Class 10 RD Sharma Solutions – Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations – Exercise 8.10
Last Updated :
13 Jan, 2021
Question 1. The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 25 cm. The difference between the lengths of the other two sides of the triangle is 5 cm. Find the lengths of these sides.
Solution:
Let the length of other two sides of the triangle be x and y.
Therefore, according to the question,
x – y = 5
or,
x = y + 5
Now the two sides are of length y and y + 5.
Applying Pythagoras theorem on the right-angled triangle, we get,
252 = y2 + (y + 5)2
625 = y2 + y2 + 25 + 10y
2y2 + 25 + 10y = 625
2y2 + 10y = 625 – 25
2y2 + 10y – 600 = 0
y2 + 5y – 300 = 0
y2 + 20y – 15y – 300 = 0 [By middle term splitting]
y(y + 20) – 15(y + 20) = 0
(y – 15)(y + 20) = 0
y -15 = 0 or y + 20 = 0
y = 15 or y = -20
As the length of a side is positive, we will take y = 15.
Therefore,
x = y + 5
x = 15 + 5
x = 20
The two sides of the triangle are 15 cm and 20 cm.
Question 2. The diagonal of a rectangular field is 60 meters more than the shorter side. If the longer side is 30 meters more than the shorter side, find the sides of the field.
Solution:
Let the shorter side of the rectangle be x.
Now, according to the question, length of rectangle is x + 60 and length of the longer side of rectangle is x + 30.
Now, we will apply Pythagoras theorem on the right-angled triangle formed by the diagonal and the two sides,
(x + 60)2 = (x + 30)2 + x2
x2 + 3600 + 120x = x2 + 900 + 60x + x2
3600 – 900 = x2 + 60x – 120x
2700 = x2 – 60x
x2 – 60x – 2700 = 0
x2 – 90x + 30x – 2700 = 0
x(x – 90) + 30(x – 90) = 0
(x + 30)(x – 90) = 0
x + 30 = 0 or x – 90 = 0
x = -30 or x = 90
We will take positive side, i.e. x = 90
Now,
length of shorter side is 90 m
length of diagonal is 90 + 60 = 150 m
length of longer side is 90 + 30 = 120 m
Question 3. The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 3√10 cm. If the smaller leg is tripled and the longer leg doubled, new hypotenuse will be 9√5 cm. How long are the legs of the triangle?
Solution:
Let the smaller and longer side of the triangle be x and y.
Now applying Pythagoras theorem, we get,
(3√10)2 = x2 + y2
x2 + y2 = 90 ……… (i)
Now the smaller and longer sides are tripled and doubled respectively,
Therefore, the new sides of the triangle will be 3x and 2y.
Applying Pythagoras theorem,
(9√5)2 = (3x)2 + (2y)2
9x2 + 4y2 = 405 ……… (ii)
Now multiplying (i) by 4 and then subtracting (i) from (ii), we get
9x2 – 5x2 + 4y2 – 4y2= 405 – 360
5x2 = 45
x2 = 9
x = 3
Substituting value of x in (i),
9 + y2 = 90
y2 = 81
y = 9
Length of smaller side is 3 cm.
Length of longer side is 9 cm.
Question 4. A pole has to be erected at a point on the boundary of a circular park of diameter 13 metres in such a way that the difference of its distances from two diametrically opposite fixed gates A and B on the boundary is 7 metres. Is it possible to do so? If yes, at what distances from the two gates should the pole be erected?
Solution:
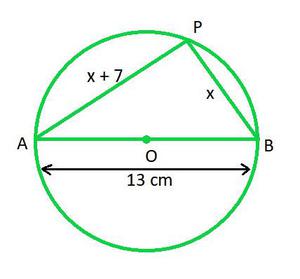
In the circle, let P be the pole on the circumference of the circle and points A and B be the two diametrically opposite fixed gates.
Let length of PB be x.
Given,
PA – PB = 7
PA = x + PB
PA = x + 7
The triangle PQR is a right-angled triangle at P, as AB is the diameter of the circle.
Now applying Pythagoras theorem,
AB2 = PA2 + PB2
132 = (x + 7)2 + x2
169 = x2 + 49 + 14x + x2
169 = 2×2 + 14x + 49
2x2 + 14x + 49 – 169 = 0
2x2 + 14x – 120 = 0
x2 + 7x – 60 = 0
x2 + 12x – 5x – 60 = 0
x(x + 12) – 5(x + 12) = 0
(x – 5)(x + 12) = 0
x = 5 or x = -12
Only x = 5 is possible.
PB = 5 m
PA = 5 + 7 = 12 m
P should be erected at a distance of 5 m from PB and 12 m from PA.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...