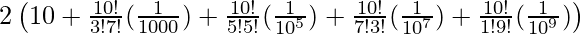
= 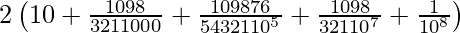
= 2.0090042
Question 12. Show that 24n+4 − 15n − 16, where n ∈ N is divisible by 225.
Solution:
We have,
24n+4 − 15n − 16 = 24(n+1) − 15n − 16
= 16n+1 − 15n − 16
= (1 + 15)n+1 − 15n − 16
= n+1C0 + n+1C1 (15)1 + n+1C2 (15)2 + n+1C3 (15)3 + n+1C4 (15)2 + n+1C5 (15)1 + .… + n+1Cn+1 (15)n+1 − 15n − 16
= 1 + 15(n+1) + 152 [ n+1C2 + n+1C3 (151) + n+1C4 (152) + … + n+1Cn+1 (15)n-1] – 15n – 16
= 15n + 16 + 225 [ n+1C2 + n+1C3 (151) + n+1C4 (152) + … + n+1Cn+1 (15)n-1] – 15n – 16
= 225 [ n+1C2 + n+1C3 (151) + n+1C4 (152) + … + n+1Cn+1 (15)n-1] , which is divisible by 225.
Therefore, 24n+4 − 15n − 16 is divisible by 225.
Hence proved.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...