Check if a string is a subsequence of another string ( using Stacks )
Last Updated :
07 Nov, 2023
Given a string S, the task is to check if the string target is a subsequence of string S or not, using a Stack.
Examples:
Input: S = ”KOTTAYAM”, target = ”KOTA”
Output: Yes
Explanation: “KOTA” is a subsequence of “KOTTAYAM”.
Input: S = ”GEEKSFORGEEKS”, target =”FORFOR”
Output: No
Approach: Follow the steps to solve the problem:
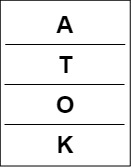
target pushed into the stack

Traversing in S

Traversing in S
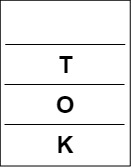
Popping from stack
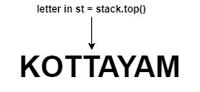
Traversing in S
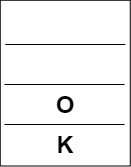
Popping from stack
Traversing in st
Popping from stack

Traversing in S

Stack becomes empty
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void checkforSubsequence(string S,
string target)
{
stack<char> s;
for (int i = 0; i < target.size(); i++) {
s.push(target[i]);
}
for (int i = (int)S.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s.empty()) {
cout << "Yes" << endl;
return;
}
if (S[i] == s.top()) {
s.pop();
}
}
if (s.empty())
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
}
int main()
{
string S = "KOTTAYAM";
string target = "KOTA";
checkforSubsequence(S, target);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.Stack;
public class GFG {
static void checkforSubsequence(String S, String target)
{
Stack<Character> s = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < target.length(); i++) {
s.push(target.charAt(i));
}
for (int i = (int)S.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s.empty()) {
System.out.println("Yes");
return;
}
if (S.charAt(i) == s.peek()) {
s.pop();
}
}
if (s.empty())
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String S = "KOTTAYAM";
String target = "KOTA";
checkforSubsequence(S, target);
}
}
|
Python3
def checkforSubsequence(S, target):
s = []
for i in range(len(target)):
s.append(target[i])
for i in range(len(S) - 1, -1, -1):
if (len(s) == 0):
print("Yes")
return
if (S[i] == s[-1]):
s.pop()
if (len(s) == 0):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if __name__ == "__main__":
S = "KOTTAYAM"
target = "KOTA"
checkforSubsequence(S, target)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static void checkforSubsequence(String S,
String target)
{
Stack<char> s = new Stack<char>();
for(int i = 0; i < target.Length; i++)
{
s.Push(target[i]);
}
for(int i = (int)S.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (s.Count == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
return;
}
if (S[i] == s.Peek())
{
s.Pop();
}
}
if (s.Count == 0)
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
String S = "KOTTAYAM";
String target = "KOTA";
checkforSubsequence(S, target);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function checkforSubsequence(S, target)
{
var s = [];
for (var i = 0; i < target.length; i++) {
s.push(target[i]);
}
for (var i = S.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s.length==0) {
document.write( "Yes");
return;
}
if (S[i] == s[s.length-1]) {
s.pop();
}
}
if (s.length==0)
document.write( "Yes" );
else
document.write( "No" );
}
var S = "KOTTAYAM";
var target = "KOTA";
checkforSubsequence(S, target);
</script>
|
Time Complexity : O(N)
Auxiliary Space : O(N)
Approach 2: Using the find() function
Another approach to check if a string is a subsequence of another string is to use the find() function. We can call find() on the second string to find the index of the first occurrence of the first character of the first string. Then, we can iterate over the first string and call find() on the second string with the starting index set to the index of the previous character plus one. If find() returns string::npos, it means that the current character in the first string is not present in the second string and hence the first string is not a subsequence of the second string.
Define a function that takes two string arguments s1 and s2.
Initialize an integer variable index to -1. This will be used to keep track of the starting index for each find() call.
Iterate over each character c in s1 using a range-based for loop.
Call the find() function on s2 with the arguments c and index + 1. The second argument specifies the starting index for the search, which is the index of the previous character plus one.
If find() returns string::npos, which indicates that the character was not found in s2, return false immediately, as s1 is not a subsequence of s2.
If find() returns a valid index, update index to the returned value.
After iterating over all the characters in s1, return true, as s1 is a subsequence of s2.
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool isSubsequence(string s1, string s2) {
int index = -1;
for (char c : s1) {
index = s2.find(c, index + 1);
if (index == string::npos) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main() {
string s1 = "KOTA";
string s2 = "KOTTAYAM";
bool check = isSubsequence(s1, s2) ;
if(check){
cout<<" yes";
}
else{
cout<<"no";
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static boolean isSubsequence(String s1, String s2) {
int index = -1;
for (char c : s1.toCharArray()) {
index = s2.indexOf(c, index + 1);
if (index == -1) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "KOTA";
String s2 = "KOTTAYAM";
boolean check = isSubsequence(s1, s2);
if (check) {
System.out.println("yes");
}
else {
System.out.println("no");
}
}
}
|
Python3
def isSubsequence(s1, s2):
index = -1
for c in s1:
index = s2.find(c, index + 1)
if index == -1:
return False
return True
s1 = "KOTA"
s2 = "KOTTAYAM"
check = isSubsequence(s1, s2)
if check:
print("yes")
else:
print("no")
|
C#
using System;
public class Program
{
static bool IsSubsequence(string s1, string s2)
{
int index = -1;
foreach (char c in s1)
{
index = s2.IndexOf(c, index + 1);
if (index == -1)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void Main()
{
string s1 = "KOTA";
string s2 = "KOTTAYAM";
bool check = IsSubsequence(s1, s2);
if (check)
{
Console.WriteLine("Yes, s1 is a subsequence of s2");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("No, s1 is not a subsequence of s2");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
function isSubsequence(s1, s2) {
let index = -1;
for (const c of s1) {
index = s2.indexOf(c, index + 1);
if (index === -1) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
const s1 = "KOTA";
const s2 = "KOTTAYAM";
const check = isSubsequence(s1, s2);
if (check) {
console.log("yes");
}
else {
console.log("no");
}
|
Time Complexity : O(M*N)
Auxiliary Space : O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...