Synthetic fibres and plastics, like natural fibres, are made up of polymers, which are very big units. Polymers are made up of a lot of little pieces. Rayon, Nylon, Polyester, and Acrylic are the names given to synthetic fibres based on the chemicals employed in their production. The strength, water absorption capacity, burning nature, cost, and durability of different types of fibres differ from one another. Plastic items come in a wide range of forms and sizes. Plastic is ubiquitous, whether indoors or outside. Plastic trash has a negative impact on the environment. We must utilise synthetic fibres and plastics in such a way that we may enjoy their benefits while also minimising the environmental risks to living communities.
Synthetic Fibres
Synthetic fibres are man-made fibres, the majority of which are manufactured from petroleum-based basic materials known as petrochemicals. Fibres are used to make all textiles, and they can come from natural or artificial sources. They are formed up of a tiny unit or polymer that is made up of numerous repeating monomers. Nylon, acrylics, polyurethane, and polypropylene are among them. Every year, millions of tonnes of these fibres are manufactured all over the world.
What is Polymer?
Synthetic fibres are made by humans and thus are called man-made fibres. They are a chain of small units that are joined together. Here, each small unit is a chemical substance where many small units combine to form a large single unit. This large single unit is called a polymer. The word ‘polymer’ is derived from two Greek words; poly which means many and mer which means part or unit. Therefore, a polymer is made of many repeating units. Synthetic fibres are more durable and affordable which makes them more popular than natural fibres.
Classification of Synthetic Fibres
Clothes and a variety of other items are made from synthetic fibres. They might be completely synthetic or somewhat synthetic. Natural polymers are used as the starting material for semisynthetic textiles like rayons. Chemicals, on the other hand, are used to create pure synthetic fibres. Acrylics, polyesters, and nylons are all synthetic fibres.
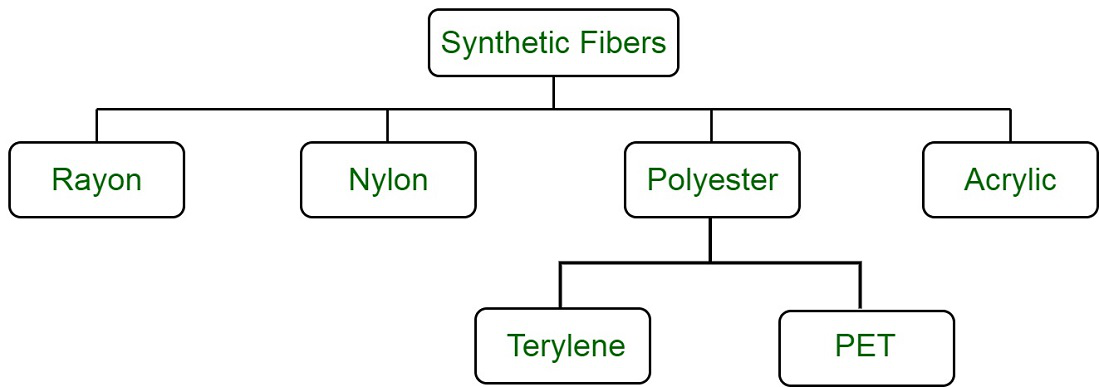
Rayon
Silk fibre which is obtained from silkworms was discovered in China. it was quite expensive. People were fascinated by its beautiful texture, so attempts were made to replicate it artificially. Towards the end of the nineteenth century, scientists were successful in obtaining a fibre having properties similar to that of silk which was obtained by chemical treatment of wood pulp and was named rayon or artificial silk.
Rayon is obtained from a natural source, wood pulp, yet it is a man-made fibre. It is also cheaper than silk and can also be woven like silk fibres. It can be dyed in a variety of colours and is mixed with cotton to make bed sheets. It can also be mixed with wool to make carpets. As a result of its natural origins, rayon is classified as a semi-synthetic fibre. Because of its tiny fibres and low weight, it is sometimes known as artificial silk. It’s used to make clothing, carpets, curtains, and blankets, among other things.
Nylon
Nylon is a man-made fibre and was first made in 1931. It was made without using any natural raw material and was prepared from coal, water and air. It was the first fully synthetic fibre. Nylon is strong, elastic and light. It is also lustrous and easy to wash. Many nylon articles are used nowadays like socks, ropes, tents, toothbrushes, car seat belts, sleeping bags, curtains, etc.
Polyester and Acrylic
Polyester is made from repeating units of a chemical called an ester. Polyester is a synthetic fibre. It doesn’t get wrinkles easily and remains crisp. It is easy to wash which makes it suitable for making dress material. Examples of it are terylene, which is a popular polyester that can be drawn into very fine fibres that can be woven like any other yarn.
PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is a very common form of polyester. PET is used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires etc. Many of this stuff are not made from natural wool, yet they appear like wool. They are prepared from a synthetic fibre which is known as acrylic. Acrylic clothes are cheap and are available in a variety of colours.
Characteristics and Advantages of Synthetic Fibres
- They possess characteristics that make them a popular choice for dress materials.
- They are cheaper. stronger and more durable than natural fibre.
- They have high resistance to wear and tear.
- Synthetic fibres have high abrasion.
- They dry up in less time as they absorb less amount of water compared to natural fibres.
- They are easy to maintain and wash and are resistant to attack by moths.
- Synthetic fibres don’t get wrinkles after washing and are extremely lightweight.
- They have a very smooth texture.
- They are more affordable.
Disadvantages of Synthetic Fibres
- They cannot absorb moisture. Thus, they are unsuitable to be worn during summers when our body sweats.
- They catch fire easily and thus it is dangerous to wear them while near fire.
- They cannot be easily ironed as they melt very easily.
Plastic
Plastic is a polymer like synthetic fibre. Some plastic has a linear arrangement while other has cross-linked. Plastic articles are available in all possible shapes and sizes and can be easily moulded in any form. They can be recycled, reused, rolled into sheets or made into wires.
Properties and Uses of Plastic
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity. Therefore, they are used in making a covering of electric wires and handles of tools.
- Plastics are highly resistant to chemicals and water.
- Plastics are lightweight, strong and durable.
- Plastic is non-reactive.
- It is non-biodegradable, takes several years to decompose and is not environment friendly and is a major cause for concern for us as it is increasing day by day.
Types of Plastics: Thermoplastic and Thermosetting Plastics
When water is added to a plastic bottle, it gets deformed. Plastic which gets deformed easily by this method, i.e. on heating and which can be bent easily is known as thermoplastics. Its examples are Polythene and PVC. They are used for manufacturing toys, combs etc.
Plastics that can’t be softened by heating after moulding once are called thermosetting plastics. Example of it is Bakelite and melamine. Bakelite is used for making electrical switches, handles of various utensils, etc. Melamine is a versatile material and can resist fire and tolerate heat better than other plastics.
Plastic and the environment
A material that gets decomposed through natural processes like action by bacteria is called biodegradable. Material that is not easily decomposed by natural processes is called non-biodegradable. Plastic takes several years to decompose and is not environment friendly. It causes environmental pollution. The burning process in the synthetic material is slow and it does not get completely burnt easily. The burning process releases poisonous fumes into the atmosphere which causes air pollution. The most obvious solution is to recycle plastic. Most of the thermoplastics can be recycled. The 5R principle of recycling are Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover and Refuse.
Following are the problems from excessive use of Plastics
- Plastics are non-biodegradable and do not decompose for several years.
- The burning process in the synthetic material is slow and it does not get completely burnt easily.
- When burnt, toxic fumes are released into the atmosphere causing pollution.
Polythene
Plastic obtained by the polymerization of a chemical compound is called ethene. It is tough and durable. It is used in making polythene bags, waterproof plastic sheets, bottles, buckets, dustbins and other such things.
Characteristics of Polythene
- It is of low strength, hardness and rigidity.
- It is highly ductile and impacts strength along with low friction.
- It shows strong creep under persistent force, which can be reduced by the addition of short fibres.
- It feels waxy when touched.
- It is a good electrical insulator and offers good electrical resistance.
Types of Polythene
- Low-density polythene: These types of polythene are prepared by doing a reaction at a temperature of 350 K – 570 K in the presence of traces of dioxygen or a peroxide initiator. This is done to give it a unique flow property in the molten state. They are used for making plastic bags and film wrap.
- High-density polythene: It is obtained when the addition polymerization of ethene takes place in a hydrocarbon solvent at a temperature of 333K-343 K in the presence of metallocene catalysts. They are chemically inert. Inert means that they don’t react and are used in making bottles, butter tubs etc.
Uses of Polythene
- They give elongation before breaking and are thus useful as plastic for moulding in various shapes such as bottles, sheets and pipes etc.
- They are used for plastic bags, stretch films because of their clear and crystalline nature.
- They have high life expectancy but can degrade by ultraviolet radiation.
- They have high chemical resistance.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is a strong and hard plastic but it is not as flexible as polythene and is used for making insulation for electric wires, pipes, garden hoses, raincoats, seat covers etc. It is made of vinyl chloride monomer by condensation polymerization and it is an example of thermoplastic polymer.
Types of PVC
PVC comes in two basic forms, i.e. rigid and flexible.
- Rigid: Rigid PVC is used in construction for pipe and in doors and windows and for making bottles, non-food packaging, and cards like a bank or club membership cards.
- Flexible: Flexible is made softer and flexible by adding plasticizers. It is used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, imitation leather, flooring, etc.
Characteristics of PVC
- It has high hardness and these properties enhance with an increase in molecular weight but decrease with an increase in temperature.
- Heat stability is poor, thus the addition of a heat stabilizer is necessary to ensure the product’s properties.
- PVC is a polymer with good insulation properties.
- PVC is chemically resistant to acids, salts, bases, fats, and alcohols, making it resistant to the corrosive effects of sewage. Therefore, it is used so much in sewer piping systems.
Bakelite
Bakelite is a polymer made up of two monomers- phenol and formaldehyde and is a thermosetting polymer. Bakelite is a very hard and tough plastic but is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. It remains hard on heating. Since it has a low electrical conductivity and high heat resistance it is used in manufacturing electrical switches, plugs and sockets and machine parts of electrical systems.
Characteristics of Bakelite
- It can be quickly moulded and very smooth moulding can be obtained.
- Bakelite mouldings are heat-resistant and scratch-resistant.
- They are also resistant to several destructive solvents.
- Bakelite is resistant to electric current.
Melamine
Melamine is a plastic that can tolerate heat much better than other plastics. It can also resist fire. Special plastic cookware made of melamine is used in microwave ovens for cooking food. It contains 67% nitrogen by mass and has fire-retardant properties.
The fire-retardant properties are due to its release of nitrogen gas when burned. It combines with formaldehyde to produce melamine resins. These resins are durable thermosetting plastic that is used in high-pressure laminates like melamine dinnerware, laminate flooring etc.
Teflon
Teflon is a special plastic on which oil and water do not stick because of its slippery surface. It can withstand high temperatures and is used for making soles of electric irons and giving non-stick coating on cookware.
Characteristics of Teflon
- It is a fluorocarbon solid at room temperature.
- It is hydrophobic, i.e. it is neither water nor water-containing substances wet.
Uses of Teflon
- It is used in making waterproof fabric and non-stick cookware.
- It is used in making an anti-friction device.
- It is used for coating medical appliances.
- Due to its high resistance to corrosion, it is used for coating the lining of laboratory appliances.
Sample Questions
Question 1: What is polymer are synthetic fibres?
Answer:
Synthetic fibres are made by human beings and thus are called man-made fibres. A synthetic fibre is a chain of small units joined together where each small unit is a chemical substance. Many small units combine to form a large single unit called a polymer.
Question 2: Write a short note on Nylon.
Answer:
Nylon is a synthetic fibre that was developed in 1931 without the use of any natural raw materials. It was the first fully synthetic fibre, made from coal, water, and air. Nylon is a strong, elastic, and lightweight fibre. It’s glossy and simple to clean. Socks, ropes, tents, toothbrushes, car seat belts, sleeping bags, curtains, and other nylon products are often used nowadays.
Question 3: What are the characteristics of synthetic fibres?
Answer:
The characteristics of synthetic fibres are-
- Synthetic fibres possess unique characteristics which make them popular dress materials and are cheaper than natural fibre.
- They are stronger and more durable than natural fibre.
- They dry up in less time.
- They are easy to maintain and wash.
- They are resistant to attack by moths.
Question 4: What are the properties and uses of plastic?
Answer:
The properties and uses of plastic are,
- Plastic are poor conductors of heat and electricity and thus, they are used to make covering of electric wires and handles of tools.
- Plastics are highly resistant to chemicals and water.
- Plastics are lightweight, strong and durable and are therefore used to make parts for aircrafts, cars etc.
- Plastic is non-reactive.
- It is non-bio degradable, takes several years to decompose and is not environment friendly.
Question 5: Differentiate between Thermoplastic and Thermosetting Plastics.
Answer:
When we add hot water to a plastic bottle, it gets deformed. Plastic which gets deformed easily on heating and can be bent easily is known as thermoplastics. E.g. Polythene and PVC. They are used for manufacturing toys, combs etc.
Plastics which moulded once, can not be softened by heating are called thermosetting plastics. Example- Bakelite and melamine. Bakelite is used for making electrical switches, handles of various utensils, etc.
Question 6: What is the impact of plastic on the environment?
Answer:
Plastic takes a long time to disintegrate and is harmful to the environment. It has a negative impact on the environment. The synthetic material’s burning process is sluggish, and it does not simply burn entirely. Poisonous gases are released into the environment during the burning process, resulting in air pollution. Recycling plastic is the most obvious answer. The majority of thermoplastics are recyclable. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover, and Refuse are the five R’s of recycling.
Question 7: Write a short note on Polythene, PVC, Bakelite, Melamine and Teflon.
Answer:
- Polythene- Plastic obtained by the polymerization of a chemical compound is ethene. It is tough and durable and is used in making polythene bags, waterproof plastic sheets, bottles, buckets, dustbins and other such things.
- PVC- PVC is a strong and hard plastic. It is not as flexible as polythene and is used for making insulation for electric wires, pipes, garden hoses, raincoats, seat cover etc. PVC is made of vinyl chloride monomer by condensation polymerization and it is an example of thermoplastic polymer.
- Bakelite- Bakelite is a polymer made up of two monomers- phenol and formaldehyde. It is a thermosetting polymer. Bakelite is a very hard and tough plastic. It is a poor conductor of heat and electricity and it doesn’t become soft on heating.
- Melamine- Melamine is a heat-resistant material that can withstand higher temperatures than other polymers. In microwave ovens, special plastic cookware composed of melamine is used to cook meals.
- Teflon- Teflon is a unique material with a slick surface that prevents oil and water from adhering to it. It can resist high temperatures and is used to make the soles of electric irons and to coat kitchenware with a non-stick coating.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...