Characters in Julia
Last Updated :
22 Mar, 2022
Julia is a dynamic, high-level programming language with high performance and speed that is used to perform operations in scientific computing. It is great for computational complex problems. It is an open-source language so all source code is available easily online.
It is as easy to use as Python but it has much faster execution compared to R and Python. Julia is a general-purpose language and can be used for various tasks such as statistical computations, data analysis, web development, game development and more.
Note: Julia programs are to be saved in a file with .jl extension.
Ways to run Julia
- Through a .jl file in an IDE
- Command by command in Julia REPL (Read Evaluate Print Loop)
It is easier to code and learn Julia as it is a lot similar to other mostly used languages syntactically.
Simple Julia Program
This is a simple program that prints GeeksforGeeks, just type the following code after the start of the interpreter.
Characters in Julia
In Julia, a Char(character) value represents a single character. Characters in Julia are 32-bit primitive data types. It has a special literal representation and appropriate arithmetic behaviours and these can be converted into a numeric value that represents a Unicode code point.
Other subtypes of AbstractChar may be defined by Julia packages. Forex: optimization of operations for other text encodings.
Let’s see the usage of characters in Julia language.
Example
This example shows how to work with Char in Julia.
Julia
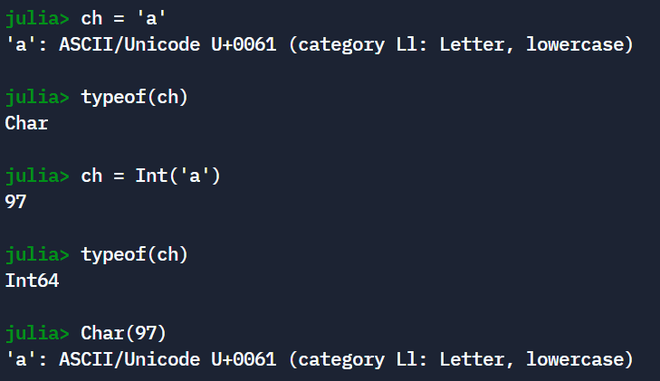
ch = 'a'
typeof(ch)
ch = Int('a')
typeof(ch);
Char(97)
|
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...