Check whether an Array is Subarray of another Array
Last Updated :
13 Sep, 2023
Given two arrays A[] and B[] consisting of 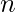 and
and 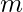 integers. The task is to check whether the array B[] is a subarray of the array A[] or not.
integers. The task is to check whether the array B[] is a subarray of the array A[] or not.
Examples:
Input : A[] = {2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2}, B[] = {3, 0, 5, 1}
Output : Yes
Input : A[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, B[] = {2, 5, 6}
Output : No
Source: Visa Interview Experience
Approach:
- Iterate through the array A[] using a loop that runs from 0 to n-m, where n and m are the sizes of arrays A[] and B[] respectively. This loop represents the starting index of the subarray of A[] that we are comparing with B[].
- For each starting index in the loop, iterate through the array B[] using another loop that runs from 0 to m-1. This loop represents the index of the elements in the subarray that we are comparing with the corresponding elements in B[].
- If the elements at the corresponding indices in the subarray of A[] and B[] are not equal, break out of the inner loop and move to the next starting index in the outer loop.
- If all the elements in the subarray of A[] match the elements in B[], return true.
- If none of the starting indices in the outer loop result in a matching subarray, return false.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isSubArray(int A[], int B[], int n, int m) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n-m; i++) {
int j;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (A[i+j] != B[j]) {
break;
}
}
if (j == m) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
int A[] = { 2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2 };
int n = sizeof(A) / sizeof(int);
int B[] = { 3, 0, 5, 1 };
int m = sizeof(B) / sizeof(int);
if (isSubArray(A, B, n, m))
cout << "YES\n";
else
cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class Main {
static boolean isSubArray(int[] A, int[] B, int n, int m) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) {
int j;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (A[i + j] != B[j]) {
break;
}
}
if (j == m) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] A = {2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2};
int n = A.length;
int[] B = {3, 0, 5, 1};
int m = B.length;
if (isSubArray(A, B, n, m))
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
|
Python3
def isSubArray(A, B):
n = len(A)
m = len(B)
for i in range(n - m + 1):
for j in range(m):
if A[i + j] != B[j]:
break
else:
return True
return False
A = [2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2]
B = [3, 0, 5, 1]
if isSubArray(A, B):
print("YES")
else:
print("NO")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static bool IsSubArray(int[] A, int[] B, int n, int m)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= n - m;
i++)
{
int j;
for (j = 0; j < m;
j++)
{
if (A[i + j] != B[j]) {
break;
}
}
if (j == m)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
static void Main()
{
int[] A = { 2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2 };
int n = A.Length;
int[] B = { 3, 0, 5, 1 };
int m = B.Length;
if (IsSubArray(A, B, n, m)) {
Console.WriteLine("YES");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
function isSubArray(A, B, n, m) {
for (let i = 0; i <= n - m; i++) {
let j;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (A[i + j] !== B[j]) {
break;
}
}
if (j === m) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
let A = [2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2];
let n = A.length;
let B = [3, 0, 5, 1];
let m = B.length;
if (isSubArray(A, B, n, m))
console.log("YES");
else
console.log("NO");
|
Time Complexity: O(n*m), where n and m are the sizes of the arrays A[] and B[], respectively.
Space Complexity: O(1) as we are not using any additional space to store the arrays or any other variables.
Efficient Approach : An efficient approach is to use two pointers to traverse both the array simultaneously. Keep the pointer of array B[] still and if any element of A[] matches with the first element of B[] then increase the pointer of both the array else set the pointer of A to the next element of the previous starting point and reset the pointer of B to 0. If all the elements of B are matched then print YES otherwise print NO.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isSubArray(int A[], int B[], int n, int m)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
if (A[i] == B[j]) {
i++;
j++;
if (j == m)
return true;
}
else {
i = i - j + 1;
j = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int A[] = { 2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2 };
int n = sizeof(A) / sizeof(int);
int B[] = { 3, 0, 5, 1 };
int m = sizeof(B) / sizeof(int);
if (isSubArray(A, B, n, m))
cout << "YES\n";
else
cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
|
Java
class gfg
{
static boolean isSubArray(int A[], int B[],
int n, int m)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m)
{
if (A[i] == B[j])
{
i++;
j++;
if (j == m)
return true;
}
else
{
i = i - j + 1;
j = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String arr[])
{
int A[] = { 2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2 };
int n = A.length;
int B[] = { 3, 0, 5, 1 };
int m = B.length;
if (isSubArray(A, B, n, m))
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
|
Python3
def isSubArray(A, B, n, m):
i = 0; j = 0;
while (i < n and j < m):
if (A[i] == B[j]):
i += 1;
j += 1;
if (j == m):
return True;
else:
i = i - j + 1;
j = 0;
return False;
if __name__ == '__main__':
A = [ 2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2 ];
n = len(A);
B = [ 3, 0, 5, 1 ];
m = len(B);
if (isSubArray(A, B, n, m)):
print("YES");
else:
print("NO");
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
static bool isSubArray(int []A, int []B,
int n, int m)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m)
{
if (A[i] == B[j])
{
i++;
j++;
if (j == m)
return true;
}
else
{
i = i - j + 1;
j = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void Main(String []arr)
{
int []A = { 2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2 };
int n = A.Length;
int []B = { 3, 0, 5, 1 };
int m = B.Length;
if (isSubArray(A, B, n, m))
Console.WriteLine("YES");
else
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function isSubArray(A, B, n,m)
{
var i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < n && j < m) {
if (A[i] == B[j]) {
i++;
j++;
if (j == m)
return true;
}
else {
i = i - j + 1;
j = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
var A = [ 2, 3, 0, 5, 1, 1, 2 ];
var n = A.length;
var B = [ 3, 0, 5, 1 ];
var m =B.length;
if (isSubArray(A, B, n, m))
document.write( "YES<br>");
else
document.write( "NO<br>");
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N*N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Related Topic: Subarrays, Subsequences, and Subsets in Array
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...