The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) conducted the Class 12 Term-1 Physics Exam on December 10, 2021, Friday. The duration of the exam was 90 minutes also the Question Paper contains a total of 55 Questions, which consisted of Objective-type (MCQs) Questions. The exam was conducted across the country following all the exam guidelines.
CBSE Class 12 Physics Term 1 exam was 35 marks, and the time allotted for this paper was 90 minutes. The physics paper consisted of three sections. All questions were MCQ type questions. Read below for a detailed analysis and structure of the paper:
Section
| Type of Questions Asked | Number of Questions Asked
| Questions to be Attempted
|
Section-A
| Conceptual and Understanding | 25
| 20
|
Section-B
| Application type and Assertion–Reason | 24
| 20
|
Section-C
| Entirely on Case–study | 06
| 06
|
Total Number of Questions
| 55
| 45
|
In terms of exam organisation and paper pattern, there have been a lot of changes this year. The CBSE board started looking at the Term-by-Term schedule for 2021-22 after examining all of the factors. So, let’s look at CBSE Class 12 Physics Term 1 Paper Series SSJ/1 – Set 4 in detail.
Although the question paper was based on NCERT, the level of difficulty was above average. Few of the questions were thought-provoking and needed a thorough understanding of the concept. Because of the calculations, several questions took longer to complete. After the exam, some candidates expressed dissatisfaction with their performance, describing the paper as “tricky.”
The paper, on the other hand, had a solid mix of conceptual and numerical questions. The paper has a tendency to focus on numerical topics. The paper was of medium difficulty. There were a couple of tough questions in there as well. Overall, the paper was well-balanced.
As the term 1 exam was from the half syllabus of the Class 12 Physics Curriculum, therefore the chapter “Current Electricity” had the highest weightage of marks, followed by Moving charges and Magnetism. Chapter Electromagnetic Induction and Electrostatic potential and capacitance had the same weightage. Total ten questions asked from chapter Electric charges and Fields giving it 18% weightage of the overall paper. Moreover, as usual, the least weightage was given to the chapter Magnetism and Matter.
Here, the Solved Questions Paper (along with the Answers and the explanation in-depth for each question) of the Physics CBSE Class 12th Term 1 Exam is provided as:
CBSE Class 12th Term 1 Physics Board Exam Question Paper and Answers Key 2021-22 (SET 4)
Subject- Physics
Term- I
Time allowed- 90 minutes
Maximum Marks- 35
General Instructions
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them:
- This question paper contains 55 questions out of which 45 questions are to be attempted. All questions carry equal marks.
- The question paper consists of three Sections – Section A, B, and C.
- Section – A contains 25 questions. Attempt any 20 questions from Question number 1 to 25.
- Section – B contains 24 questions. Attempt any 20 questions from Question number 26 to 49.
- Section – C contains 6 Questions. Attempt any 6 Questions from Question number 50 to 55.
- There is only one correct option for every Multiple Choice Question (MCQ). Marks will not be awarded for answering more than one option.
- There is no negative marking.
SECTION – A
Question 1: A negatively charged object X is repelled by another charged object Y. However, an object Z is attracted to object Y. Which of the following is the most possible for object Z?
(a) positively charged only
(b) negatively charged only
(c) neutral or positively charged
(d) neutral or negatively charged
Answer: (c)
Question 2: In an experiment, three microscopic latex spheres are sprayed into a chamber and become charged with charges +3e, +5e and -3e respectively. All the three spheres came in contact simultaneously for a moment and got separated. Which one of the following are possible values for the final charge on the spheres?
(a) +5e, -4e, +5e
(b) +6e, +6e, -7e
(c) -4e, +3.5e, +5.5e
(d) +5e, -80, +7e
Answer: (b)
Question 3: An object has charge of 1 C and gains 5.0 x 1018 electrons. The net charge on the object becomes –
(a) – 0.80 C
(b) + 0.80 C
(c) +1.80 C
(d) +0.20 C
Answer: (d)
Question 4: Kirchhoff’s first rule ∑I = 0 and second rule ∑IR = ∑E (where the symbols have their usual meanings) are respectively based on –
(a) conservation of momentum and conservation of charge
(b) conservation of energy, conservation of charge
(c) conservation of charge, conservation of momentum
(d) conservation of charge, conservation of energy
Answer: (d)
Question 5: The electric power consumed by a 220 V – 100 W bulb when operated at 110 V is
(a) 25 W
(b) 30 W
(c) 35 W
(d) 45 W
Answer: (a)
Question 6: Which of the following has a negative temperature coefficient of resistivity?
(a) metal
(b) metal and semiconductor
(c) semiconductor
(d) metal and alloy
Answer: (c)
Question 7: Two wires carrying currents I, and I. lie. one slightly above the other, in a horizontal plane as shown in the figure. The region of the vertically upward strongest magnetic field is

(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer: (b)
Question 8: Two parallel conductors carrying current of 4.0 A and 10.0 A are placed 2.5 cm apart in vacuum. The force per unit length between them is –
(a) 6.4 × 10-5 N/m
(b) 6.4 × 10-2 N/m
(c) 4.6 × 10-4 N/m
(d) 3.2 × 10-4 N/m
Answer: (d)
Question 9: If an ammeter is to be used in place of a voltmeter, then we must connect with the ammeter a –
(a) low resistance in parallel
(b) low resistance in series
(c) high resistance in parallel
(d) high resistance in series
Answer: (a)
Question 10: The magnetic field at the centre of a current-carrying circular loop of radius R, is B1. The magnetic field at a point on its axis at a distance R from the centre of the loop is B2. Then the ratio (B1/B2) is
(a) 2√2
(b) 1/√2
(c) √2
(d) 2
Answer: (c)
Question 11: The self-inductance of a solenoid of 600 turns is 108 mH. The self-inductance of a coil having 500 turns with the same length, the same radius and the same medium will be
(a) 95 mH
(b) 90 mH
(c) 85 mH
(d) 75 mH
Answer: (d)
Question 12: The RMS current in a circuit connected to a 50 Hz ac source is 15 A. The value of the current in the circuit Circuit, after the instant the current is zero, is –
(a) 15/√2 A
(b) 15√2 A
(c) √215 A
(d) 8
Answer: (a)
Question 13: In a circuit, the phase difference between the alternating current and the source voltage is π/2. Which of the following cannot be the element(s) of the circuit?
(a) only c
(b) only L
(c) L and R
(d) L and C
Answer: (a)
Question 14: The electric potential V at any point (x, y, z) is given by V = 3 x2 where x is in metres and V in volts. The electric field at the point (1 m, 0, 2 m) is –
(a) 6 V/m along -x-axis.
(b) 6 V/m along +x-axis
(c) 1.5 V/m along –x-axis
(d) 1.5 V/m along +x-axis
Answer: (a)
Question 15: Which of the diagrams correctly represents the electric field between two charged plates if a neutral conductor is placed in between the plates?

Answer: (d)
Question 16: A variable capacitor is connected to a 200 V battery. If its capacitance is changed from 2 μF to X μF, the decrease in energy of the capacitor is 2 × 10-2 J. The value of X is –
(a) 1 μF
(b) 2 μF
(c) 3 μF
(d)) 4 μF
Answer: (d)
Question 17: A potential difference of 200 V is maintained across a conductor of resistance 100 Ω. The number of electrons passing through it in 1 s is
(a) 1.25 × 1019
(b) 2.5 × 1018
(c) 1.25 × 1018
(d) 2.5 × 1016
Answer: (a)
Question 18: The impedance of a series LCR circuit is –
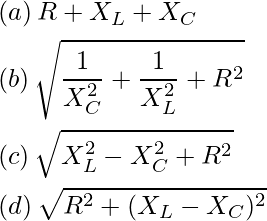
Answer: (d)
Question 19: When an alternating voltage E = E0 sin ωt is applied to a circuit, a current I = I0 sin (ωt + π/2) flows through it. The average power dissipated in the circuit is
(a) Erms. Irms
(b) E0 I0
(c) E0 I0/√2
(d) Zero
Answer: (d)
Question 20: A current-carrying wire kept in a uniform magnetic field will experience a maximum force when it is
(a) perpendicular to the magnetic field
(b) parallel to the magnetic field
(c) at an angle of 45° to the magnetic field
(d) at an angle of 60° to the magnetic field
Answer: (a)
Question 21: The voltage across a resistor, an inductor, and a capacitor connected in series to an ac source is 20 V, 15 V and 30 V respectively. The resultant voltage in the circuit is
(a) 5 V
(b) 20 V
(c) 25 V
(d) 65 V
Answer: (c)
Question 22: In a dc circuit, the direction of current inside the battery and outside the battery respectively are –
(a) positive to the negative terminal and negative to the positive terminal
(b) positive to the negative terminal and positive to negative terminal
(c) negative to the positive terminal and positive to the negative terminal
(d) negative to the positive terminal and negative to the positive terminal
Answer: (c)
Question 23: The magnitude of electric field due to a point charge 2q, at distance r, is E. Then the magnitude of electric field due to a uniformly charged thin spherical shell of radius R with total charge q at a distance r/2 (r >> R) will be
(a) E/4
(b) 0
(c) 2E
(d) 4E
Answer: (c)
Question 24: The horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field at a place is 0.2 G whereas the total magnetic field is 0.4 G. The angle of dip at the place is
(a) 30°
(b) 45°
(c) 60°
(d) 90°
Answer: (c)
Question 25: The current in the primary coil of a pair of coils changes from 7 A to 3 A in 0.04 s. The mutual inductance between the two coils is 0.5 H. The induced emf in the secondary coil is –
(a) 50 V
(b) 75 V
(c) 100 V
(d) 220 V
Answer: (a)
SECTION – B
Question 26: A square sheet of side ‘a’ is lying parallel to the XY plane at z = a. The electric field in the region is
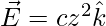
The electric flux through the sheet is
(a) a4c
(b) ⅓ a3c
(c) ⅓ a4c
(d) 0
Answer: (a)
Question 27: Three charges q, -q and q0 are placed as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the net force on the charge q0 at point O is
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \left[k=\dfrac{1}{4\pi\epsilon_0}\right]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4085acbc6432b0c7dbd35296c3f72ea3_l3.png)

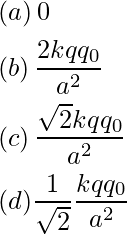
Answer:
Question 28: A + 3.0 nC charge Q is initially at rest at a distance of r1 = 10 cm from a + 5.0 nC charge q fixed at the origin. The charge Q is moved away from q to a new position at r2 = 15 cm. In this process work done by the field is
(a) 1.29 × 10-5 J
(b) 3.6 × 105 J
(c) -4.5 × 10-7 J
(d) 4.5 × 10-7 J
Answer: (d)
Question 29: A car battery is charged by a 12 V supply, and energy stored in it is 7.20 × 105 J. The charge passed through the battery is –
(a) 6.0 × 104 C
(b) 5.8 × 103 J
(c) 8.64 × 106 J
(d) 1.6 × 106 C
Answer: (c)
Question 30: A straight conducting rod of length I and mass m is suspended in a horizontal plane by a pair of flexible strings in a magnetic field of magnitude B. To remove the tension in the supporting strings, the magnitude of the current in the wire is
(a) mgB/l
(b) mgl/B
(c) mg/lB
(d) lB/mg
Answer: (c)
Question 31: A constant current is flowing through a solenoid. An iron rod is inserted in the solenoid along its axis. Which of the following quantities will not increase?
(a) The magnetic field at the centre
(b) The magnetic flux linked with the solenoid
(c) The rate of heating
(d) The self-inductance of the solenoid
Answer: (c)
Question 32: A circuit is connected to an ac source of variable frequency. As the frequency of the source is increased, the current first increases and then decreases. Which of the following combinations of elements is likely to comprise the circuit?
(a) L, C and R
(b) L and C
(c) L and R
(d) R and C
Answer: (a)
Question 33: If n, e, τ and m have their usual meanings, then the resistance of a wire of length l and cross-sectional area A is given by –
Answer: (b)
Question 34: A proton and an alpha particle move in circular orbits in a uniform magnetic field. Their speeds are in the ratio of 9 : 4. The ratio of radii of their circular orbits (rp/ralpha) is
(a) 3/4
(b) 4/3
(c) 8/9
(d) 9/8
Answer: (d)
Question 35: A coil of area 100 cm2 is kept at an angle of 30° with a magnetic field of 10-1 T. The magnetic field is reduced to zero in 10-4 s. The induced emf in the coil is –
(a) 5√3 V
(b) 50√3 V
(c) 5.0 V
(d) 50.0 V
Answer: (a)
Question 36: A 15 Ω resistor, an 80 mH inductor and a capacitor of capacitance C are connected in series with a 50 Hz ac source. If the source voltage and current in the circuit are in phase, then the value of capacitance is
(a) 100 μF
(b) 127 μF
(c) 142 μF
(d) 160 μF
Answer: (b)
Question 37: Four objects W, X, Y and Z, each with charge +q are held fixed at four points of a square of side d as shown in the figure. Objects X and Z are on the midpoints of the sides of the square. The electrostatic force exerted by object W on object X is F. Then the magnitude of the force exerted by object W on Z is

(a) F/7
(b) F/5
(c) F/3
(d) F/2
Answer: (b)
Question 38: Two sources of equal emf are connected in series. This combination is, in turn, connected to an external resistance R. The internal resistance of two sources are r1 and r2 (r2 >r1). If the potential difference across the source of internal resistance r2 is zero, then R equals to
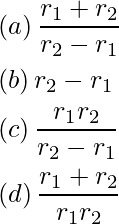
Answer: (b)
Question 39: Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Magnetic field lines do not form closed loops.
(b) Magnetic field lines start from the north pole and end at the south pole of a magnet.
(c) The tangent at a point on a magnetic field line represents the direction of the magnetic field at that point.
(d) Two magnetic field lines may intersect each other.
Answer: (c)
Question 40: The equivalent resistance between A and B of the network shown in the figure is

(a) 3R Ω
(b) (3/2)R Ω
(c) 2R Ω
(d) (2/3) RΩ
Answer: (c)
Question 41: A bar magnet has magnetic dipole moment 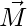 . Its initial position is parallel to the direction of uniform magnetic field
. Its initial position is parallel to the direction of uniform magnetic field 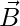 . In this position, the magnitudes of torque and force acting on it respectively are –
. In this position, the magnitudes of torque and force acting on it respectively are –
(a) 0 and MB
(b) MB and MB
(c) 0 and 0
(d) 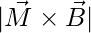 and 0
and 0
Answer: (c)
Question 42: Two charges 14 μC and -4 μC are placed at (-12 cm, 0, 0) and (12 cm, 0, 0) in an external electric field E = (B/r2), where B = 1.2 × 106 N/(cm2) and r is metres. The electrostatic potential energy of the configuration is
(a) 97.9 J
(b) 102.1 J
(c) 2.1 J
(d) -97. 9 J
Answer: (a)
Question 43: A 300 Ω resistor and a capacitor of (25/π) μF are connected in series to a 200 V- 50 Hz ac source. The current in the circuit is –
(a) 0.1 A
(b) 0.4 A
(c) 0.6 A
(d) 0.8 A
Answer: (b)
Question 44: The core of a transformer is laminated to reduce the effect of:
(a) flux leakage
(b) copper loss
(c) hysteresis loss
(d) eddy current
Answer: (d)
Question numbers 45 to 49 are Assertion and Reason Type Questions. Given below are the two statements labelled – Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is also false.
Question 45: Assertion (A): A negative charge in an electric field moves along the direction of the electric field.
Reason (R): On a negative charge a force acts in the direction of the electric field.
Answer: (d)
Question 46: Assertion (A): The poles of a bar magnet cannot be separated.
Reason (R): Magnetic monopoles do not exist.
Answer: (a)
Question 47: Assertion (A): When the radius of a current-carrying loop is doubled, its magnetic moment becomes four times.
Reason (R): The magnetic moment of a current-carrying loop is directly proportional to the area of the loop.
Answer: (a)
Question 48: Assertion (A): Higher the range, lower is the resistance of an ammeter.
Reason (R): To increase the range of an ammeter additional shunt is added in series to it.
Answer: (c)
Question 49: Assertion (A): A step-up transformer cannot be used as a step-down transformer.
Reason (R): A transformer works only in one direction.
Answer: (d)
SECTION – C
Question 50: Equipotentials at a large distance from a collection of charges whose total sum is not zero are:
(a) spheres
(b) planes
(c) ellipsoids
(d) paraboloids
Answer: (a)
Question 51: Four charges -q, -q, +q and +q are placed at the corners of a square of side 2 L is shown in the figure. The electric potential at point A midway between the two charges +q and +q is:

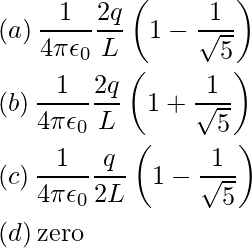
Answer: (a)
Case Study:
An experiment was set up with the circuit diagram shown in figure. Given that R1 = 10 Ω, R2 = R3 = 5 Ω, r = 0 Ω and E = 5 V

Question 52: The points with the same potential are:
(a) b, c, d
(b) f, h, j
(c) d, e, f
(d) a, b, j
Answer: (b)
Question 53: The current through branch bg is:
(a) 1 A
(b) 1/3 A
(c) 1/2 A
(d) 2/3 A
Answer: (c)
Question 54: The power dissipated in R1 is:
(a) 2 W
(b) 2.5 W
(c) 3 W
(d) 4.5 W
Answer: (d)
Question 55: The potential difference across R3 is:
(a) 1.5 V
(b) 2 V
(c) 2.5 V
(d) 3 V
Answer: (b)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...