Class 11 RD Sharma Solutions – Chapter 15 Linear Inequations – Exercise 15.1 | Set 2
Last Updated :
28 Apr, 2021
Question 15. Solve: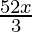 <
< − 5 in R.
− 5 in R.
Solution:
Given: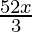 <
< − 5
− 5
⇒ 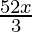 <
<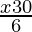
⇒ 6(5−2x) < 3(x−30)
⇒ 30 − 12x < 3x − 90
⇒ 15x > 120
⇒ x > 8
Thus, the solution set is (8, ∞).
Question 16. Solve: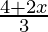 ≥
≥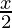 − 3.
− 3.
Solution:
Given: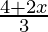 ≥
≥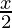 − 3.
− 3.
⇒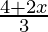 ≥
≥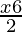
⇒ 2(4+2x) ≥ 3(x−60)
⇒ 8 + 4x ≥ 3x − 180
⇒ x ≥ −26
Thus, the solution set is [−26, ∞).
Question 17. Solve: − 2 <
− 2 <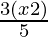 .
.
Solution:
Given: − 2 <
− 2 <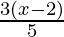
⇒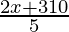 <
<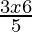
⇒ 2x + 3 − 10 < 3x − 6
⇒ x > −1
Thus, the solution set is (−1, ∞).
Question 18. Solve: x−2 ≤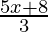
Solution:
Given: x−2 ≤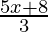
⇒ 3(x−2) ≤ 5x+8
⇒ 3x − 6 ≤ 5x + 8
⇒ 2x ≥ −14
⇒ x ≥ −7
Thus, the solution set is [−7, ∞).
Question 19. Solve: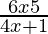 < 0.
< 0.
Solution:
Given: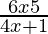 < 0.
< 0.
Case I: When 6x − 5 > 0 and 4x +1 < 0
⇒ x > 5/6 and x < −1/4, which is clearly impossible.
Case II: When 6x − 5 < 0 and 4x +1 > 0
⇒ x < 5/6 and x > −1/4
Thus, the solution set is (−1/4, 5/6).
Question 20. Solve: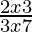 > 0.
> 0.
Solution:
Given: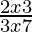 > 0.
> 0.
Case I: When 2x−3 > 0 and 3x−7 > 0
⇒ x > 3/2 and x > 7/3
⇒ x > 7/3 ….(a)
Case II: When 2x−3 < 0 and 3x−7 < 0
⇒ x < 3/2 and x < 7/3
⇒ x < 3/2 ….(b)
From (a) and (b), we get:
The solution set is (− ∞, 3/2)∪ (7/3, ∞).
Question 21. Solve: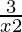 < 1.
< 1.
Solution:
Given: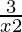 < 1
< 1
⇒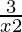 −1 < 0
−1 < 0
⇒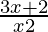 < 0
< 0
⇒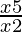 > 0
> 0
Case I: When x−5 > 0 and x−2 > 0
⇒ x > 5 and x > 2
⇒ x > 5 ….(a)
Case II: When x−5 < 0 and x−2 < 0
⇒ x < 5 and x < 2
⇒ x < 2 ….(b)
From (a) and (b), we get:
The solution set is (− ∞, 2)∪ (5, ∞).
Question 22. Solve: ≤ 2.
≤ 2.
Solution:
Given: ≤ 2
≤ 2
⇒ − 2 ≤ 0
− 2 ≤ 0
⇒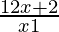 ≤ 0
≤ 0
⇒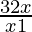 ≤ 0
≤ 0
Case I: When 3−2x ≥ 0 and x−1 < 0
⇒ x ≥ 3/2 and x < 1
⇒ x < 1 …..(a)
Case II: 3−2x ≤ 0 and x−1 > 0
⇒ x ≥ 3/2 and x > 1
⇒ x ≥ 3/2 ….(b)
From (a) and (b), we get:
The solution set is (− ∞, 1)∪ (3/2, ∞).
Question 23. Solve: < 6
< 6
Solution:
Given: < 6
< 6
⇒ −6 < 0
−6 < 0
⇒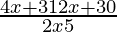 < 0
< 0
⇒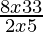 < 0
< 0
Case I: When 8x−33 > 0 and 2x−5 > 0
⇒ x > 33/8 and x > 5/2
⇒ x > 33/8 ….(a)
Case II: When 8x−33 < 0 and 2x−5 < 0
⇒ x < 33/8 and x <5/2
⇒ x < 5/2 ….(b)
From (a) and (b), we get:
The solution set is (− ∞, 5/2)∪ (33/8, ∞).
Question 24. Solve: < 1.
< 1.
Solution:
Given: < 1
< 1
⇒ − 1 < 0
− 1 < 0
⇒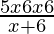 < 0
< 0
⇒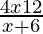 < 0
< 0
Case I: When 4x−12 > 0 and x+6 < 0
⇒ x > −3 and x < −6, which is clearly not possible.
Case II: When 4x−12 < 0 and x+6 > 0
⇒ x < −3 and x > −6
The solution set is (− 3, 6).
Question 25. Solve: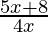 < 2.
< 2.
Solution:
Given: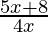 < 2
< 2
⇒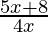 − 2 < 0
− 2 < 0
⇒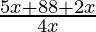 < 0
< 0
⇒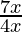 < 0
< 0
Case I: When 7x > 0 and 4−x < 0
⇒ x > 0 and x > 4
⇒ x > 4 ….(a)
Case II: When 7x < 0 and 4−x > 0
⇒ x < 0 and x > 4
⇒ x < 0 ….(b)
From (a) and (b), we get:
The solution set is (− ∞, 0)∪ (4, ∞).
Question 26. Solve: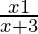 > 2.
> 2.
Solution:
Given: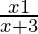 > 2.
> 2.
⇒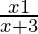 − 2 > 0
− 2 > 0
⇒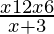 > 0
> 0
⇒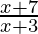 < 0
< 0
Case I: When x+7 > 0 and x+3 < 0
⇒ x > −7 and x < −3
Case II: When x+7 < 0 and x+3 > 0
⇒ x < −7 and x > −3, which is clearly not possible.
The solution set is (−7, −3).
Question 27. Solve: > 4.
> 4.
Solution:
Given: > 4
> 4
⇒ − 4 > 0
− 4 > 0
⇒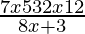 > 0
> 0
⇒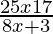 > 0
> 0
⇒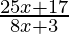 < 0
< 0
Case I: When 25x+17 > 0 and 8x+3 < 0
⇒ x > −17/25 and x < −3/8
Case II: When 25x+17 < 0 and 8x+3 > 0
⇒ x < −17/25 and x > −3/8, which is not clearly possible.
Hence the solution set is (−17/25, −3/8).
Question 28. Solve: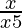 > 1/2.
> 1/2.
Solution:
Given: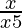 > 1/2.
> 1/2.
⇒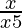 − 1/2 > 0
− 1/2 > 0
⇒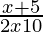 > 0
> 0
Case I: When x+5 > 0 and 2x−10 > 0
⇒ x > −5 and x > 5
⇒ x > 5 ….(a)
Case II: When x+5 < 0 and 2x−10 < 0
⇒ x < −5 and x < 5
⇒ x < −5 ….(b)
From (a) and (b), we get:
The solution set is (− ∞, −5)∪ (5, ∞).
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...