Check if given sorted sub-sequence exists in binary search tree
Last Updated :
11 Sep, 2023
Given a binary search tree and a sorted sub-sequence. the task is to check if the given sorted sub-sequence exist in binary search tree or not.
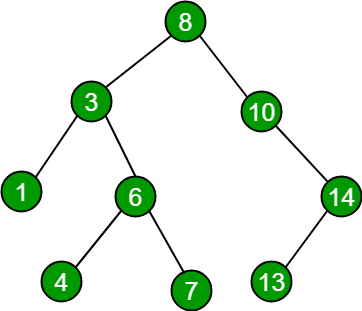
Examples:
// For above binary search tree
Input : seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 14}
Output: "Yes"
Input : seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 12, 13}
Output: "No"
A simple solution is to store inorder traversal in an auxiliary array and then by matching elements of sorted sub-sequence one by one with inorder traversal of tree , we can if sub-sequence exist in BST or not. Time complexity for this approach will be O(n) but it requires extra space O(n) for storing traversal in an array.
An efficient solution is to match elements of sub-sequence while we are traversing BST in inorder fashion. We take index as a iterator for given sorted sub-sequence and start inorder traversal of given bst, if current node matches with seq[index] then move index in forward direction by incrementing 1 and after complete traversal of BST if index==n that means all elements of given sub-sequence have been matched and exist as a sorted sub-sequence in given BST.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
struct Node* newNode(int num)
{
struct Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = num;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
struct Node* insert(struct Node* root, int key)
{
if (root == NULL)
return newNode(key);
if (root->data > key)
root->left = insert(root->left, key);
else
root->right = insert(root->right, key);
return root;
}
void seqExistUtil(struct Node *ptr, int seq[], int &index)
{
if (ptr == NULL)
return;
seqExistUtil(ptr->left, seq, index);
if (ptr->data == seq[index])
index++;
seqExistUtil(ptr->right, seq, index);
}
bool seqExist(struct Node *root, int seq[], int n)
{
int index = 0;
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
return (index == n);
}
int main()
{
struct Node* root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
int seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 14};
int n = sizeof(seq)/sizeof(seq[0]);
seqExist(root, seq, n)? cout << "Yes" :
cout << "No";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
};
static class INT
{
int a;
}
static Node newNode(int num)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = num;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
static Node insert( Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return newNode(key);
if (root.data > key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
return root;
}
static void seqExistUtil( Node ptr, int seq[], INT index)
{
if (ptr == null)
return;
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index);
if (ptr.data == seq[index.a])
index.a++;
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index);
}
static boolean seqExist( Node root, int seq[], int n)
{
INT index = new INT();
index.a = 0;
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
return (index.a == n);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
int seq[] = {4, 6, 8, 14};
int n = seq.length;
if(seqExist(root, seq, n))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
def insert(root, key):
if root == None:
return Node(key)
if root.data > key:
root.left = insert(root.left, key)
else:
root.right = insert(root.right, key)
return root
def seqExistUtil(ptr, seq, index):
if ptr == None:
return
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index)
if ptr.data == seq[index[0]]:
index[0] += 1
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index)
def seqExist(root, seq, n):
index = [0]
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index)
if index[0] == n:
return True
else:
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = None
root = insert(root, 8)
root = insert(root, 10)
root = insert(root, 3)
root = insert(root, 6)
root = insert(root, 1)
root = insert(root, 4)
root = insert(root, 7)
root = insert(root, 14)
root = insert(root, 13)
seq = [4, 6, 8, 14]
n = len(seq)
if seqExist(root, seq, n):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
};
public class INT
{
public int a;
}
static Node newNode(int num)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = num;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
static Node insert( Node root, int key)
{
if (root == null)
return newNode(key);
if (root.data > key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
return root;
}
static void seqExistUtil( Node ptr, int []seq, INT index)
{
if (ptr == null)
return;
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index);
if (ptr.data == seq[index.a])
index.a++;
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index);
}
static bool seqExist( Node root, int []seq, int n)
{
INT index = new INT();
index.a = 0;
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
return (index.a == n);
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
int []seq = {4, 6, 8, 14};
int n = seq.Length;
if(seqExist(root, seq, n))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node
{
constructor()
{
this.data = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
};
class INT
{
constructor()
{
this.a = 0;
}
}
function newNode(num)
{
var temp = new Node();
temp.data = num;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
function insert( root, key)
{
if (root == null)
return newNode(key);
if (root.data > key)
root.left = insert(root.left, key);
else
root.right = insert(root.right, key);
return root;
}
function seqExistUtil( ptr, seq, index)
{
if (ptr == null)
return;
seqExistUtil(ptr.left, seq, index);
if (ptr.data == seq[index.a])
index.a++;
seqExistUtil(ptr.right, seq, index);
}
function seqExist( root, seq, n)
{
var index = new INT();
index.a = 0;
seqExistUtil(root, seq, index);
return (index.a == n);
}
var root = null;
root = insert(root, 8);
root = insert(root, 10);
root = insert(root, 3);
root = insert(root, 6);
root = insert(root, 1);
root = insert(root, 4);
root = insert(root, 7);
root = insert(root, 14);
root = insert(root, 13);
var seq = [4, 6, 8, 14];
var n = seq.length;
if(seqExist(root, seq, n))
document.write("Yes");
else
document.write("No");
</script>
|
Time complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n) for call stack since using recursion, where n is total no of nodes in BST
Approach 2 :- Optimal solution in O(N) time complexity and O(h) space complexity
The existsSubsequence function takes a BST root and a vector seq representing the sorted sub-sequence to be searched. It first checks if the seq is empty, in which case it returns true. Otherwise, it calls the findSequence function with the root, seq, and index i set to 0. The findSequence function recursively searches for the elements in the seq starting from index i in the BST. If the current node has the same value as the element at index i, it increments i and recursively calls the findSequence function on the left and right subtrees with the updated value of i. If i reaches the end of seq, it means that the sub-sequence exists in the BST, and the function returns true. If the current node does not have the same value as the element at index i, the function returns false.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
bool findSequence(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& seq, int i) {
if (root == NULL) {
return false;
}
if (root->val == seq[i]) {
i++;
if (i == seq.size()) {
return true;
}
return findSequence(root->left, seq, i) || findSequence(root->right, seq, i);
}
return false;
}
bool existsSubsequence(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& seq) {
if (seq.empty()) {
return true;
}
return findSequence(root, seq, 0);
}
int main() {
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(5);
root->left = new TreeNode(3);
root->right = new TreeNode(7);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(4);
root->right->left = new TreeNode(6);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(8);
vector<int> seq1 = {2, 3, 4};
if (existsSubsequence(root, seq1)) {
cout << "The sequence {2, 3, 4} exists in the BST" << endl;
} else {
cout << "The sequence {2, 3, 4} does not exist in the BST" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
public class Main {
public static boolean findSequence(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> seq, int i) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.val == seq.get(i)) {
i++;
if (i == seq.size()) {
return true;
}
return findSequence(root.left, seq, i) || findSequence(root.right, seq, i);
}
return false;
}
public static boolean existsSubsequence(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> seq) {
if (seq.isEmpty()) {
return true;
}
return findSequence(root, seq, 0);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(5);
root.left = new TreeNode(3);
root.right = new TreeNode(7);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(4);
root.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
root.right.right = new TreeNode(8);
ArrayList<Integer> seq1 = new ArrayList<>();
seq1.add(2);
seq1.add(3);
seq1.add(4);
if (existsSubsequence(root, seq1)) {
System.out.println("The sequence {2, 3, 4} exists in the BST");
} else {
System.out.println("The sequence {2, 3, 4} does not exist in the BST");
}
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
def findSequence(root, seq, i):
if (root == None):
return False
if (root.val == seq[i]):
i = i + 1
if (i == len(seq)):
return True
return findSequence(root.left, seq, i) or findSequence(root.right, seq, i)
return False
def existsSubsequence(root, seq):
if (len(seq) == 0):
return True
return findSequence(root, seq, 0)
root = Node(5)
root.left = Node(3)
root.right = Node(7)
root.left.left = Node(2)
root.left.right = Node(4)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(8)
seq1 = [2, 3, 4]
if (existsSubsequence(root, seq1)):
print("The sequence {2, 3, 4} exists in the BST")
else:
print("The sequence {2, 3, 4} does not exist in the BST")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
public class Program {
public static bool FindSequence(TreeNode root,
List<int> seq, int i)
{
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.val == seq[i]) {
i++;
if (i == seq.Count) {
return true;
}
return FindSequence(root.left, seq, i)
|| FindSequence(root.right, seq, i);
}
return false;
}
public static bool ExistsSubsequence(TreeNode root,
List<int> seq)
{
if (seq.Count == 0) {
return true;
}
return FindSequence(root, seq, 0);
}
public static void Main()
{
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(5);
root.left = new TreeNode(3);
root.right = new TreeNode(7);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(4);
root.right.left = new TreeNode(6);
root.right.right = new TreeNode(8);
List<int> seq1 = new List<int>{ 2, 3, 4 };
if (ExistsSubsequence(root, seq1)) {
Console.WriteLine(
"The sequence {2, 3, 4} exists in the BST");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine(
"The sequence {2, 3, 4} does not exist in the BST");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(val){
this.val = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function findSequence(root, seq, i) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.val == seq[i]) {
i++;
if (i == seq.length) {
return true;
}
return findSequence(root.left, seq, i) || findSequence(root.right, seq, i);
}
return false;
}
function existsSubsequence(root, seq) {
if (seq.length == 0) {
return true;
}
return findSequence(root, seq, 0);
}
let root = new Node(5);
root.left = new Node(3);
root.right = new Node(7);
root.left.left = new Node(2);
root.left.right = new Node(4);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(8);
let seq1 = [2, 3, 4];
if (existsSubsequence(root, seq1)) {
console.log("The sequence {2, 3, 4} exists in the BST");
} else {
console.log("The sequence {2, 3, 4} does not exist in the BST");
}
|
Output
The sequence {2, 3, 4} does not exist in the BST
Time complexity –The time complexity of the given program depends on the height of the BST and the length of the input sequence. In the worst case, where the input sequence is a valid subsequence of the BST and has a length of k, and the height of the BST is h, the time complexity of the program will be O(k*h).
The reason for this is that the program performs a depth-first search on the BST to find the nodes in the input sequence, and the search may need to visit up to k nodes in the BST. Since the search is a recursive function that traverses the tree from the root to the leaves, the worst-case time complexity is O(k*h).
Space complexity – The space complexity of the program depends on the height of the BST and the length of the input sequence. In the worst case, where the input sequence is a valid subsequence of the BST and has a length of k, and the height of the BST is h, the space complexity of the program will be O(h).
The reason for this is that the program uses a recursive function to traverse the BST, and the maximum number of function calls that can be on the call stack at any given time is equal to the height of the BST. In the worst case, where the input sequence is a valid subsequence of the BST and has a length of k, and the height of the BST is h, the space complexity is O(h).
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...