Check if sum of arr[i] / j for all possible pairs (i, j) in an array is 0 or not
Last Updated :
29 Apr, 2021
Given an array arr[] consisting of N integers, the task is to check if the sum of all possible values of (arr[i] / j) for all pairs (i, j) such that 0 < i ? j < (N – 1) is 0 or not. If found to be true, then print “Yes”. Otherwise, print “No”.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {1, -1, 3, -2, -1}
Output: Yes
Explanation:
For all possible pairs (i, j), such that 0 < i <= j < (N – 1), required sum = 1/1 + -1/2 + 3/3 + -2/4 + -1/5 + -1/2 + 3/3 + -2/4 + -1/5 + 3/3 + -2/4 + -1/5 + -2/ 4 + -1/5 + -1/5 = 0.
Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Output: No
Approach: The given problem can be solved based on the following observations:
- For every possible value of i over the range [0, N – 1] and for every possible values of j following are the expressions:
- j = 1:
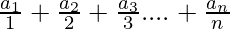
- j = 2:
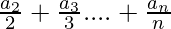
- j = 3:
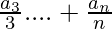 3rd line and so on…
3rd line and so on…
- Therefore, the sum of all the above expression is given by:
=> 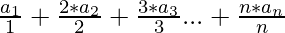
=> 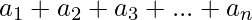
From the above observations, if the sum of the array is 0, then print Yes. Otherwise, print No.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void check(int arr[], int N)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum == 0)
cout << "Yes";
else
cout << "No";
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, -1, 3, -2, -1 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
check(arr, N);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static void check(int arr[], int N)
{
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum == 0)
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, -1, 3, -2, -1 };
int N = arr.length;
check(arr, N);
}
}
|
Python3
def check(arr, N):
sum = 0
for i in range(N):
sum += arr[i]
if (sum == 0):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [ 1, -1, 3, -2, -1 ]
N = len(arr)
check(arr, N)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void check(int[] arr, int N)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum == 0)
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 1, -1, 3, -2, -1 };
int N = arr.Length;
check(arr, N);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function check(arr , N) {
var sum = 0;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum == 0)
document.write("Yes");
else
document.write("No");
}
var arr = [ 1, -1, 3, -2, -1 ];
var N = arr.length;
check(arr, N);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...